Price Competition

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
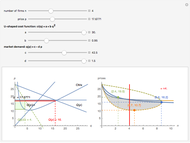
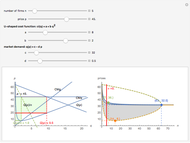
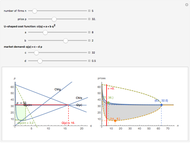
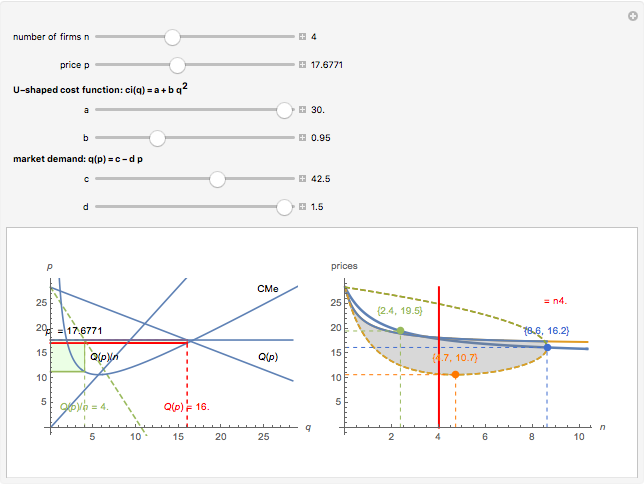
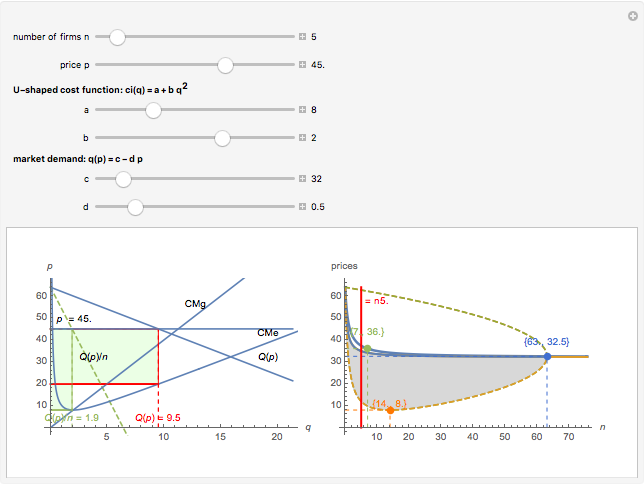
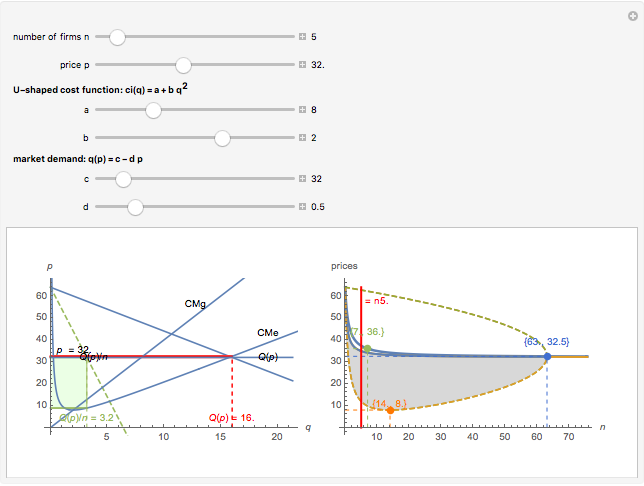
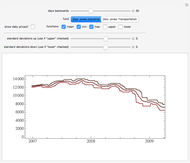
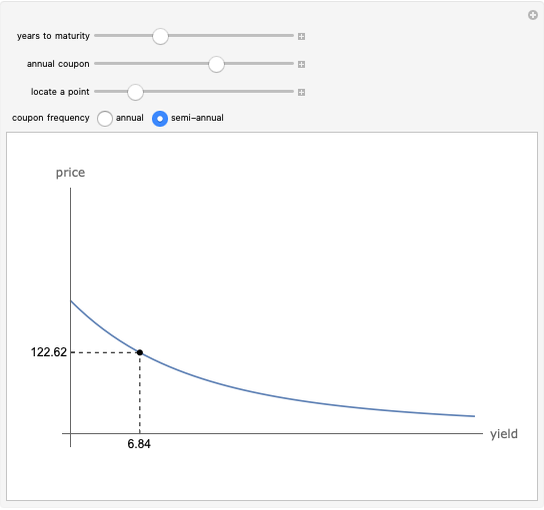
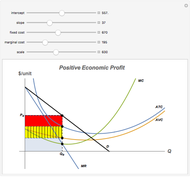
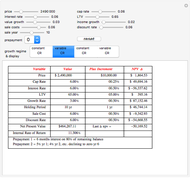
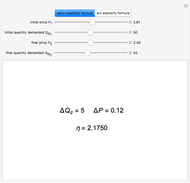
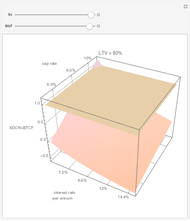
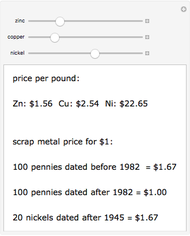
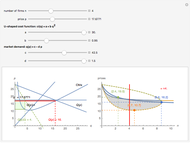
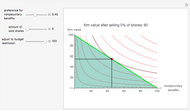
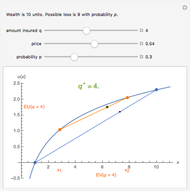
We show equilibrium prices when firms compete on the basis of price (Bertrand), but with a U-shaped average cost function. The graph on the left shows total market demand, one firm's demand function (the total demand at price  , denoted
, denoted  , divided by
, divided by  ), one firm's cost function, and the average and marginal cost function. The graph on the left also shows, for each price
), one firm's cost function, and the average and marginal cost function. The graph on the left also shows, for each price  , the profit level when the firm covers all or only a fraction,
, the profit level when the firm covers all or only a fraction,  , of the market demand. When profit covering all the demand is lower than profit covering only the
, of the market demand. When profit covering all the demand is lower than profit covering only the  part of the demand,
part of the demand,  is an equilibrium price (i.e., there are no incentives to slightly lower the price). On the right, you can see how equilibrium prices (the shadowed area) change as a function of the number of firms in the industry.
is an equilibrium price (i.e., there are no incentives to slightly lower the price). On the right, you can see how equilibrium prices (the shadowed area) change as a function of the number of firms in the industry.
Contributed by: Loreto Llorente (February 2009)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation