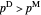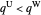Double Marginalization and Supply Chains

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
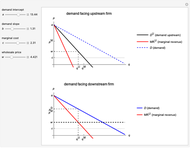
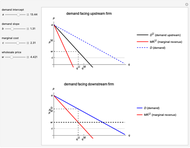
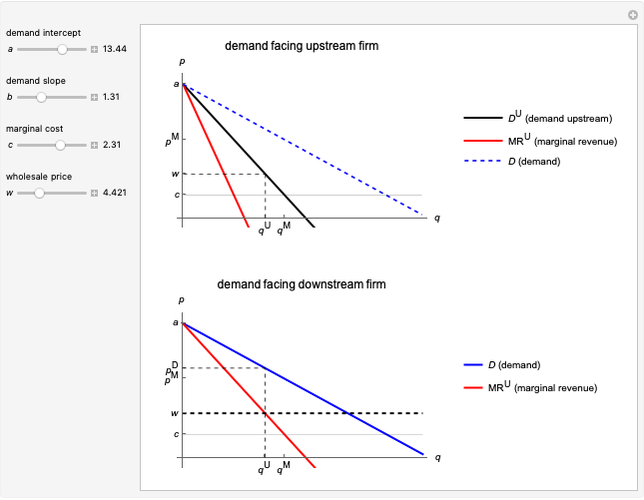
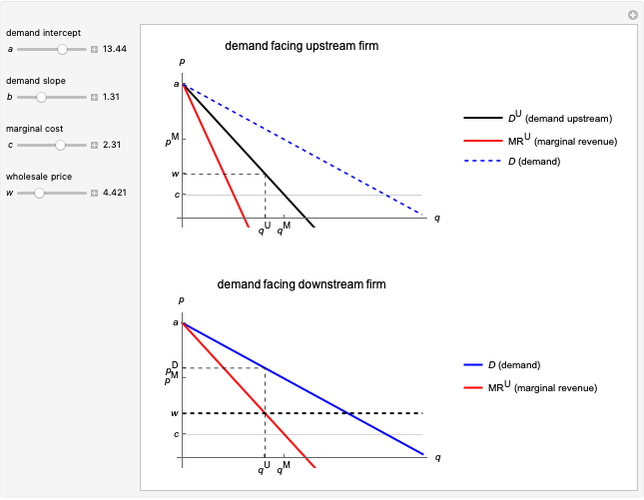
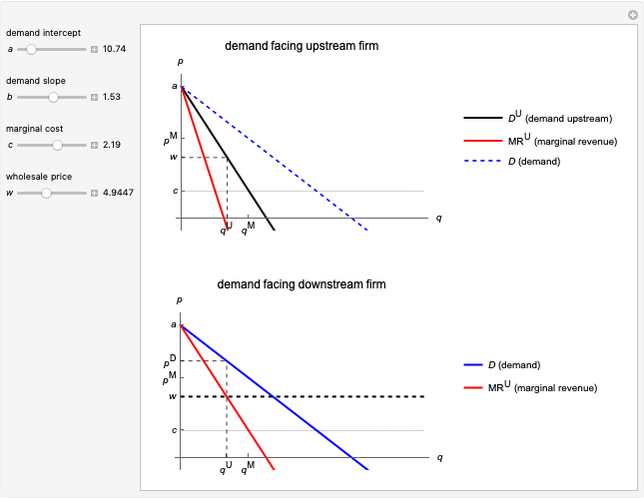
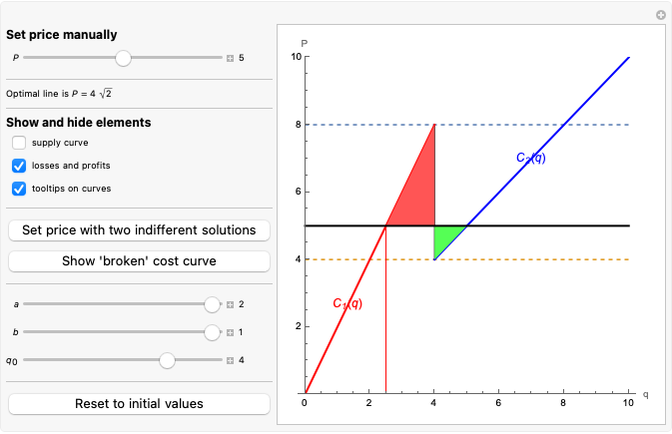
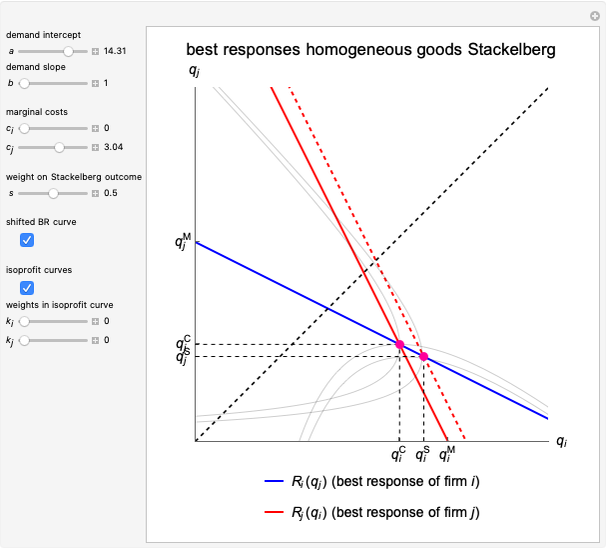
This Demonstration illustrates the issue of double marginalization in a vertical market with an upstream monopolist firm and a downstream monopolist firm facing inverse demand function 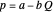 . The upstream firm has constant marginal costs
. The upstream firm has constant marginal costs  . The lower graph shows the demand (blue) and marginal revenue (red) curves of the downstream firm, while the upper graph shows the induced demand (black) and marginal revenue (red) curves of the upstream firm. The coefficients of the market demand are
. The lower graph shows the demand (blue) and marginal revenue (red) curves of the downstream firm, while the upper graph shows the induced demand (black) and marginal revenue (red) curves of the upstream firm. The coefficients of the market demand are 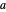 (demand intercept) and
(demand intercept) and  (demand slope). The marginal cost is
(demand slope). The marginal cost is  and the wholesale price is
and the wholesale price is 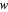 . For a given wholesale price
. For a given wholesale price 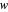 , the lower graph can be used to understand how the downstream firm chooses how much to produce (and hence demand from the upstream firm) and which price to charge. The graphs show the monopoly price
, the lower graph can be used to understand how the downstream firm chooses how much to produce (and hence demand from the upstream firm) and which price to charge. The graphs show the monopoly price 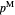 and quantity
and quantity 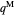 , as well as the upstream quantity
, as well as the upstream quantity 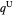 and downstream price
and downstream price 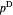 .
.
Contributed by: Flavio Toxvaerd (August 2022)
(University of Cambridge)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] Wikipedia. "Double Marginalization." (Oct 5, 2021) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Double_marginalization.
Permanent Citation