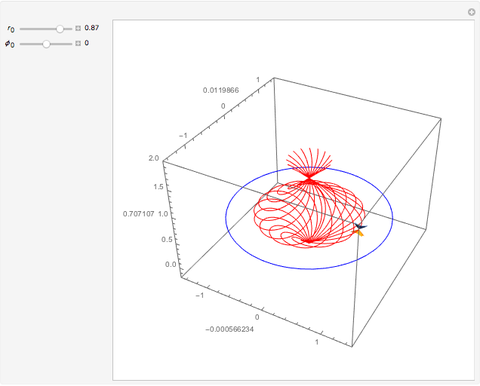
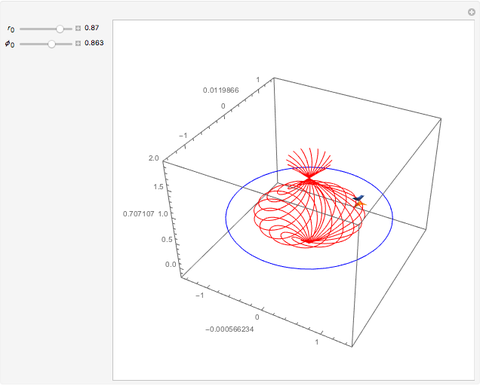
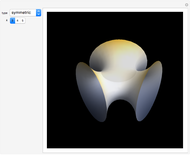
Gödel's Universe

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
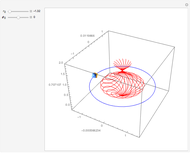
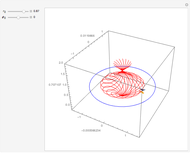
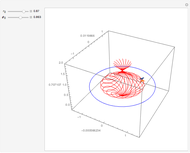
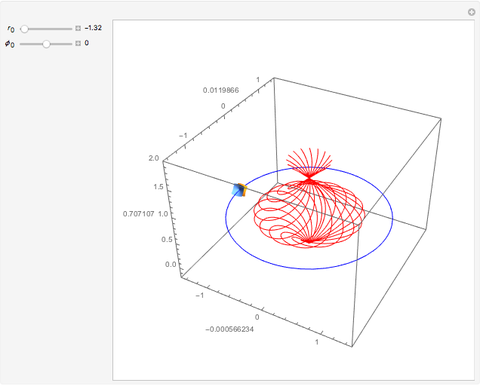
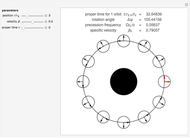
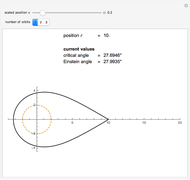
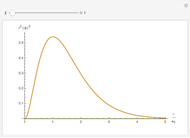
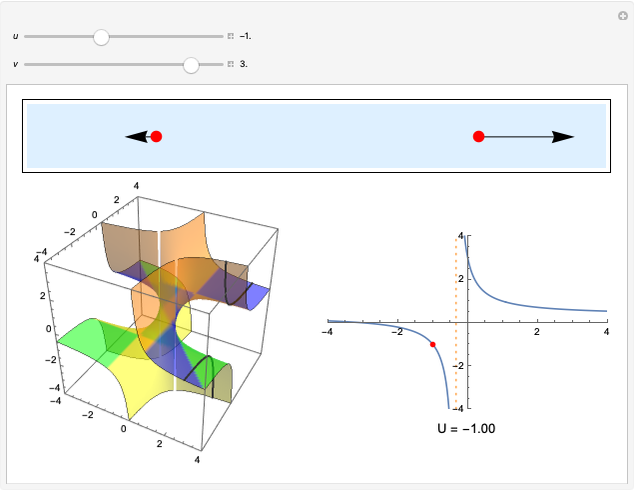
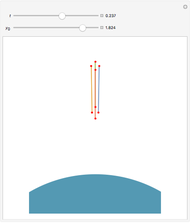
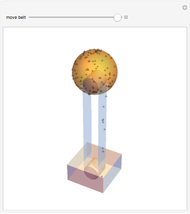
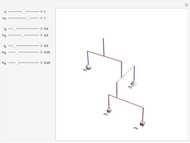
In 1949, Kurt Gödel found a solution of Einstein's field equations and gave it to Einstein on his birthday [1]. This solution describes a homogeneous, anisotropic, and rotationally symmetric spacetime in which matter takes the form of a pressure-free perfect fluid with negative cosmological constant, where closed timelike world lines exist. Theoretically, traveling along such a world line allows an observer to travel into their own past. For an astounding and detailed visualization of how an observer would perceive such a travel, see [2, 3].
[more]
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (August 2013)
Based on a program by: Torsten Schönfeld
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
In cylindrical-polar coordinates  , Gödel's metric is given by
, Gödel's metric is given by
 ,
,
where  is a constant. The coordinate
is a constant. The coordinate  does not appear in the metric.
does not appear in the metric.
References
[1] W. Rindler, “Gödel, Einstein, Mach, Gamow, and Lanczos: Gödel’s Remarkable Excursion into Cosmology,” American Journal of Physics, 77(6), 2009 pp. 498–510. doi:10.1119/1.3086933.
[2] M. Buser, E. Kajari, and W. P. Schleich, "Visualization of the Gödel Universe," New Journal of Physics, 15, 2013 013063. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/15/1/013063.
[3] S. Ceurstemont, "First Time-Travel Movies Reveal Surreal Universe," New Scientist TV (blog). (Jan 2013) www.newscientist.com/blogs/nstv/2013/01/first-time-travel-movies-reveal-surreal-universe.html.
[4] S. Hawking and G. F. R. Ellis, The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1973 section 5.7.
[5] I. Németi, J. X. Madarász, H. Andréka, and A. Andai, "Visualizing Ideas about Gödel-Type Rotating Universes," in Gödel-Type Spacetimes: History and New Developments (M. Scherfner and M. Plaue, eds.). Kurt Gödel Society: Collegium Logicum X, 2010 pp. 77–127. www.math-inst.hu/pub/algebraic-logic/godunivisu-revised.pdf.
[6] T. Schönfeld. "GeodesicGeometry." (Aug 10, 2013) www.math-inst.hu/pub/algebraic-logic/godunivisu-revised.pdf.
Permanent Citation