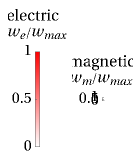
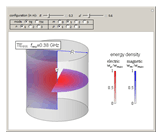
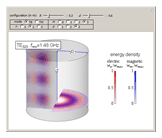
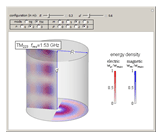
Cylindrical Cavity Resonator

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
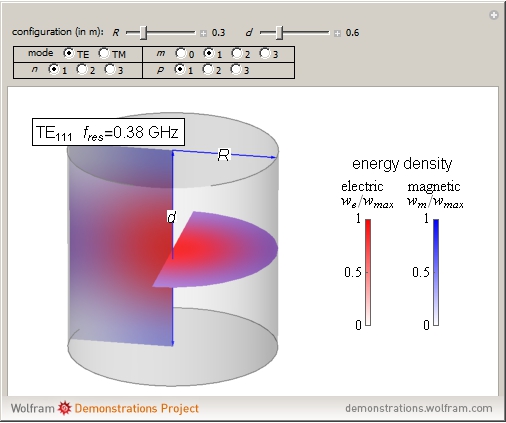
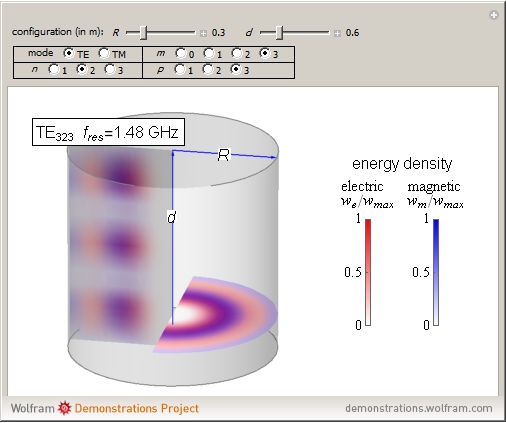
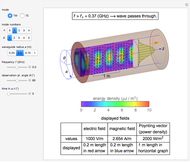
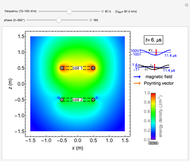
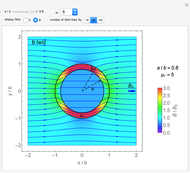
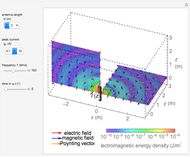
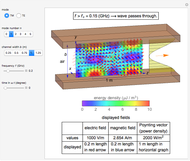
An electromagnetic wave can be confined inside a space surrounded by conducting walls, which is called a cavity. Consider a cylindrical cavity with inner radius  and height
and height  . There are two possible wave modes: transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM). For appropriate field variables for those modes, separation of variables leads to harmonic solutions to the wave equation (from Maxwell's equations) of the form
. There are two possible wave modes: transverse electric (TE) and transverse magnetic (TM). For appropriate field variables for those modes, separation of variables leads to harmonic solutions to the wave equation (from Maxwell's equations) of the form  , where
, where  is a Bessel function of the first kind. The constant
is a Bessel function of the first kind. The constant  is an integer
is an integer  . Noting that
. Noting that  is an eigenvalue of the Helmholtz equation and taking into account the boundary condition for the trigonometric function
is an eigenvalue of the Helmholtz equation and taking into account the boundary condition for the trigonometric function  , introduce the additional integer indices:
, introduce the additional integer indices:  ,
,  (TE), and
(TE), and  (TM).
(TM).
Contributed by: Y. Shibuya (August 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] J. D. Jackson, Classical Electrodynamics, 3rd ed., New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1999.
[2] W. K. H. Panofsky and M. Phillips, Classical Electricity and Magnetism, 2nd ed., New York: Dover Publications, 2005.
Permanent Citation