Chaotic Dynamics for Ball Bouncing between Two Constant Slopes

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
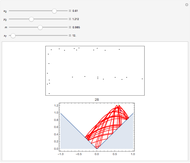
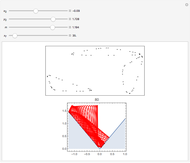
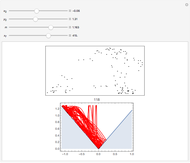
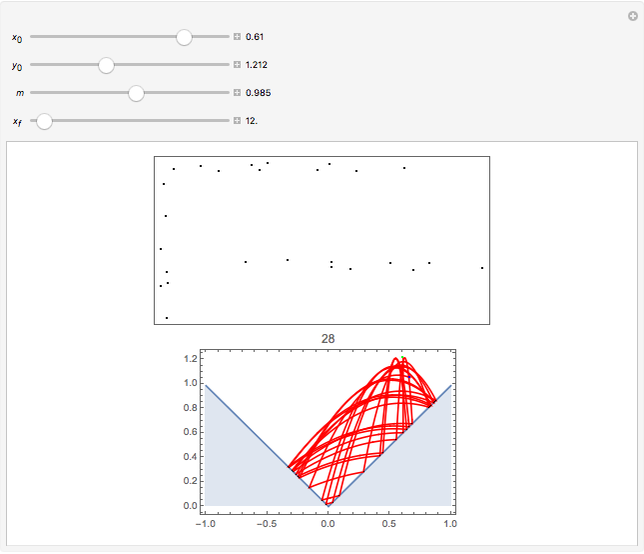
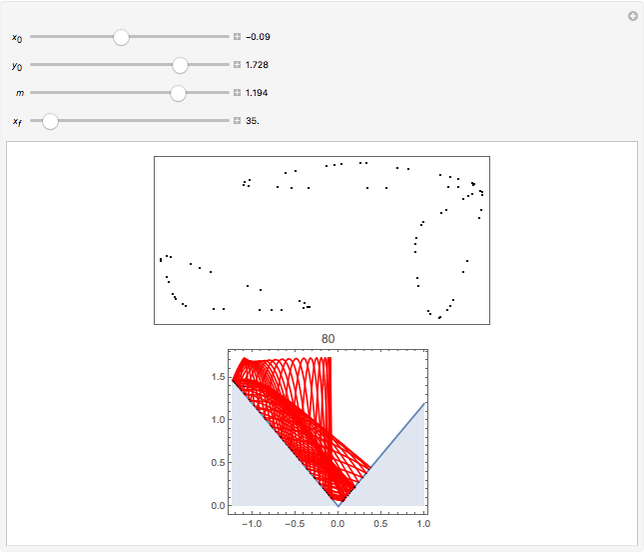
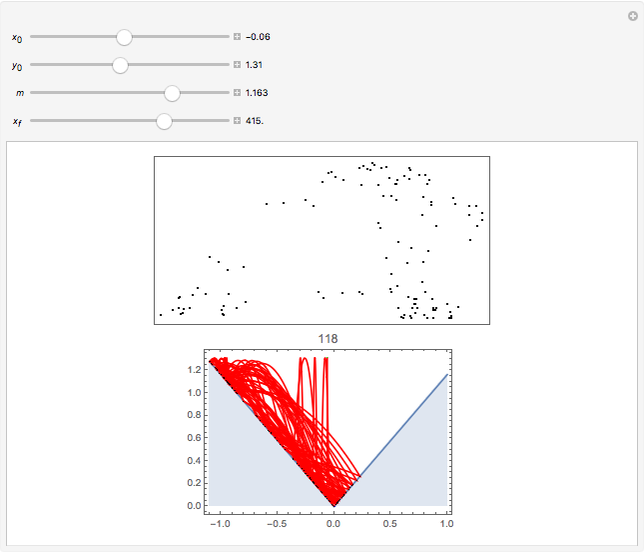
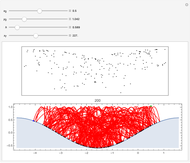
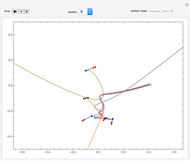
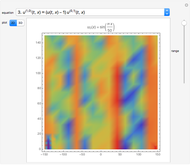
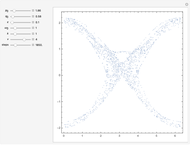
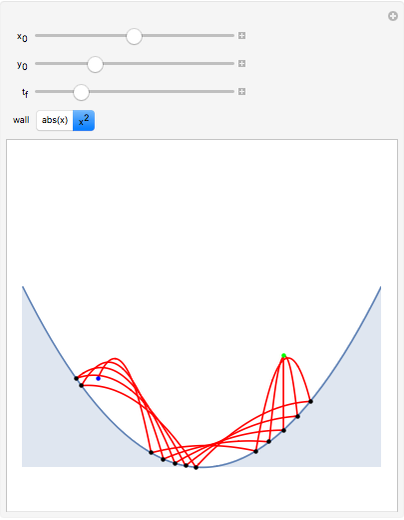
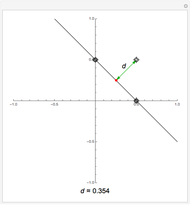
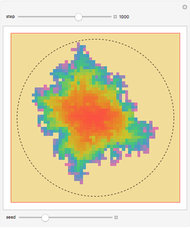
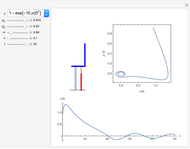
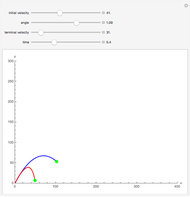
Perhaps the simplest situation of elastic collisions that exhibit chaotic motion is a ball bouncing between two constant slopes of opposite sign. Here the ball starts at position 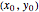 (green point), the slope is
(green point), the slope is 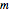 , and the bounces are traced ending at a blue point at time
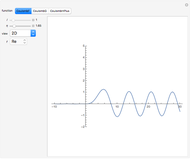
, and the bounces are traced ending at a blue point at time 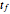 but with a maximum of 200 bounces (the count appears at the top of the graphic). The Poincaré map is shown in the above the graphic.
but with a maximum of 200 bounces (the count appears at the top of the graphic). The Poincaré map is shown in the above the graphic.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (September 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] T. Tél and M. Gruiz, Chaotic Dynamics: An Introduction Based on Classical Mechanics, Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press, 2006.
Poincaré map
chaos
Permanent Citation
"Chaotic Dynamics for Ball Bouncing between Two Constant Slopes"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ChaoticDynamicsForBallBouncingBetweenTwoConstantSlopes/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 4 2012