Beta Distributions for a Given Mean, Median or Mode

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
The beta distribution 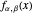 of a random variable
of a random variable 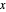 , where
, where 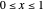 and
and 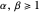 , has mode
, has mode  , mean
, mean 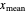 , median
, median 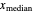 and variance
and variance 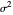 , which are determined by
, which are determined by 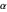 and
and 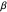 in a nonintuitive manner. However, once
in a nonintuitive manner. However, once  ,
,  or
or 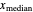 has been chosen,
has been chosen,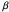 can be expressed as a function of its value and
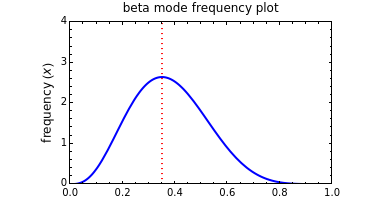
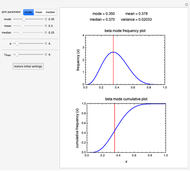
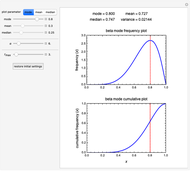
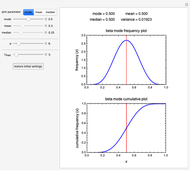
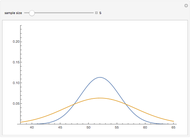
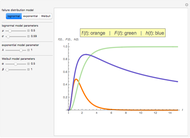
can be expressed as a function of its value and 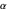 becomes the sole determinant of the distribution's spread. This Demonstration calculates and plots the beta distribution's probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) for chosen values of the mode, mean or median and displays the numerical values of all three, as well as the corresponding variance.
becomes the sole determinant of the distribution's spread. This Demonstration calculates and plots the beta distribution's probability density function (PDF) and cumulative distribution function (CDF) for chosen values of the mode, mean or median and displays the numerical values of all three, as well as the corresponding variance.
Contributed by: Mark D. Normand and Micha Peleg (April 2019)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
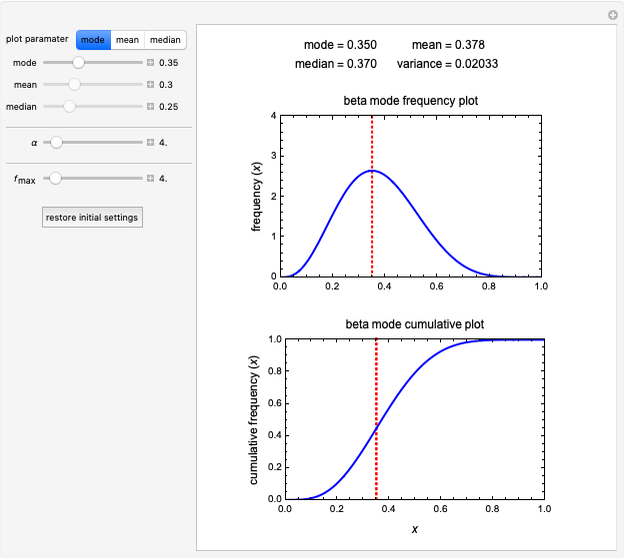
Snapshot 1: beta distribution function with a fixed mode and left skewness
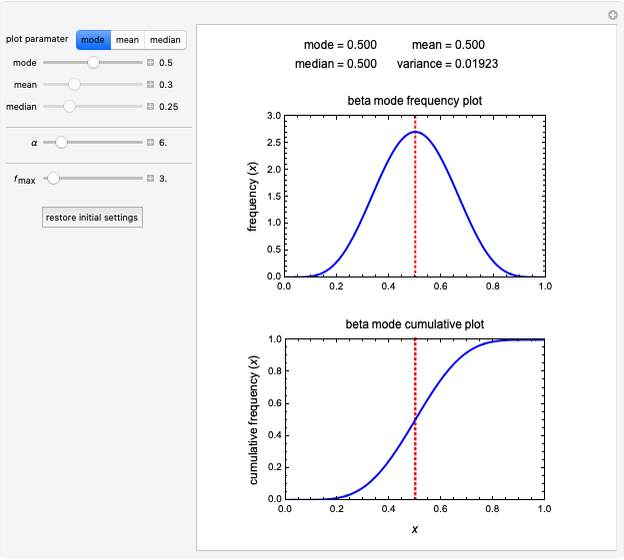
Snapshot 2: symmetric beta distribution function where the mode, mean and median coincide
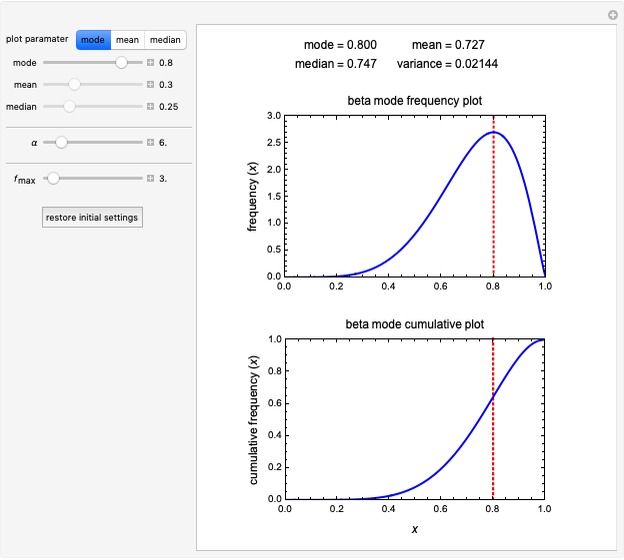
Snapshot 3: wide beta distribution function with a fixed mean and right skewness
Snapshot 4: narrow beta distribution function with a fixed median and left skewness
Snapshot 5: beta distribution function with a fixed mode and right skewness resembling a truncated distribution, reminiscent of the coarse fraction after sieving the fines
Snapshot 6: beta distribution function with a fixed mean and left skewness resembling a truncated distribution, reminiscent of the fine fraction after sieving
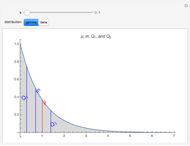
The beta distribution is a convenient flexible function for a random variable 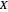 in a finite absolute range from
in a finite absolute range from 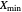 to
to 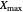 , determined by empirical or theoretical considerations. A corresponding normalized dimensionless independent variable
, determined by empirical or theoretical considerations. A corresponding normalized dimensionless independent variable 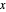 can be defined by
can be defined by
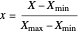 ,
,
or, when the 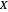 spread is over orders of magnitude,
spread is over orders of magnitude,
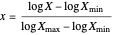 ,
,
which restricts its domain to 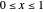 in either case.
in either case.
The beta distribution function, with two parameters  and
and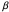 , can be written in the form [1–3]
, can be written in the form [1–3]
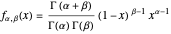
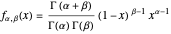 InlineMath.
InlineMath.
When both 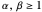 ,
, 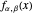 is a unimodal distribution. When α = β
is a unimodal distribution. When α = β it is symmetric around
it is symmetric around 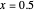 and for
and for 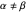 its skewness direction is determined by whether
its skewness direction is determined by whether 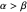 or
or  .
.
Since for 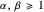 the beta distribution's mode is
the beta distribution's mode is
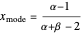 ,
,
its mean

and its median
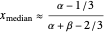 ,
,
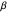 can be expressed explicitly in terms of
can be expressed explicitly in terms of 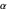 and the mode, mean or median, that is,
and the mode, mean or median, that is,
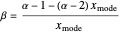 ,
, 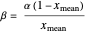 and
and 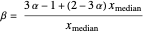 ,
,
respectively. These terms, in turn, can be used to calculate and plot the beta distribution function for any chosen (fixed) value of the mode, mean or median, as a function of 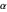 alone.
alone.
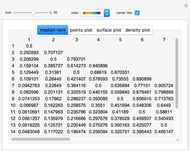
Choose the parameter to be fixed (mode, mean or median) with the "plot parameter" setter bar and enter its selected value using the slider. The value of 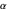 can then also be entered and varied with its slider to calculate and plot the PDF and CDF forms of the beta distribution for the current setting. The numerical values of the other parameters and corresponding variance are then calculated and displayed above the plots.
can then also be entered and varied with its slider to calculate and plot the PDF and CDF forms of the beta distribution for the current setting. The numerical values of the other parameters and corresponding variance are then calculated and displayed above the plots.
Except for the mode, the mean, median and variance can also be calculated with the built-in Wolfram Language functions Mean, Median and Variance, and for simplicity we have used the median's commonly accepted approximation formula for 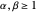 and not the more elaborate general form [4]. Also note that certain entered control settings may produce parameters that violate the condition
and not the more elaborate general form [4]. Also note that certain entered control settings may produce parameters that violate the condition 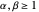 and thus should be discarded.
and thus should be discarded.
References
[1] E. W. Weisstein. "Beta Distribution" from Wolfram MathWorld—A Wolfram Web Resource. mathworld.wolfram.com/BetaDistribution.html (Wolfram MathWorld).
[2] Wikipedia. "Beta Distribution." (Apr 24, 2019) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_distribution.
[3] Engineering Statistics Handbook, "Beta Distribution." (Apr 24, 2019) www.itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366h.htm.
[4] J. Kerman, "A Closed-Form Approximation for the Median of the Beta Distribution." arxiv.org/abs/1111.0433v1.
Permanent Citation