Adaptive Thresholding of Images

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
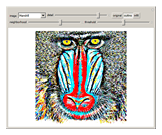
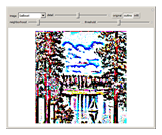
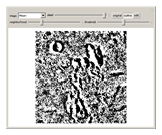
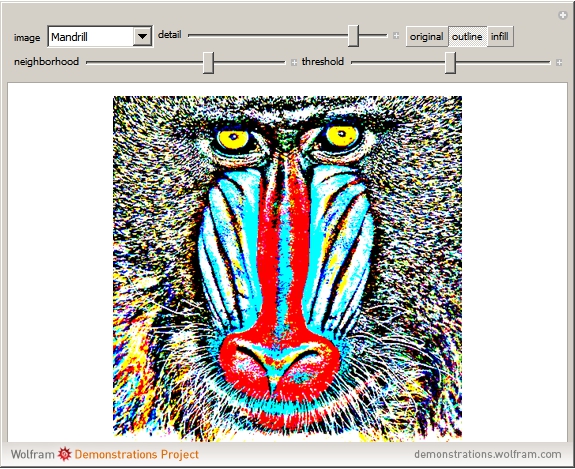
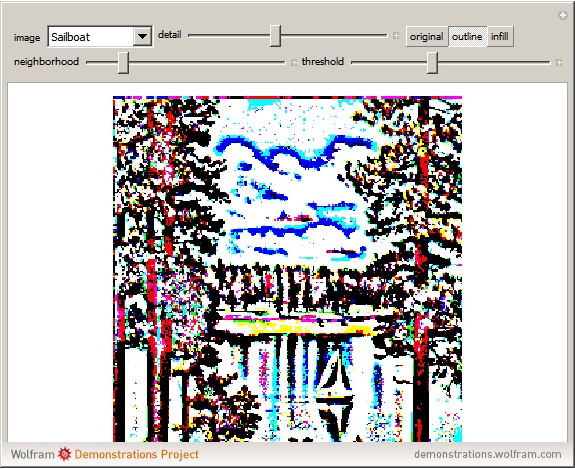
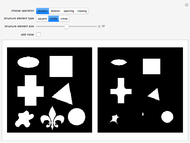
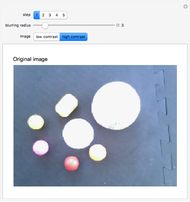
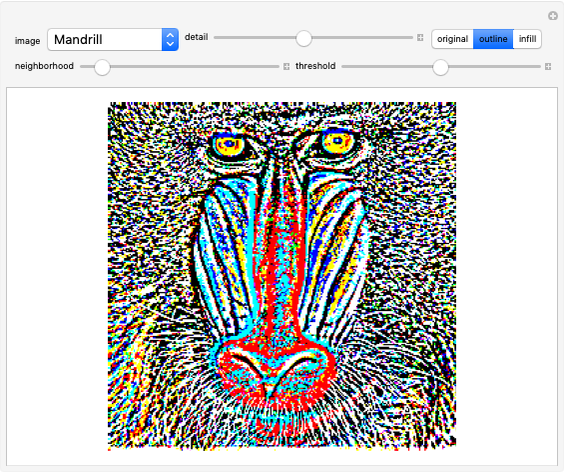
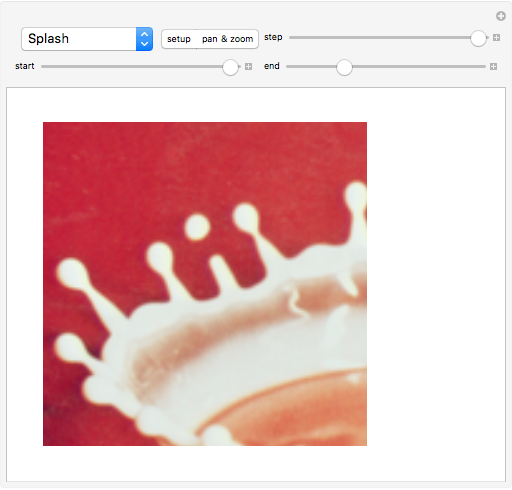
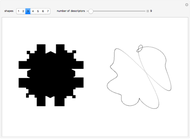
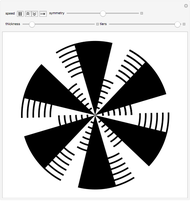
An adaptive threshold binarizes a grayscale image based on the local character of the image (which you can select from any of the photos in the Wolfram image library).
[more]
Contributed by: William Sethares (November 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The filter has two controls: the size of the neighborhood and the threshold value. As the neighborhood is decreased, smaller features are revealed. As the threshold is increased, the image reliably darkens (it is lighter as the threshold is decreased). The checkbox lets you compare the original image, the outlined-thresholded image, and the infilled version. The "detail" slider lets you choose between a smaller image (faster) and better fidelity (slower to calculate).
Permanent Citation
"Adaptive Thresholding of Images"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/AdaptiveThresholdingOfImages/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: November 1 2012