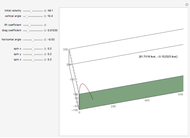
Thermokinetic Oscillator

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
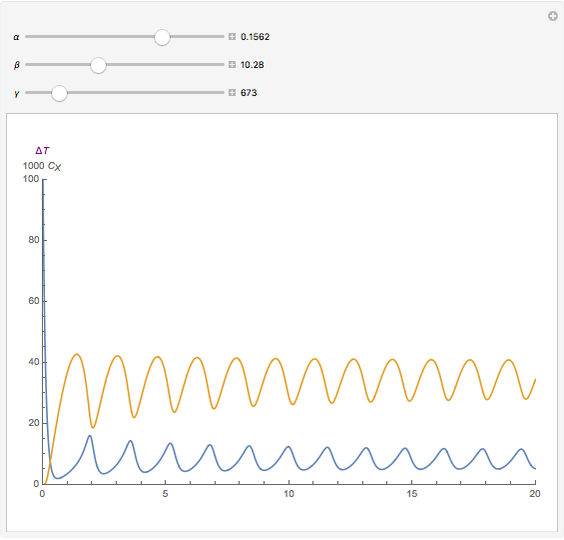
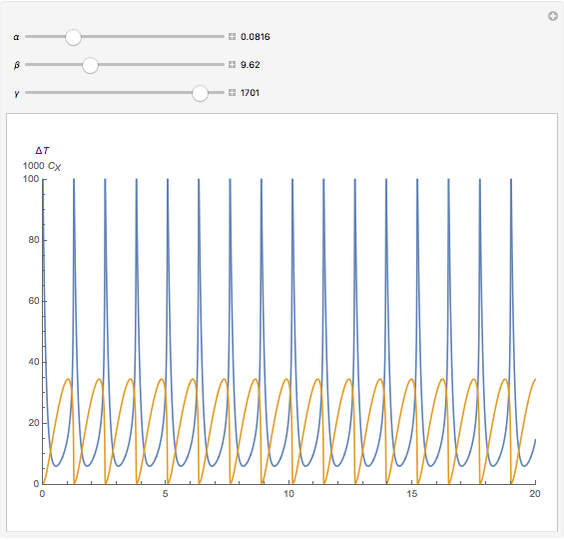
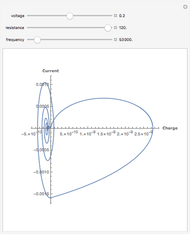
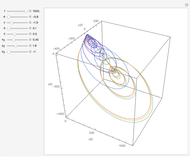
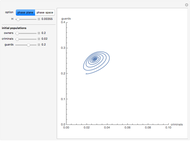
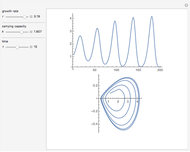
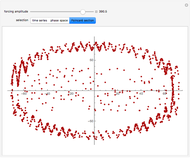
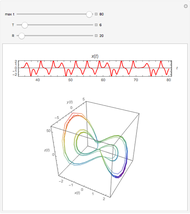
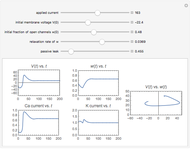
For a thermokinetic oscillator, the reaction scheme is  ,
,  . The second reaction is exothermic with a reaction enthalpy
. The second reaction is exothermic with a reaction enthalpy 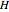 ; it has a substantial activation energy
; it has a substantial activation energy 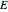 . The concentration of component
. The concentration of component 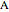 is constant, the temperature of the surroundings is
is constant, the temperature of the surroundings is 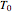 , the density and specific heat of the reaction mixture are
, the density and specific heat of the reaction mixture are  and
and 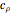 , the area for heat transfer is
, the area for heat transfer is 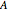 , the volume of the system is
, the volume of the system is  ,
, 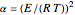 ,
, 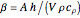 , and
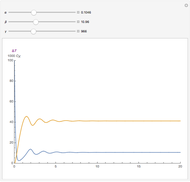
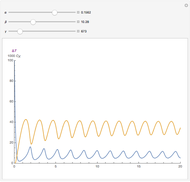
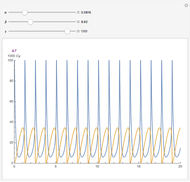
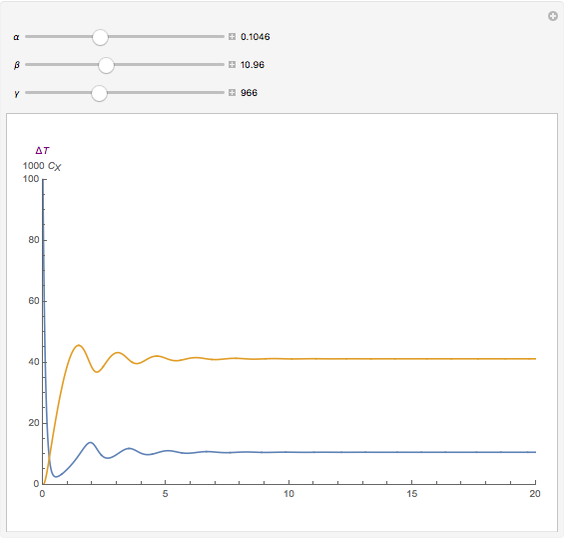
, and 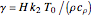 . The relevant rate equations are solved and plotted for
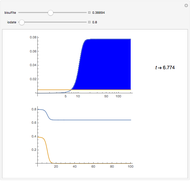
. The relevant rate equations are solved and plotted for  and
and  , the latter scaled up by 1000 for convenience.
, the latter scaled up by 1000 for convenience.
Contributed by: Benson R. Sundheim (January 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
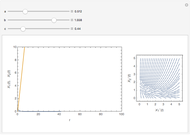
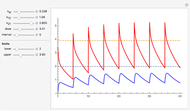
The reaction produces heat, accelerating the reaction and reducing the concentration of  . As you vary the parameters, the interplay of these opposing tendencies can produce oscillations and bifurcation behavior.
. As you vary the parameters, the interplay of these opposing tendencies can produce oscillations and bifurcation behavior.
References
[1] P. Gray and S. K. Scott, Chapter 4, Chemical Oscillations and Instabilities, New York: Oxford University Press, 1990.
[2] D. A. Frank-Kamenetskii and I. E. Salnikov. Zhur. Fiz. Khim., 17, 1943 p. 79.
[3] xmds.org. thermkin.xmds. (Dec 28 2012)
Permanent Citation