Kinetics of DNA Methylation in Eukaryotes

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
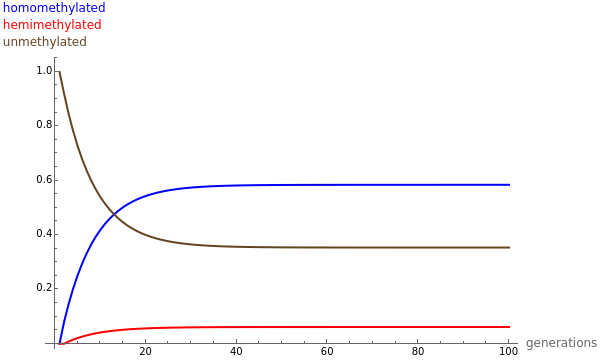
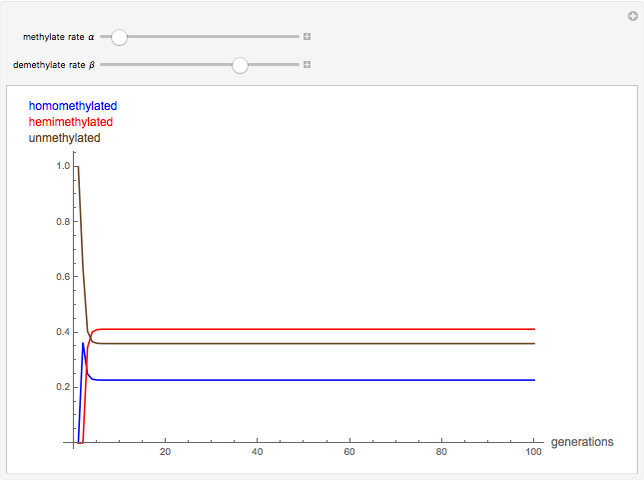
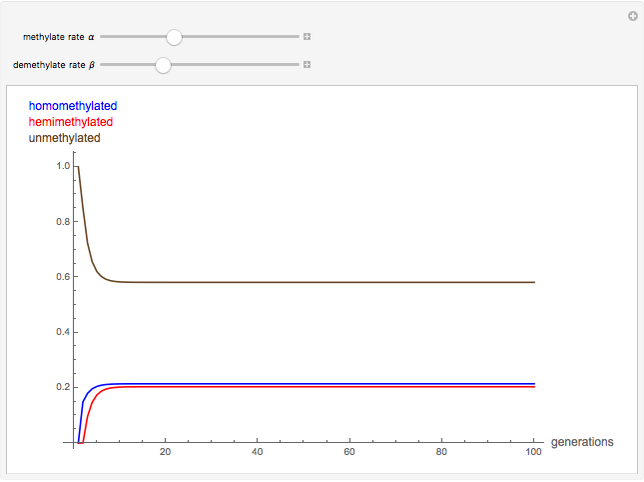
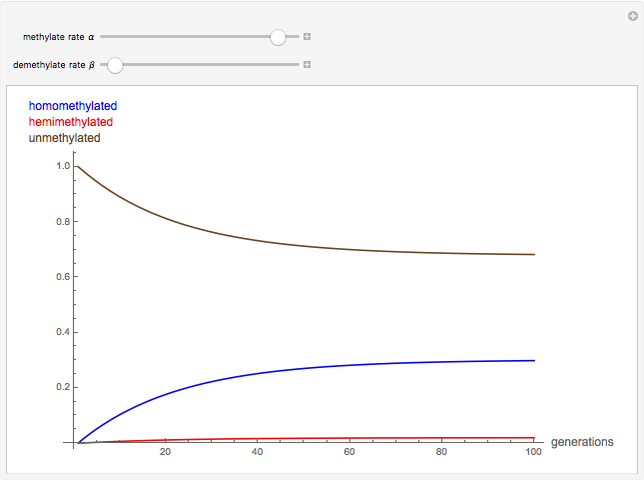
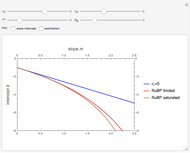
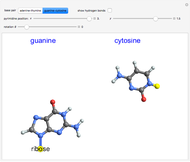
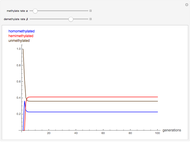
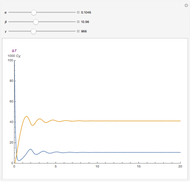
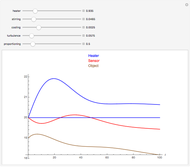
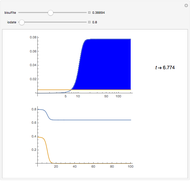
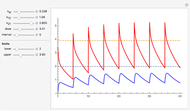
The methylation and demethylation of the 5-position in cytosine, which stops the expression of the gene in vertebrates, is passed along on one strand of DNA. The daughter cells may spontaneously methylate (at rate  ) or demethylate (at rate
) or demethylate (at rate  ). At the
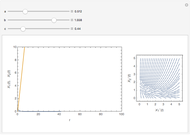
). At the  step of successive divisions, the probabilities of the cell having one, two, or none of its labile sites methylated are denoted by
step of successive divisions, the probabilities of the cell having one, two, or none of its labile sites methylated are denoted by 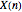 ,
, 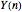 , and
, and 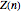 , which give the proportion of homomethylated, hemi-methylated, and unmethylated sites, respectively, in generation
, which give the proportion of homomethylated, hemi-methylated, and unmethylated sites, respectively, in generation  .
.
Contributed by: Benson R. Sundheim (May 2013)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The kinetic equations,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
are recast as:

and the time evolution of 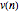 is calculated by recursion.
is calculated by recursion.
Reference
[1] S. P. Otto and V. Walbot, "DNA Methylation in Eukaryotes: Kinetics of Demethylation and de Novo Methylation During the Life Cycle," Genetics, 124(2), 1990 pp. 429–437. www.genetics.org/content/124/2/429.full.pdf.
Permanent Citation