Compressibility Factors Using the Soave-Redlich-Kwong Equation of State

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
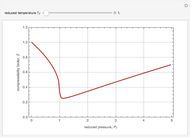
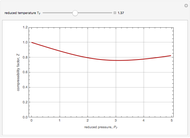
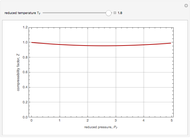
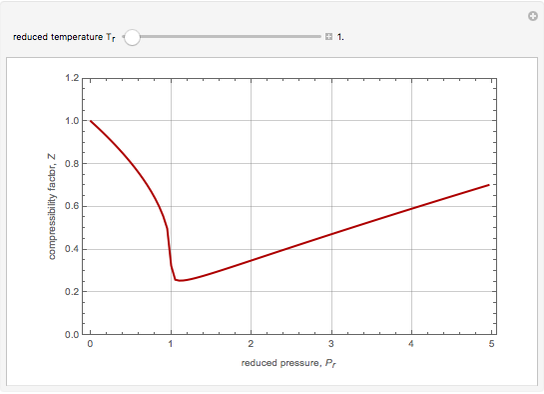
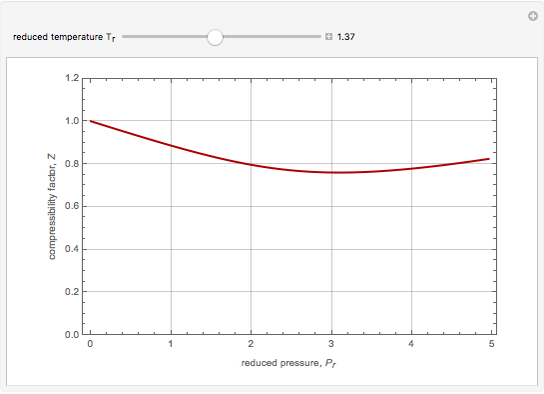
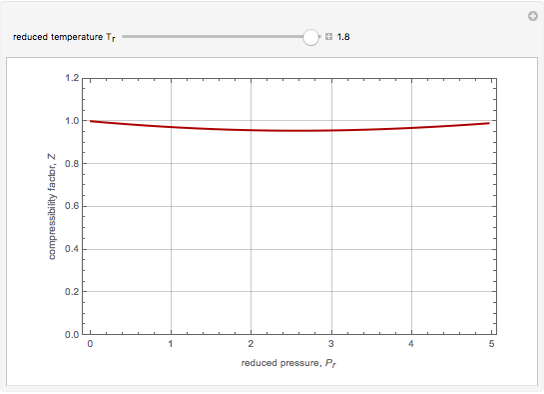
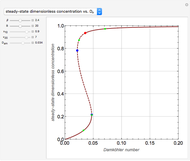
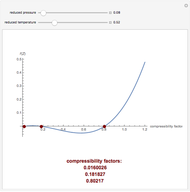
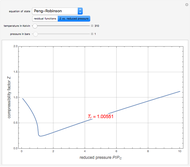
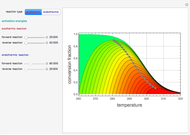
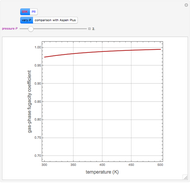
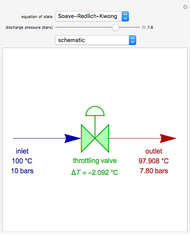
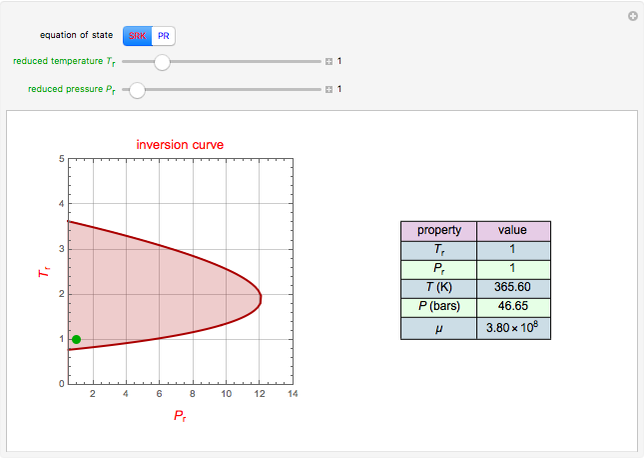
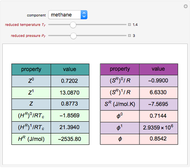
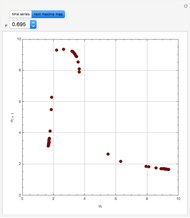
The Soave–Redlich–Kwong equation of state can accurately describe a compound in both liquid and vapor phases. This Demonstration applies this equation of state to estimate and plot the compressibility factor, 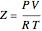 , versus reduced pressure,
, versus reduced pressure, 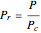 , for ethane at various values of the reduced temperature,
, for ethane at various values of the reduced temperature, 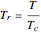 .
.
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
In the Soave–Redlich–Kwong equation of state, the compressibility factor is a solution of the following cubic equation:
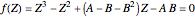 ,
,
where 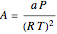 and
and 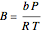 with
with 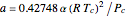 ,
, 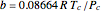 ,
, 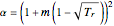 , and
, and 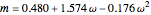 . Here
. Here  is the acentric factor,
is the acentric factor, 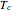 and
and 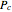 are the critical temperature and pressure, and
are the critical temperature and pressure, and 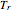 =
=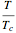 is the reduced temperature.
is the reduced temperature.
For ethane, 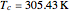 ,
, 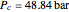 , and
, and 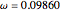 .
.
For more information on the compressibility factor, see http://en.citizendium.org/wiki/Compressibility_factor.
Reference
[1] Z. Nasri and H. Binous, "Applications of the Soave-Redlich-Kwong Equation of State Using Mathematica," Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 40(6), 2007 pp. 534–538.
Permanent Citation