A Simple 2x2 Cooperative Game

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
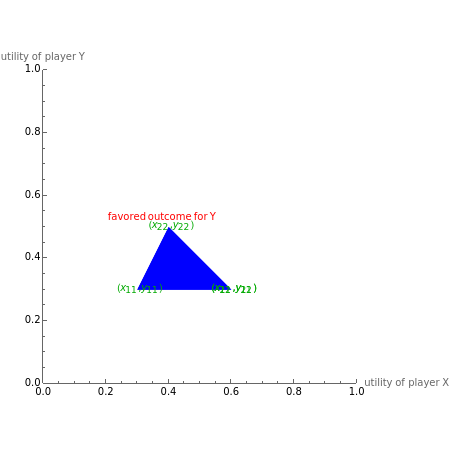
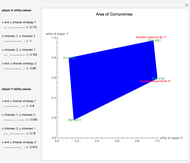
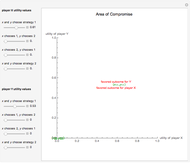
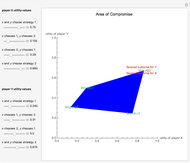
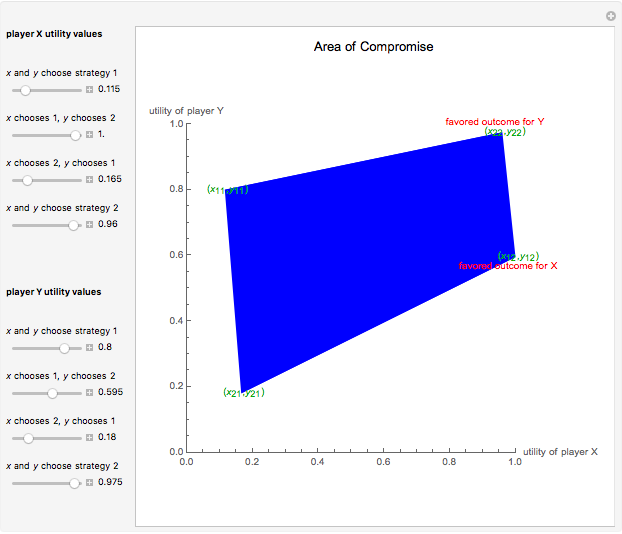
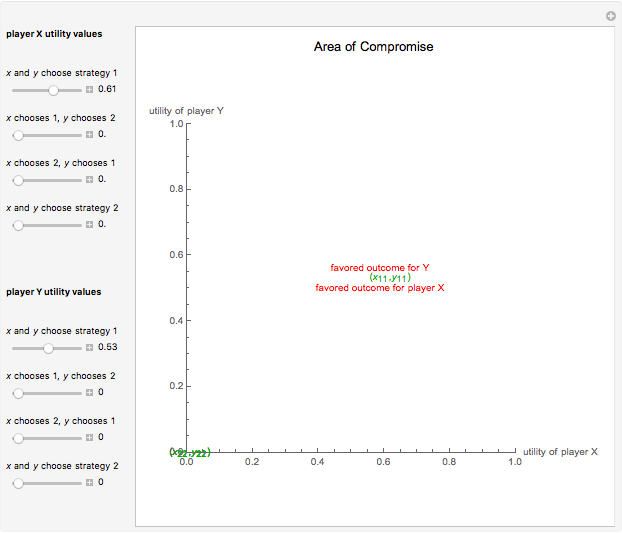
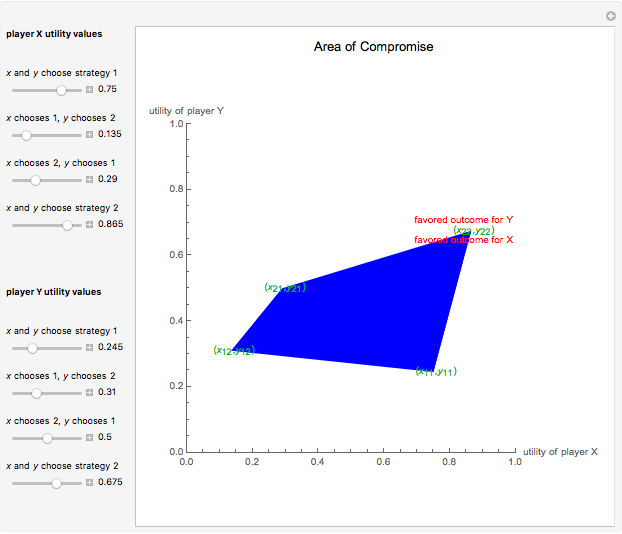
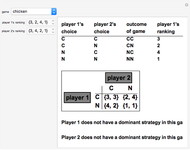
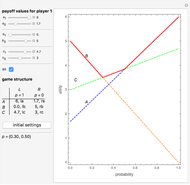
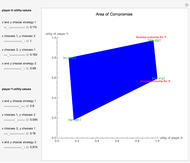
This Demonstration shows a geometric representation of a two-person 2×2 cooperative game, where the players have two strategies to choose from and can discuss how to play the game before it starts. The shaded area of compromise is the set of all possible outcomes for the game. These possible outcomes are displayed in coordinate form in terms of utility (the amount of satisfaction experienced by a player, with 1 being most favorable and 0 being least favorable). If the players X and Y have the same point as their favored outcome, they should both follow the corresponding strategies. If the players have different points as their favored outcomes, the point of compromise lies on the line segment with endpoints as the favored outcomes of players X and Y, respectively.
Contributed by: Darren Edmonds (April 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
While this Demonstration involves linear utility functions, it is also possible to have nonlinear utility functions that are not necessarily orthogonal over the solution space.
Reference
[1] R. D. Luce and H. Raiffa, Games and Decisions: Introduction and Critical Survey, New York: Dover Publications, 1989.
Permanent Citation
"A Simple 2x2 Cooperative Game"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ASimple2x2CooperativeGame/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: April 22 2015