Classical Relativistic Particle in a Linearly Polarized Laser Field

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
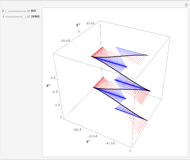
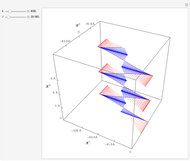
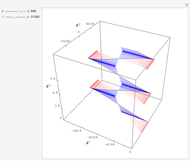
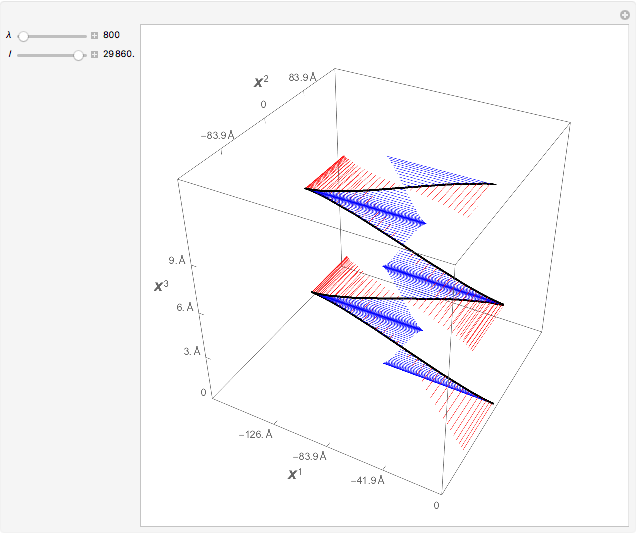
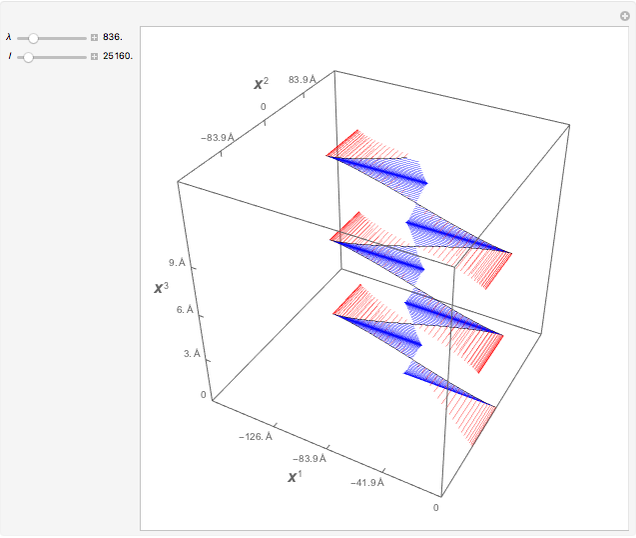
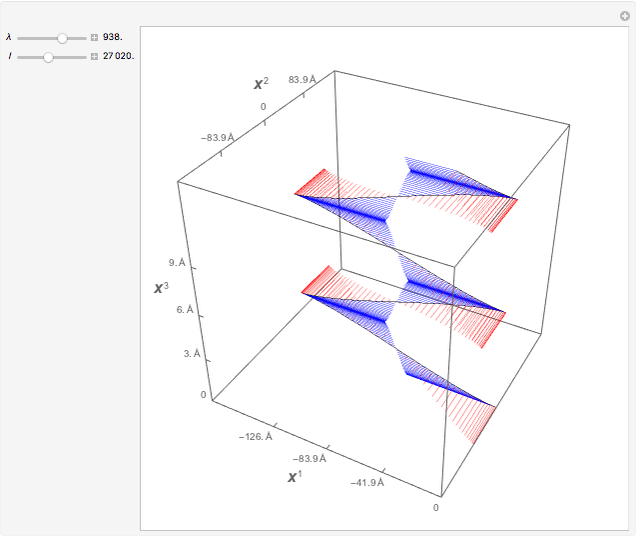
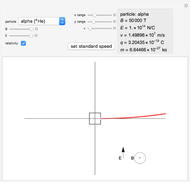
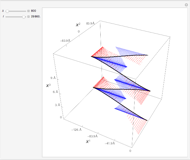
This Demonstration shows the trajectory of a relativistic particle represented by a black curve as it moves in a laser field propagating in the vertical direction. The laser field is monochromatic with wavelength 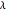 , in nanometers. The amplitude of the reduced vector potential, as defined in [2], is given by
, in nanometers. The amplitude of the reduced vector potential, as defined in [2], is given by 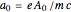 . The intensity of the laser field is then given by
. The intensity of the laser field is then given by  in units of
in units of 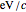 .
.
Contributed by: Renan Cabrera (September 2017)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] W. E. Baylis, Electrodynamics: A Modern Geometric Approach, Boston: Birkhäuser, 1999.
[2] W. E. Baylis and Y. Yao,"Relativistic Dynamics of Charges in Electromagnetic Fields: An Eigenspinor Approach," Physical Review A, 60(2), 1999 pp. 785–795. doi:10.1103/PhysRevA.60.785.
Permanent Citation
"Classical Relativistic Particle in a Linearly Polarized Laser Field"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ClassicalRelativisticParticleInALinearlyPolarizedLaserField/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 15 2017