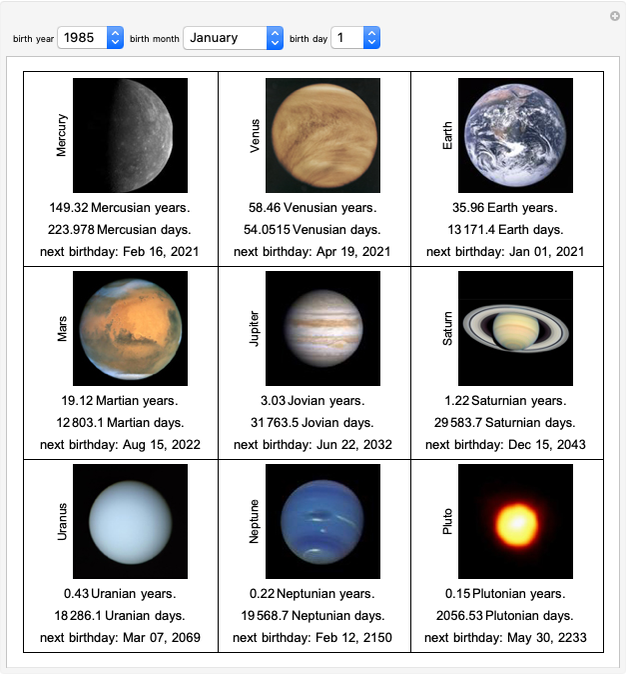
A Signed Rank Test of Hypotheses about a Median

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
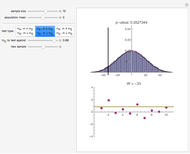
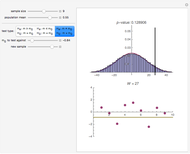
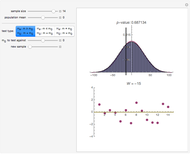
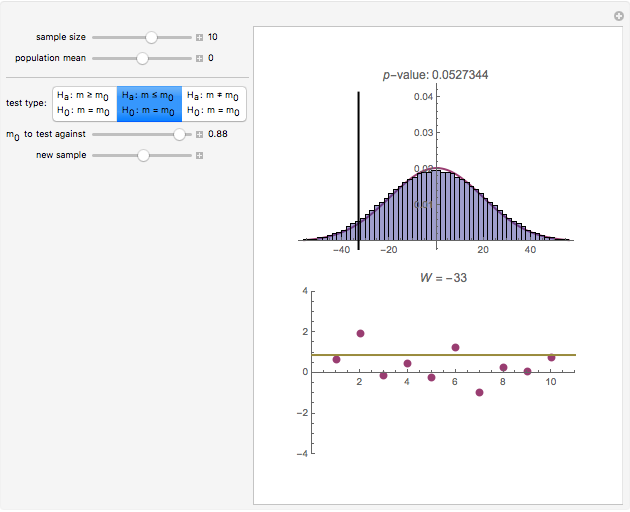
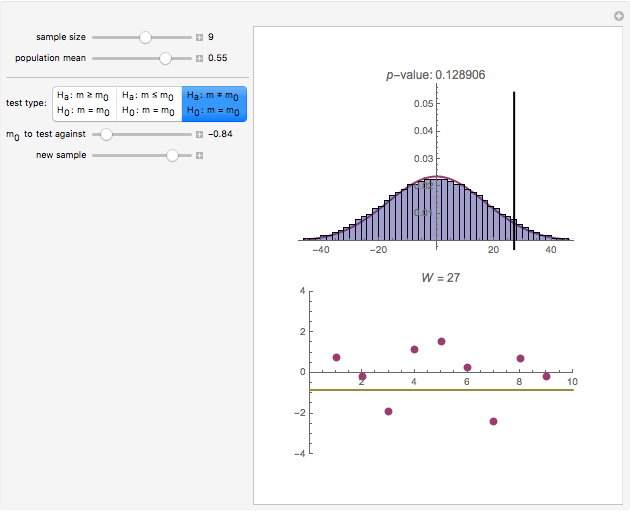
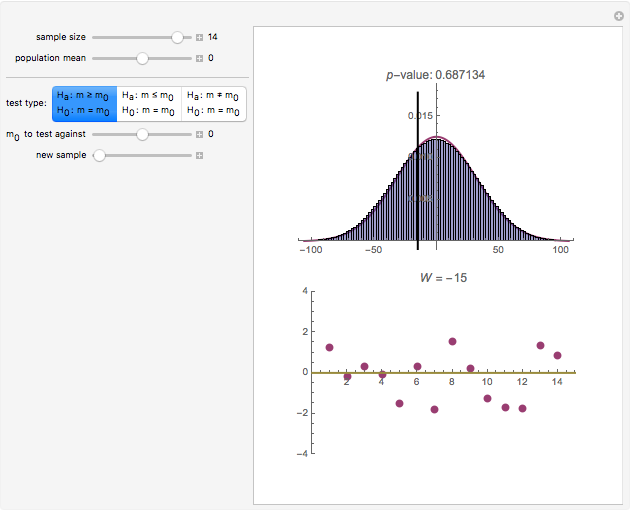
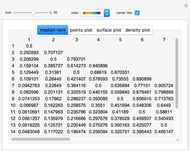
The statistic  on which this test is based is computed by assigning to each value in the dataset its ranking in the list of the absolute differences
on which this test is based is computed by assigning to each value in the dataset its ranking in the list of the absolute differences  multiplied by the sign of
multiplied by the sign of  (so values below
(so values below  get assigned a negative rank). These signed ranks are then summed to produce
get assigned a negative rank). These signed ranks are then summed to produce  . If the null hypothesis is true, that is, if
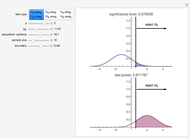
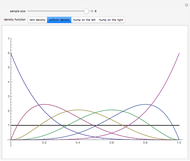
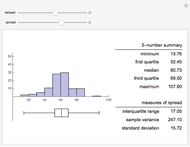
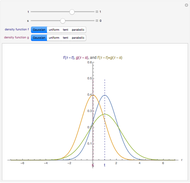
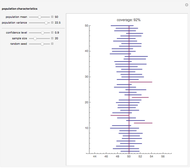
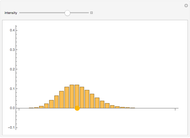
. If the null hypothesis is true, that is, if  is the median of the distribution from which the sample comes, then the signs of the differences can be regarded as Bernoulli trials. Using this to assign probabilities to all the possible signed rank sums gives the distribution which is shown in blue in the upper image above. The mean of this distribution is zero and its variance is
is the median of the distribution from which the sample comes, then the signs of the differences can be regarded as Bernoulli trials. Using this to assign probabilities to all the possible signed rank sums gives the distribution which is shown in blue in the upper image above. The mean of this distribution is zero and its variance is  . The purple curve is the density of a normal distribution with this mean and variance, which gives a good approximation to this distribution for all but very small sample sizes.
. The purple curve is the density of a normal distribution with this mean and variance, which gives a good approximation to this distribution for all but very small sample sizes.
Contributed by: Chris Boucher (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
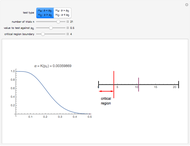
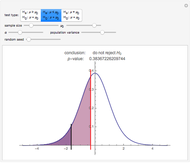
Snapshots
Details
The fact that the signs of the values  can be regarded as independent Bernoulli random variables can serve as the basis of a sign test of the hypothesis
can be regarded as independent Bernoulli random variables can serve as the basis of a sign test of the hypothesis  . An objection to such a test is that it fails to account for the magnitudes of the differences
. An objection to such a test is that it fails to account for the magnitudes of the differences  . Signed rank tests like the one above address this objection. Some tests—generally called "Wilcoxon Signed Rank Tests"—use the statistic obtained by summing only those absolute values
. Signed rank tests like the one above address this objection. Some tests—generally called "Wilcoxon Signed Rank Tests"—use the statistic obtained by summing only those absolute values  for which the difference
for which the difference  is positive or negative. These two statistics together with the statistic
is positive or negative. These two statistics together with the statistic  used in this Demonstration are referred to in various places as "Wilcoxon statistics". These tests can be used to assess the statistical evidence for one variable
used in this Demonstration are referred to in various places as "Wilcoxon statistics". These tests can be used to assess the statistical evidence for one variable  being larger than another
being larger than another  by using the data
by using the data  and taking
and taking  .
.
Permanent Citation