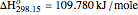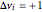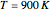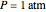Gas-Phase Catalytic Dehydrogenation of 1-Butene to 1,3-Butadiene

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
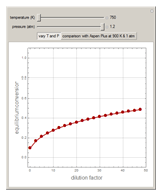
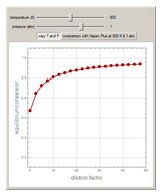
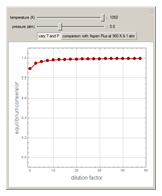
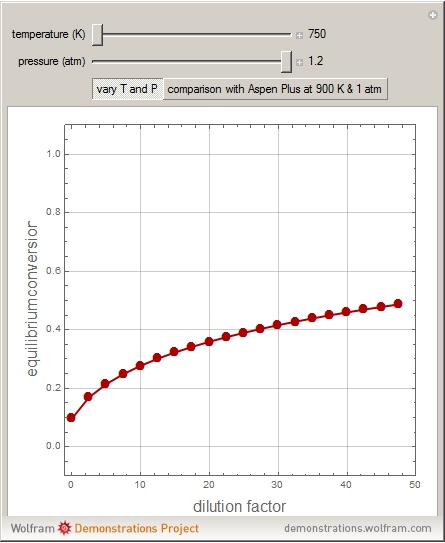
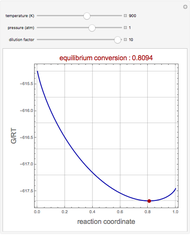
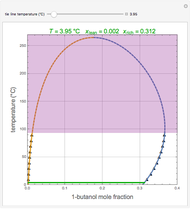
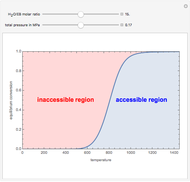
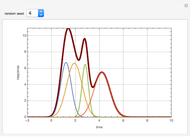
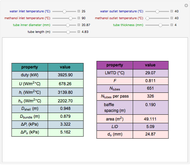
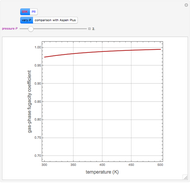
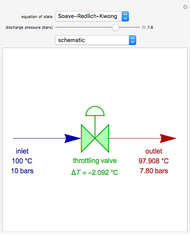
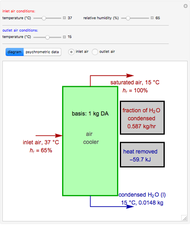
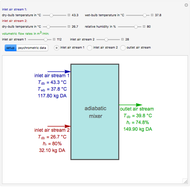
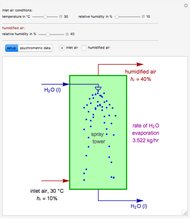
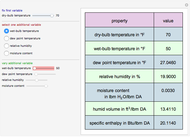
1,3-Butadiene can be produced by gas-phase catalytic dehydrogenation of 1-Butene in the reaction  . To suppress the reverse reaction, steam (acting as an inert gas) is added. The dilution factor is equal to the number of moles of steam added per mole of 1-Butene. The Demonstration computes the equilibrium conversion vs. the dilution factor using Gibbs free energy minimization. The user can set values of the temperature
. To suppress the reverse reaction, steam (acting as an inert gas) is added. The dilution factor is equal to the number of moles of steam added per mole of 1-Butene. The Demonstration computes the equilibrium conversion vs. the dilution factor using Gibbs free energy minimization. The user can set values of the temperature  , expressed in Kelvin, as well as the pressure
, expressed in Kelvin, as well as the pressure  , expressed in atm. Here, only low to moderate values of the pressure are allowed. Thus, the gas mixture behaves as an ideal gas.
, expressed in atm. Here, only low to moderate values of the pressure are allowed. Thus, the gas mixture behaves as an ideal gas.
Contributed by: Housam Binous, Mohammad Mozahar Hossain, and Ahmed Bellagi (January 2016)
(King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, KSA; ENIM, University of Monastir, Tunisia)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] J. R. Elliott and C. T. Lira, Introductory Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics, 2nd ed., Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall, 2012.
Permanent Citation