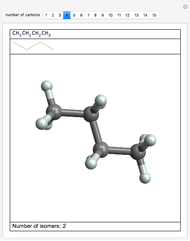
Classes of Isomers

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
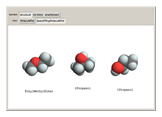
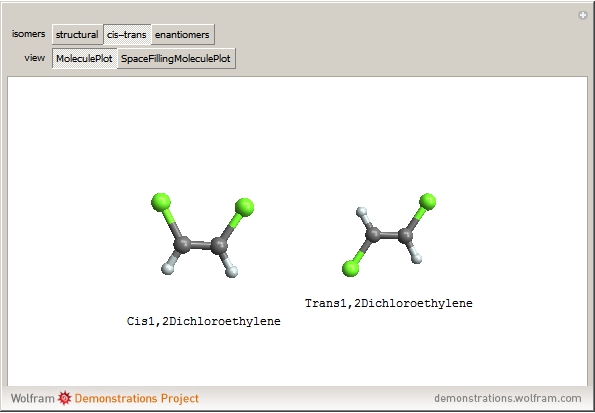
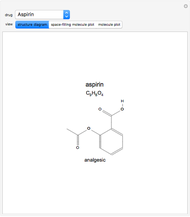
Isomers are compounds with the same chemical composition but with different structures. There are two categories: structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomerism is exemplified by the molecules 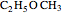 (ethylmethylether) and
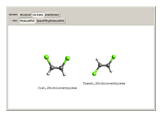
(ethylmethylether) and 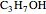 (1- and 2-propanol). Examples of stereoisomerism are the cis and trans modifications of specific groups of atoms within a molecule, for example
(1- and 2-propanol). Examples of stereoisomerism are the cis and trans modifications of specific groups of atoms within a molecule, for example  (1,2-dichloroethene). Another type known as enantiomers are two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, which occurs in different forms of
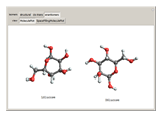
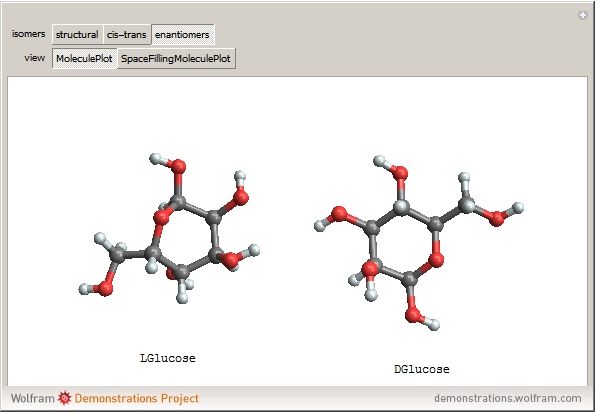
(1,2-dichloroethene). Another type known as enantiomers are two stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other, which occurs in different forms of 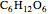 (glucose).
(glucose).
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (December 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Permanent Citation
"Classes of Isomers"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ClassesOfIsomers/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 15 2011