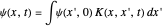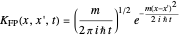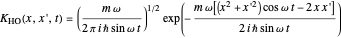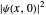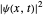Dynamics of Free Particle and Harmonic Oscillator Using Propagators

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
The time evolution of a one-dimensional quantum system from an initial state 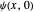 can be represented, in terms of the propagator, by [1, 2]
can be represented, in terms of the propagator, by [1, 2]
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (February 2020)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
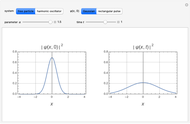
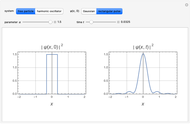
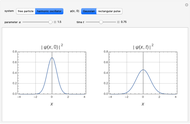
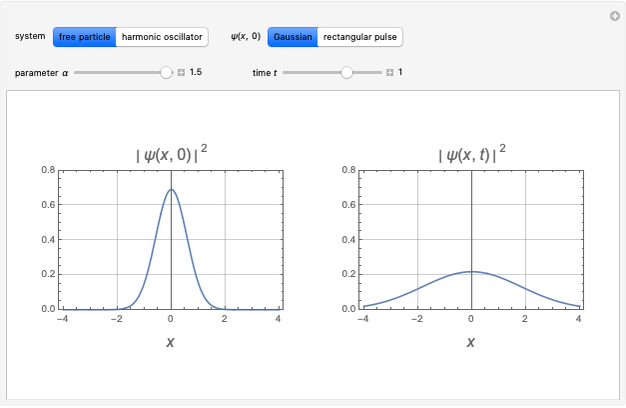
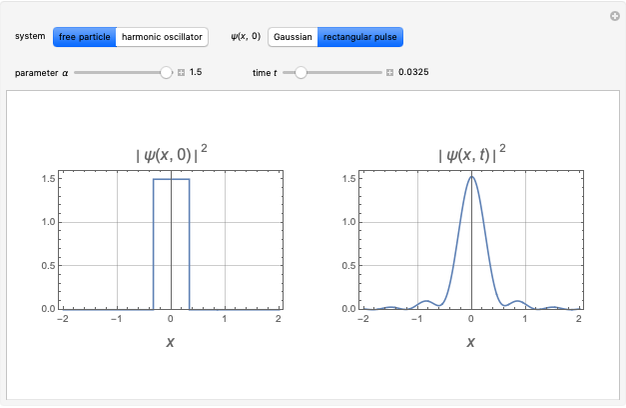
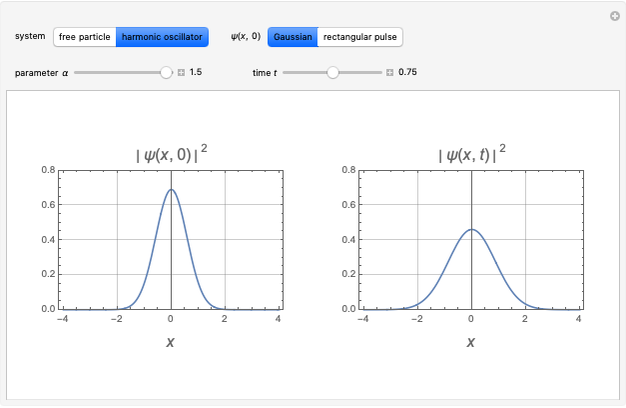
Snapshots
Details
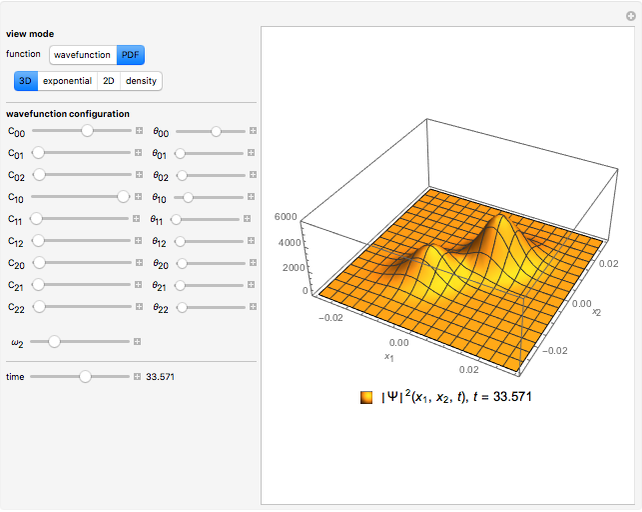
For the free particle with initial Gaussian wave packet 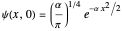 , we find
, we find
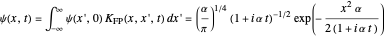 .
.
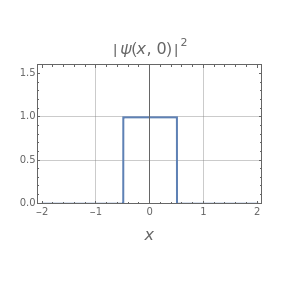
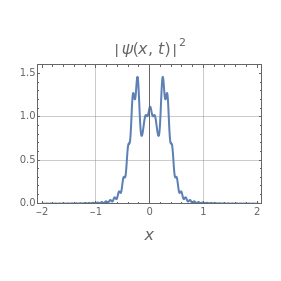
For initial rectangular pulse 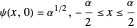 ,
,
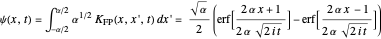 .
.
For the harmonic oscillator with initial Gaussian wave packet,
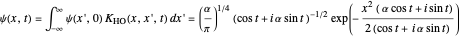 .
.
(For 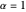 , this reduces to the time-dependent ground-state eigenfunction
, this reduces to the time-dependent ground-state eigenfunction 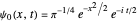 .)
.)
For initial rectangular pulse,
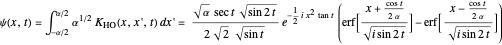 .
.
References
[1] R. P. Feynman and A. R. Hibbs, Quantum Mechanics and Path Integrals, New York: McGraw-Hill, 1965.
[2] Wikipedia. "Propagator." (Feb 24, 2020) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Propagator.
Permanent Citation