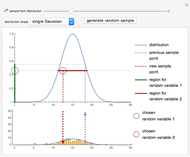
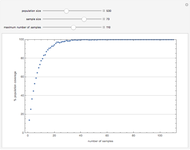
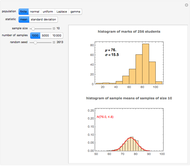
Sampling Theorem
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
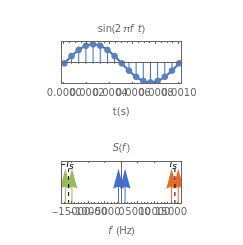
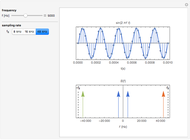
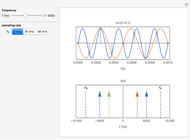
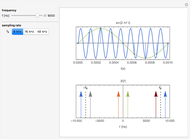
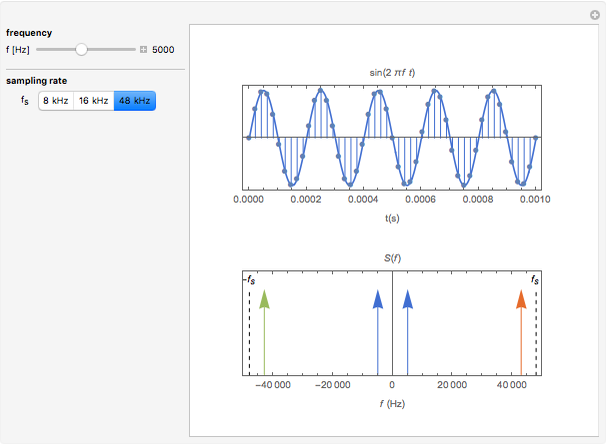
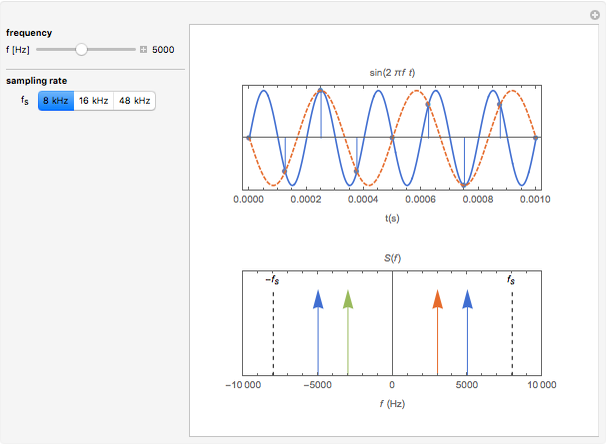
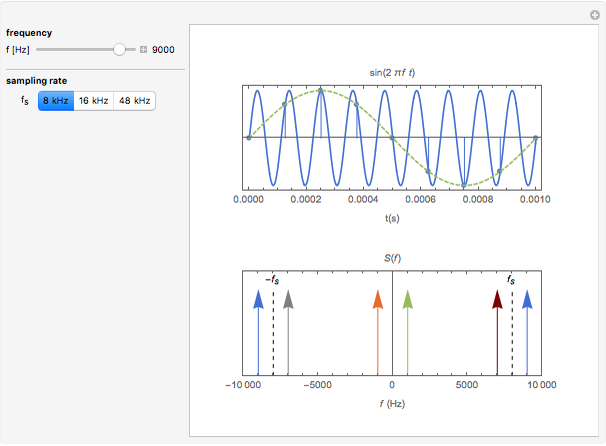
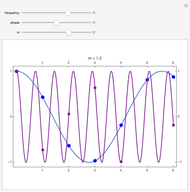
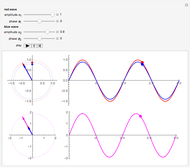
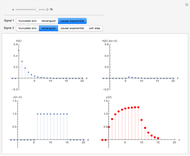
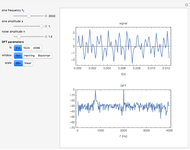
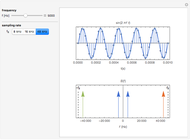
The top figure shows a sine wave of frequency  and its samples. The bottom figure shows the Fourier spectrum
and its samples. The bottom figure shows the Fourier spectrum  of the sampled signal. It consists of two spectral lines at
of the sampled signal. It consists of two spectral lines at  , repeated periodically at integer multiples of the sampling rate
, repeated periodically at integer multiples of the sampling rate  .
.
Contributed by: Carsten Roppel (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation