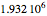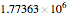Rigorous Steady-State Simulation of a Multicomponent Distillation Column

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
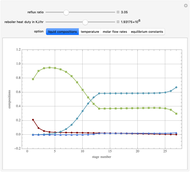
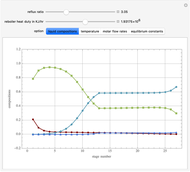
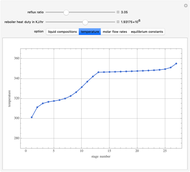
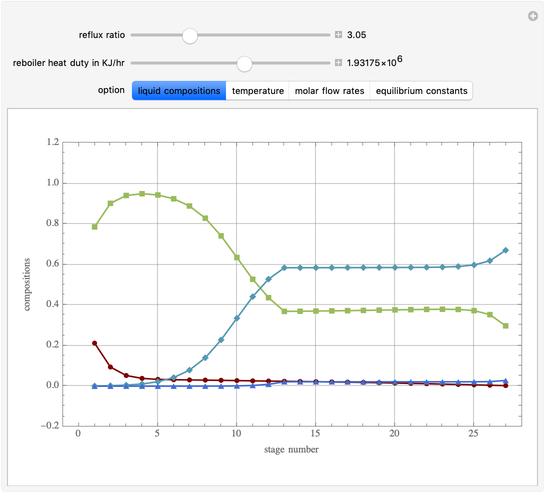
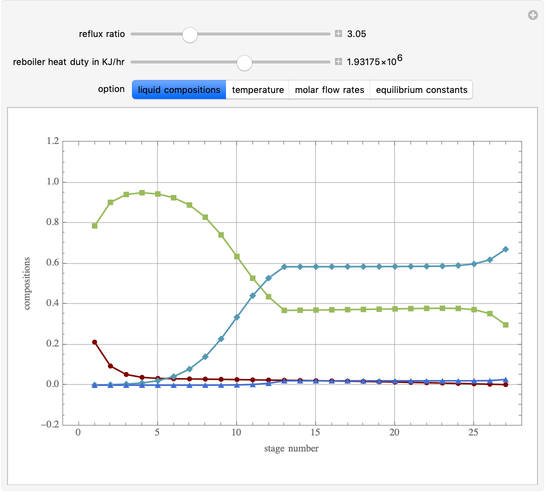
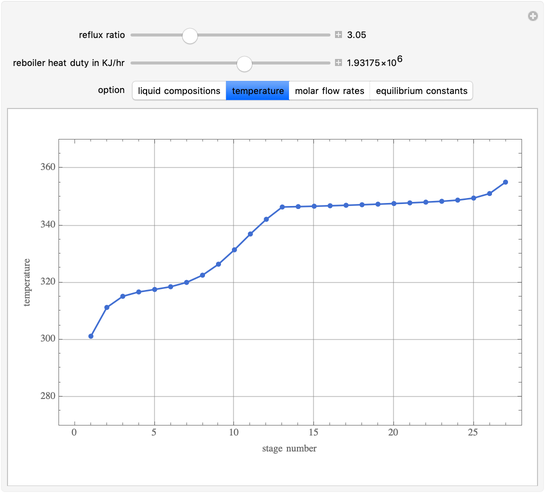
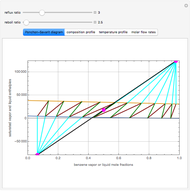
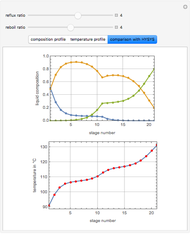
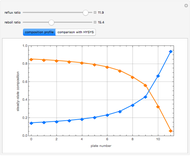
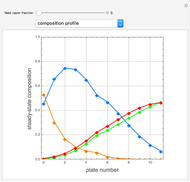
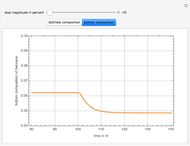
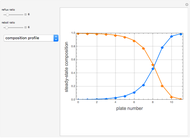
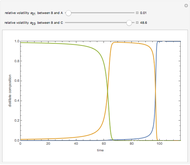
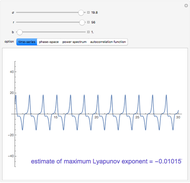
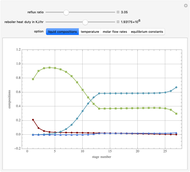
This Demonstration simulates a multicomponent distillation column in steady-state. In order to describe the vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) relationships and to compute the vapor and liquid phase enthalpies, the Soave-Redlich-Kwong equation of state (SRK EOS) is used (Soave, 1972 and Nasri and Binous, 2007). Rigorous modeling is performed by solving both mass and energy balance equations. All steady-state results are found to agree perfectly with those obtained using HYSYS 3.2, a major process simulator by Aspen Technology, Inc. Consider a multicomponent mixture to be fed to a distillation column containing 27 theoretical stages, a total condenser, and a partial reboiler and operating at a pressure of 16.212 bar.
[more]
Contributed by: Housam Binous and Zakia Nasri (December 2008)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The Mathematica built-in command used to solve the system of nonlinear algebraic equations is FindRoot. We have solved a system of 297 nonlinear algebraic equations in less than 1.8 seconds using an Intel® Core™ 2 DUO CPU T8300 at 2.4 GHz with 3 GB of memory.
References:
G. Soave, "Equilibrium Constants from a Modified Redlich-Kwong Equation of State," Chemical Engineering Science, 27(6), 1972 pp. 1197–1203.
Z. Nasri and H. Binous, "Applications of the Soave-Redlich-Kwong Equation of State Using Mathematica," Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 40(6), 2007 pp. 534–538.
Y. S. Choe and W. L. Luyben, "Rigorous Dynamic Models of Distillation Columns," Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 26(10), 1987 pp. 2158–2161.
Z. Nasri and H. Binous, "Rigorous Distillation Dynamics Simulations Using a Computer Algebra," Computer Applications in Engineering Education, 20(2), 2012 pp. 193–202.
Permanent Citation