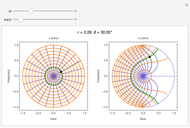
Transformation of s-Reflection Coefficient between Normal and Oblique Incidence

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
If 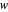 denotes an interface Fresnel reflection or transmission coefficient for
denotes an interface Fresnel reflection or transmission coefficient for  - or
- or 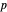 -polarized light at an oblique angle of incidence
-polarized light at an oblique angle of incidence  , and
, and  denotes the same coefficient at normal incidence, then it can be shown that w is an analytic function of
denotes the same coefficient at normal incidence, then it can be shown that w is an analytic function of  that depends parametrically on the angle of incidence
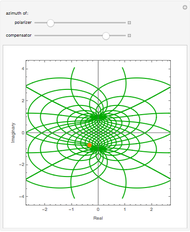
that depends parametrically on the angle of incidence  . The mapping
. The mapping  between the complex
between the complex  and
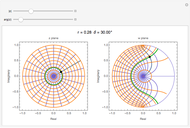
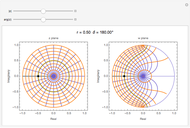
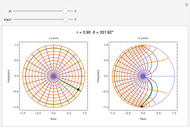
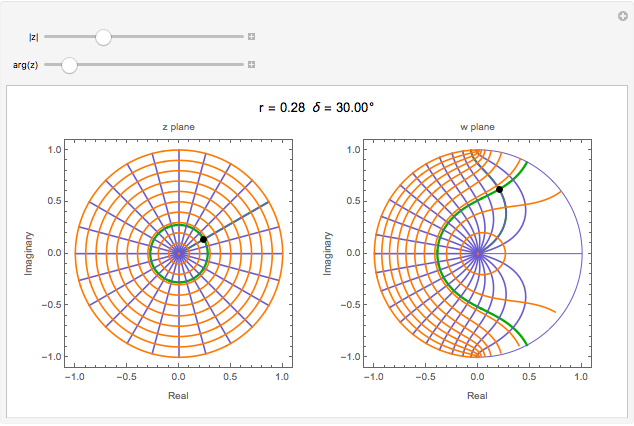
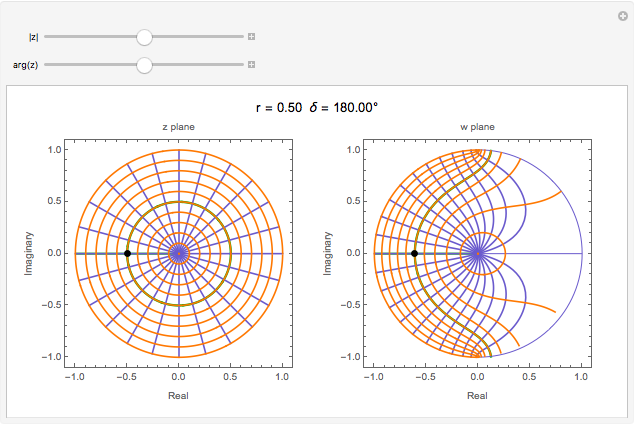
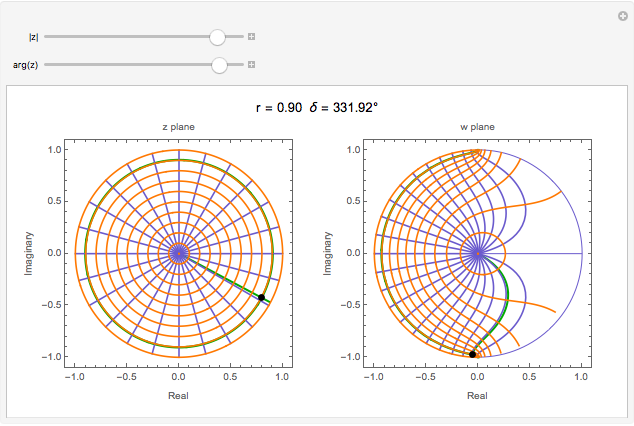
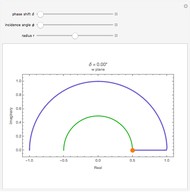
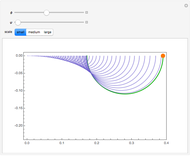
and 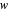 planes is illustrated here by one of the Fresnel coefficients (for s reflection) at normal incidence and one oblique angle of incidence (45°). Here
planes is illustrated here by one of the Fresnel coefficients (for s reflection) at normal incidence and one oblique angle of incidence (45°). Here 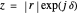 , where
, where 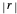 and
and  are the normal-incidence amplitude reflectance and phase shift.
are the normal-incidence amplitude reflectance and phase shift.
Contributed by: Siva Perla (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
R. M. A. Azzam, "Transformation of Fresnel's interface reflection and transmission coefficients between normal and oblique incidence," Journal of Optical Society of America, 69(4), 1979 pp. 590-596.
Permanent Citation