Gradients in 2D and 3D
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
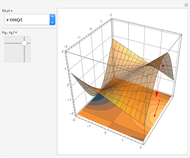
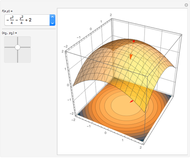
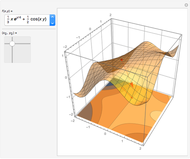
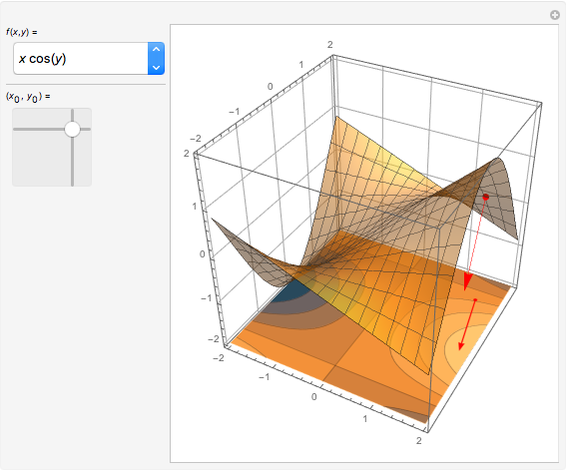
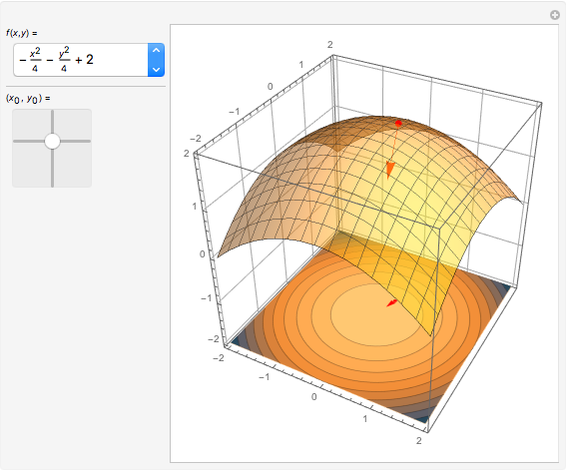
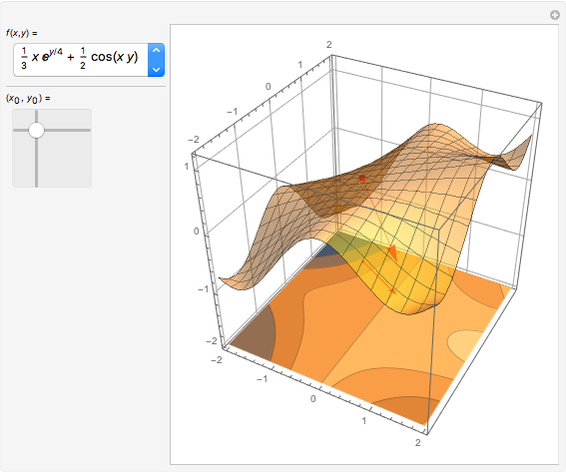
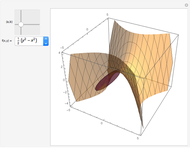
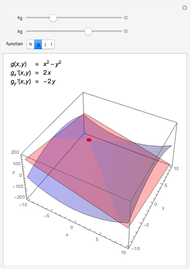
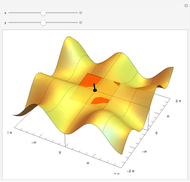
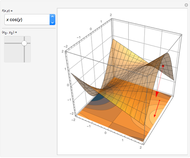
For a smooth surface  in 3D, representing a function
in 3D, representing a function  , the gradient at a point
, the gradient at a point  on
on  is a vector in the direction of maximum change of
is a vector in the direction of maximum change of  . Also shown is the corresponding contour plot, which is the projection of
. Also shown is the corresponding contour plot, which is the projection of  onto the
onto the  -
- plane. The red arrows on the surface and contour plots show the magnitude and direction of the gradient.
plane. The red arrows on the surface and contour plots show the magnitude and direction of the gradient.
Contributed by: Quentin Davis (November 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation