Time Constant in an Electrochemical Cell

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
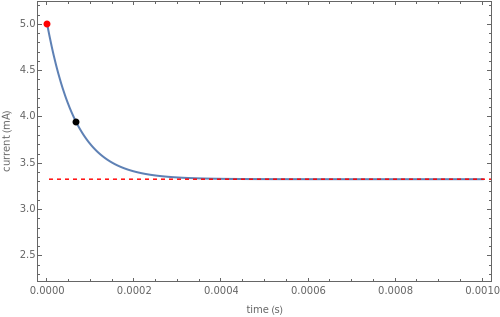
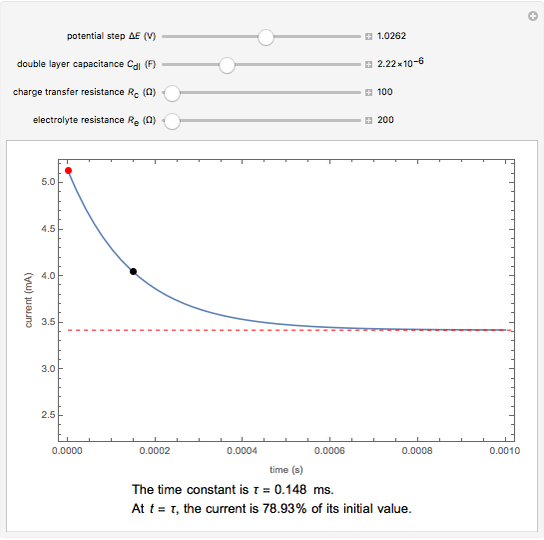
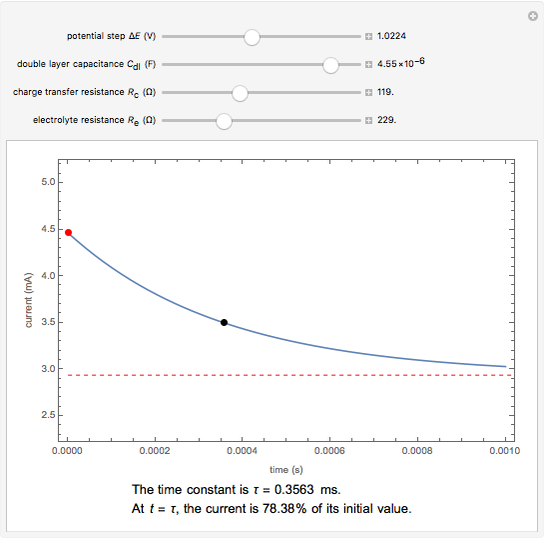
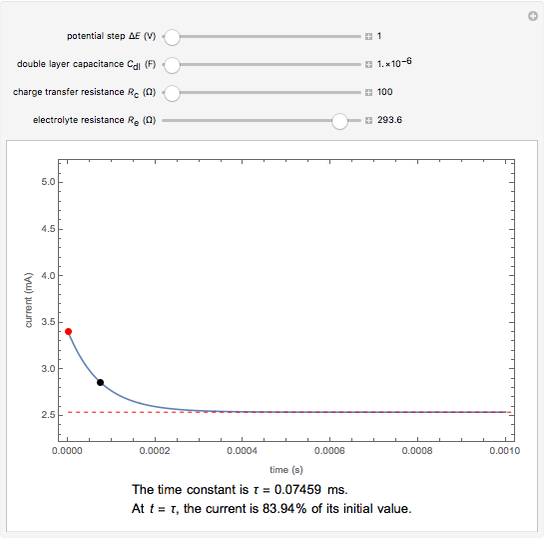
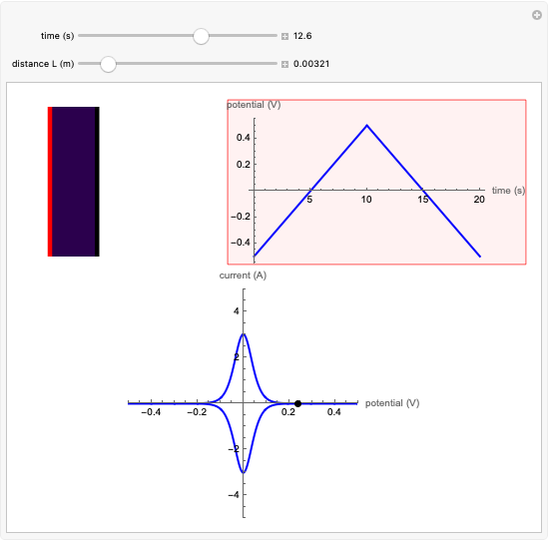
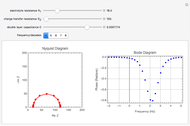
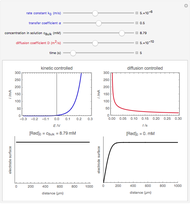
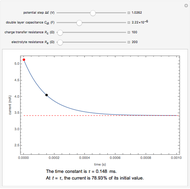
The rate at which the charged interface of an electrode (the electrical double layer) is established is described by the time constant  of the electrochemical cell. This Demonstration shows the impact of
of the electrochemical cell. This Demonstration shows the impact of  on the current flowing between the electrode and solution in response to a potential step.
on the current flowing between the electrode and solution in response to a potential step.
Contributed by: Quang-Dao Trinh and Adam Coyne (June 2016)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
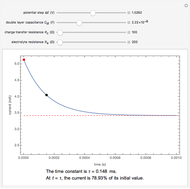
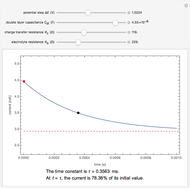
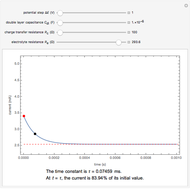
Snapshots
Details
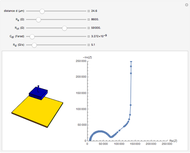
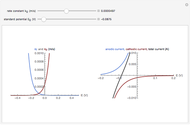
The double layer formed by contact of an ionic solution with an electrode acts as a capacitor. During a potential step experiment, a non-faradaic current is discharged at the electrode surface. The time constant  determines the rate at which the charged interface of an electrode is established.
determines the rate at which the charged interface of an electrode is established.
Permanent Citation