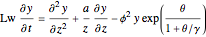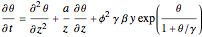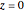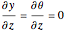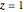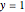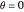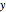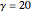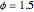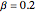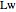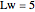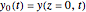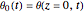Nonstationary Heat and Mass Transfer in a Porous Catalyst Particle

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
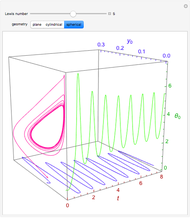
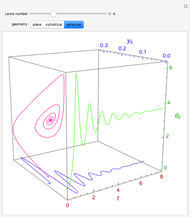
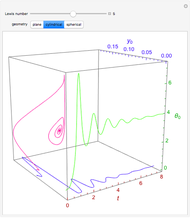
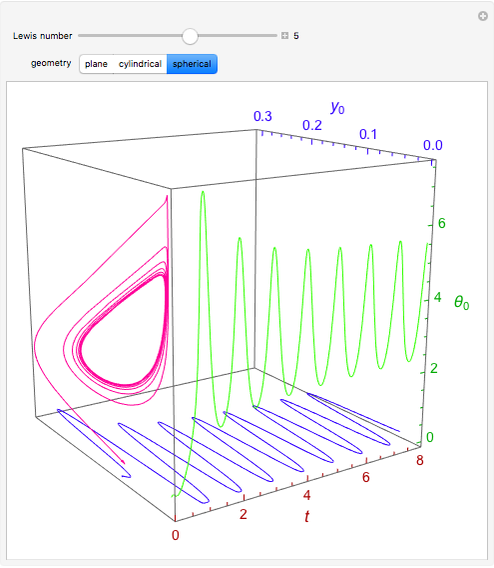
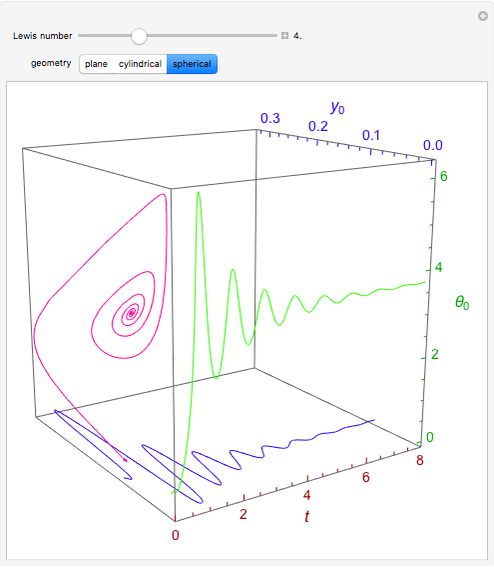
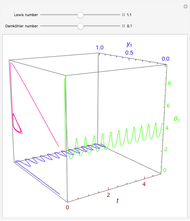
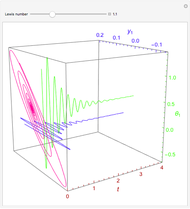
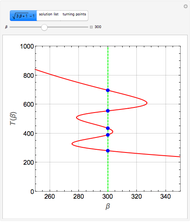
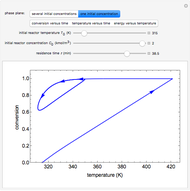
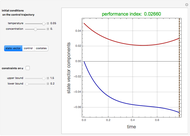
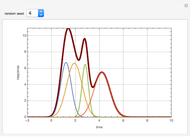
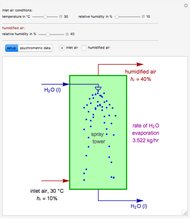
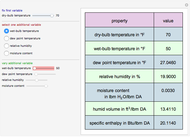
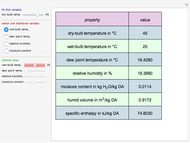
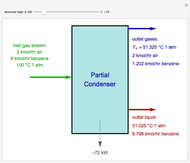
Consider the nonisothermal diffusion and reaction within a porous catalyst particle in which a first-order exothermic reaction takes place [1–4]. This system is governed by the following two dimensionless parabolic partial differential equations and boundary conditions BC1 and BC2:
[more]
Contributed by: Housam Binous, Abdullah A. Shaikh, and Ahmed Bellagi (February 2016)
(King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, KSA; ENIM, University of Monastir, Tunisia)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] V. Hlaváček, M. Kubíček, and M. Marek, "Analysis of Nonstationary Heat and Mass Transfer in a Porous Catalyst Particle I," Journal of Catalysis, 15(1), 1969 pp. 17–30. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(69)90004-9.
[2] V. Hlaváček, M. Kubíček, and M. Marek, "Analysis of Nonstationary Heat and Mass Transfer in a Porous Catalyst Particle II," J. Catalysis, 15(1), 1969 pp. 31–42. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(69)90005-0.
[3] R. Aris, The Mathematical Theory of Diffusion and Reaction in Permeable Catalysts, Vols. I and II. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1975.
[4] M. Kubíček, and M. Marek, Computational Methods in Bifurcation Theory and Dissipative Structures, Springer Series in Computational Physics, New York: Springer-Verlag, 1983.
Permanent Citation