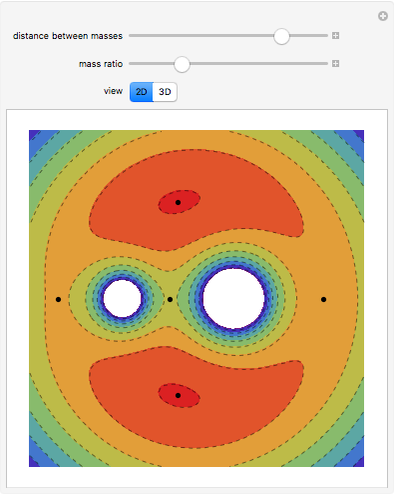
Linear Oscillator Perturbed by Plane Electrostatic Waves

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
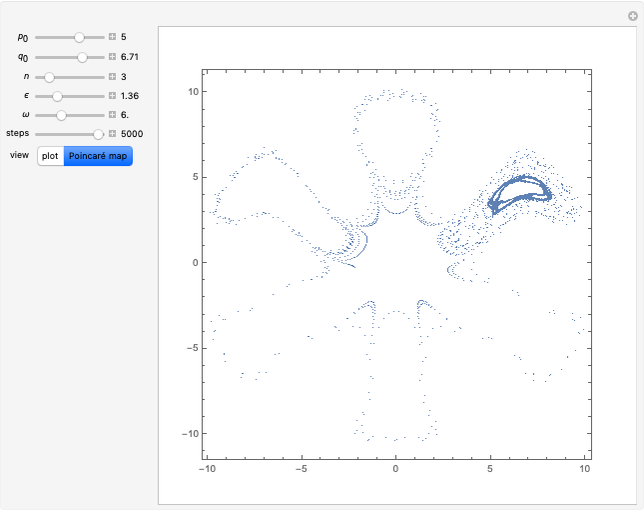
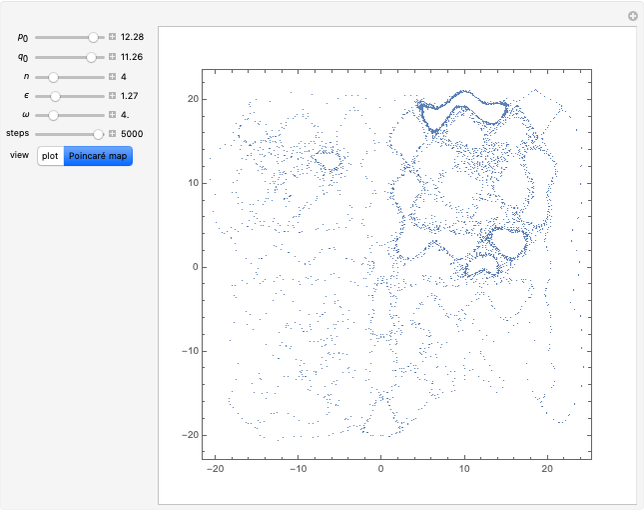
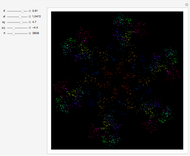
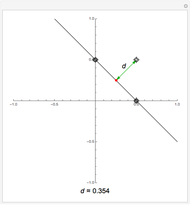
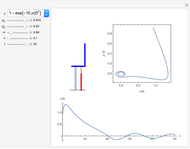
A charged particle gyrating in a uniform magnetic field directed along the  axis interacts with
axis interacts with  electrostatic waves, with equal wavenumbers and amplitudes but differing frequencies
electrostatic waves, with equal wavenumbers and amplitudes but differing frequencies  , propagating along the
, propagating along the  axis. Resonance occurs when
axis. Resonance occurs when  (where
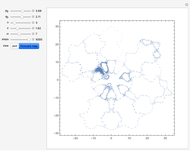
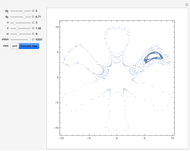
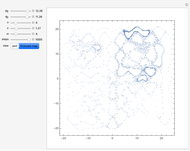
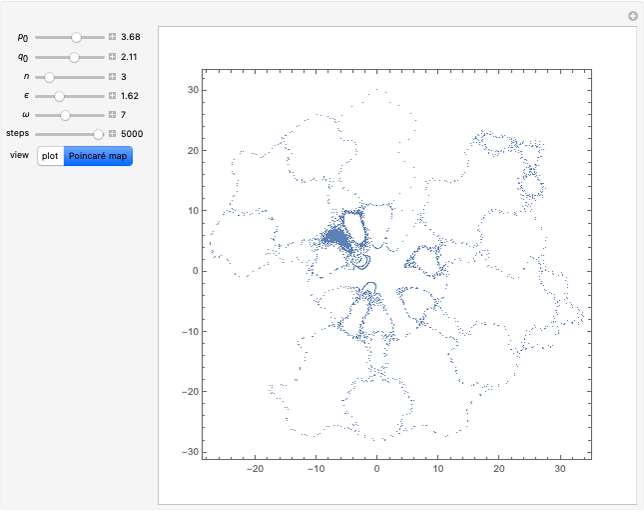
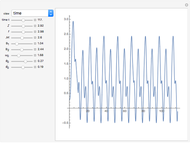
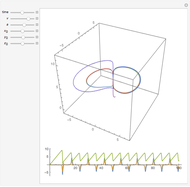
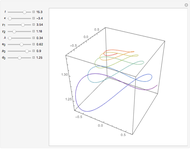
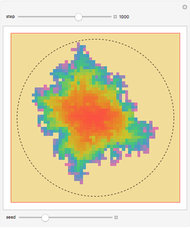
(where  is the cyclotron frequency). A stochastic web is then generated, as can be observed from its Poincaré map.
is the cyclotron frequency). A stochastic web is then generated, as can be observed from its Poincaré map.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (April 2013)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The equation of motion is
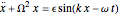 ,
,
where  is the temporal frequency of the electrostatic wave. Thus we can derive the Hamiltonian, choosing
is the temporal frequency of the electrostatic wave. Thus we can derive the Hamiltonian, choosing  :
:
 .
.
References
[1] J. Meiss, "Hamiltonian Systems," Scholarpedia, 2(8): 1943, 2007. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.1943.
[2] A. Lichtenberg and M. Lieberman, Regular and Chaotic Dynamics, 2nd ed., New York: Springer 1992 p. 238.
[3] J. Candy and W. Rozmus, "A Symplectic Integration Algorithm for Separable Hamiltonian Functions," Journal of Computational Physics 92, 1991 pp. 230–256. doi:10.1016/0021-9991(91)90299-Z.
[4] G. Zaslavsky, "Zaslavsky Web Map," Scholarpedia, 2(10): 3369, 2007. doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.3369.
Permanent Citation