Bifurcation Analysis of a Cubic Memristor Model

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
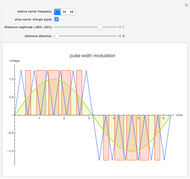
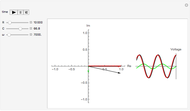
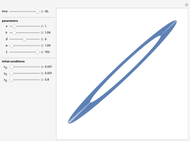
The memristor, named as a contraction for "memory resistor", is supposed to be the fourth fundamental electronic element, in addition to the well-known resistor, inductor, and capacitor. Its theoretical existence was postulated in 1971 by L. O. Chua [1], but its physical realization was announced only recently in a paper published in the May 2008 issue of Nature by a research team from Hewlett–Packard [2]. It has attracted worldwide attention due to its potential applications in the construction of electronic circuits, especially for newer-generation computers.
[more]
Contributed by: Vanessa Botta, Marcelo Messias, and Cristiane Néspoli (November 2009)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
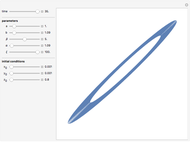
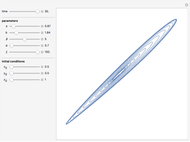
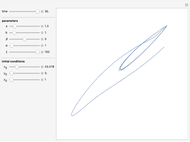
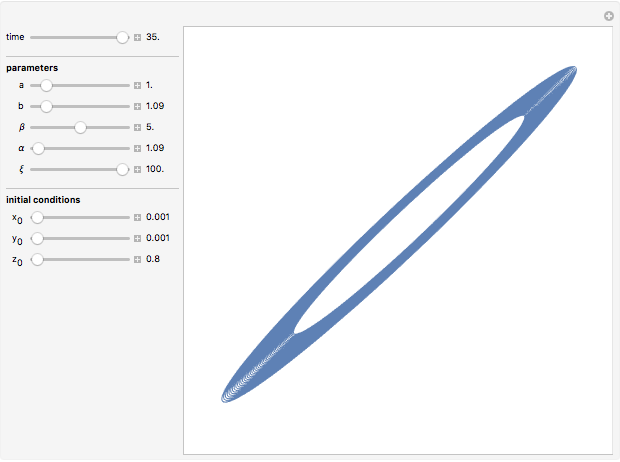
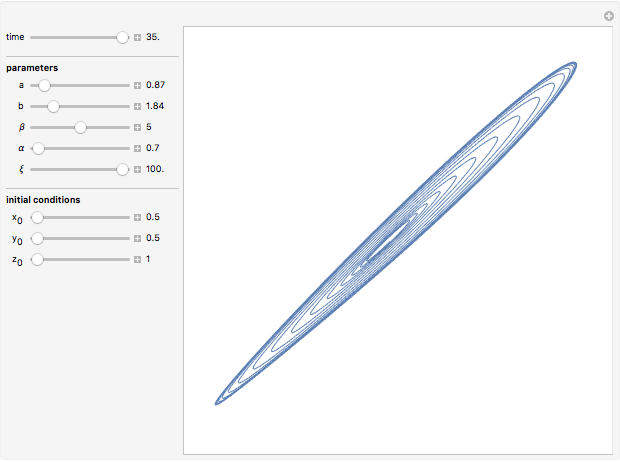
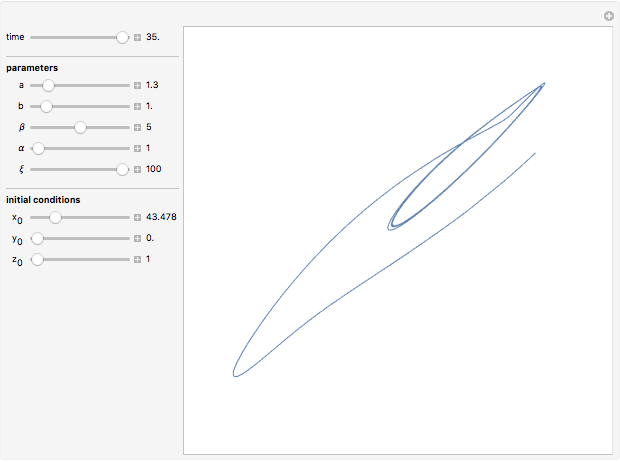
Snapshots
Details
References:
[1] L. O. Chua, "Memristor—The Missing Circuit Element," IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory, 18(5), 1971 pp. 507–519.
[2] D. B. Strukov, G. S. Snider, G. R. Stewart, and R. S. Williams, "The Missing Memristor Found," Nature, 453, 2008 pp. 80–83.
[3] M. Messias, C. Néspoli, and V. Botta, "Hopf Bifurcation from Lines of Equilibria without Parameters in Memristor Oscillators," Internationl Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos (to appear).
Links:
Permanent Citation
"Bifurcation Analysis of a Cubic Memristor Model"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BifurcationAnalysisOfACubicMemristorModel/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: November 6 2009