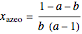Binary Distillation of Non-Ideal Mixtures Using Driving-Force Diagrams

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
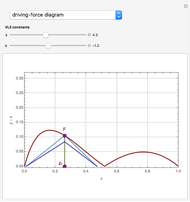
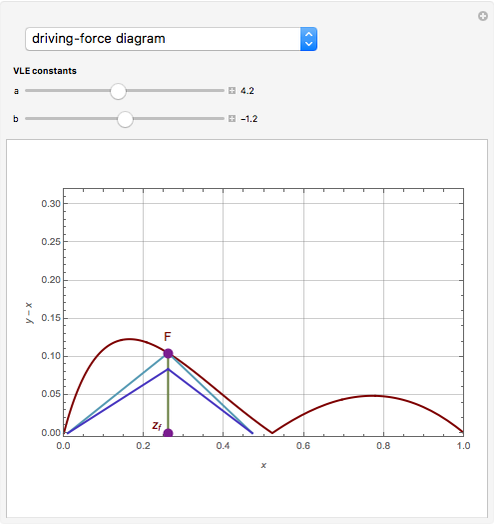
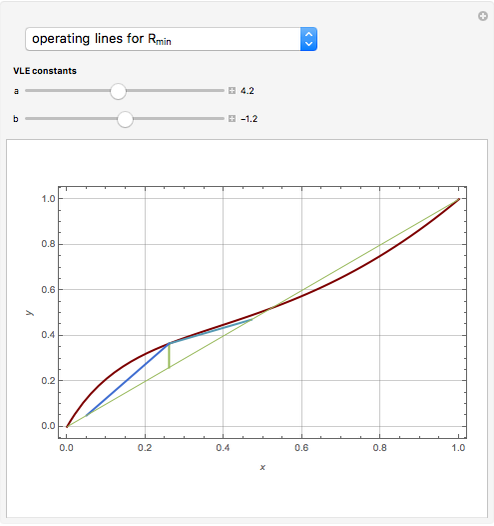
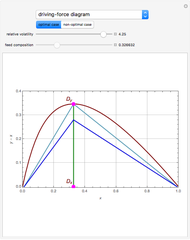
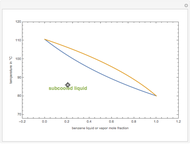
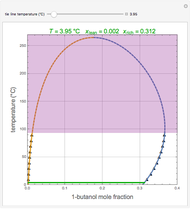
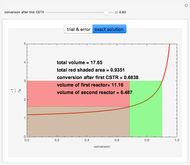
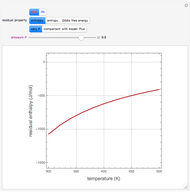
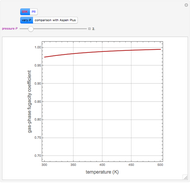
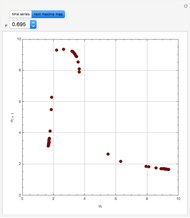
The driving-force diagram for a binary mixture is obtained by plotting  versus
versus  , where
, where  and
and 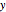 are the liquid and vapor mole fractions of the light component. Indeed, the driving force is
are the liquid and vapor mole fractions of the light component. Indeed, the driving force is  , where
, where  and
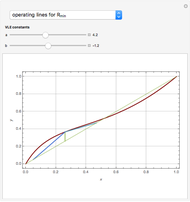
and  are the vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) constants. For example, VLE behavior of a binary mixture composed of pentane and dichloromethane is predicted by setting
are the vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) constants. For example, VLE behavior of a binary mixture composed of pentane and dichloromethane is predicted by setting  and
and  .
.
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
(Kind Fahd University Petroleum & Minerals)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
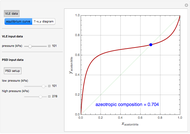
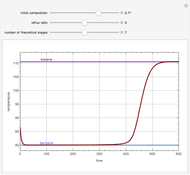
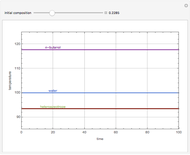
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] R. Gani and E. Bek–Pedersen, "Simple New Algorithm for Distillation Column Design," AIChE Journal, 46(6), 2000 pp. 1271–1274.
[2] E. Bek–Pedersen, R. Gani, and O. Levaux, "Determination of Optimal Energy Efficient Separation Schemes Based on Driving Forces," Computers and Chemical Engineering, 24(2-7), 2000 pp. 253–259.
[3] E. Bek–Pedersen and R. Gani, "Design and Synthesis of Distillation Systems Using a Driving-Force-Based Approach," Chemical Engineering and Processing, 43(3), 2004 pp. 251–262.
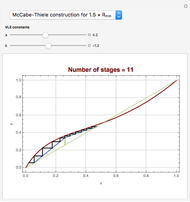
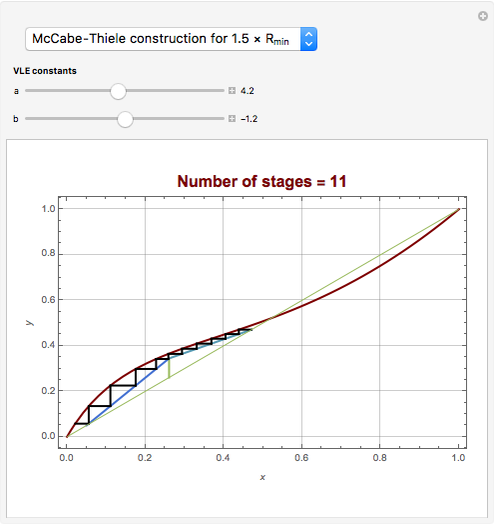
[4] W. L. McCabe and E. W. Thiele, "Graphical Design of Fractionating Columns," Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 17(6), 1925 pp. 605–611.
Permanent Citation