Bolzano's Function

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
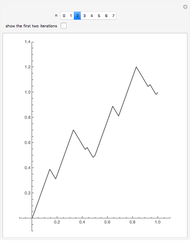
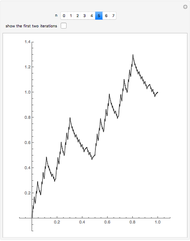
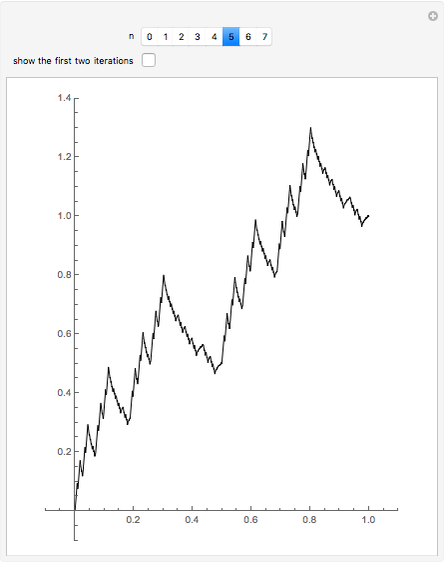
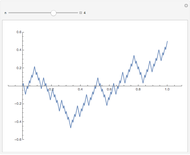
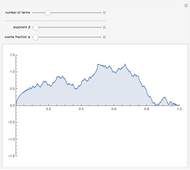
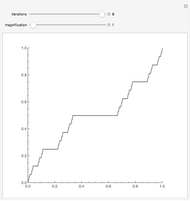
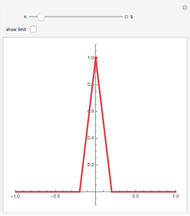
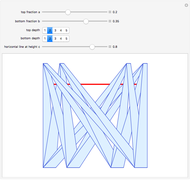
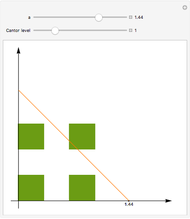
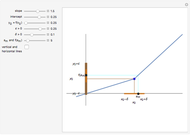
This Demonstration shows the graphs of the first seven approximations to a continuous nowhere differentiable function.
Contributed by: Izidor Hafner (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
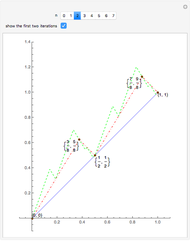
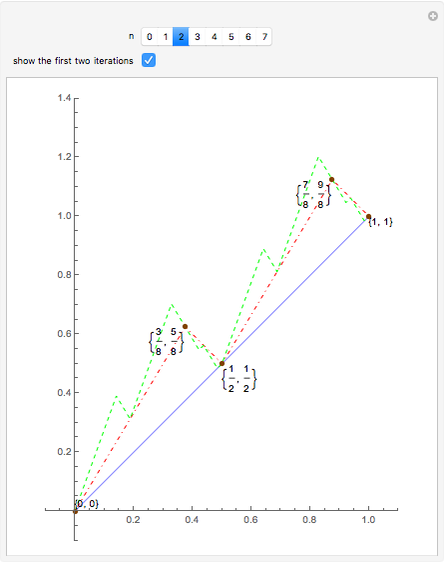
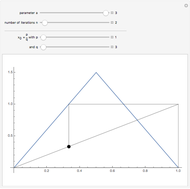
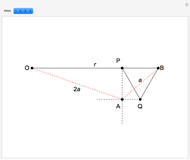
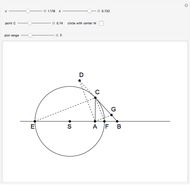
Bolzano's function is the limit of functions defined in the following way, described in terms of their graphs. Each iteration consists of connected line segments. The first graph is the line from (0, 0) to (0, 1). Suppose that  and
and  are the endpoints of a segment in some iteration. In the next iteration the segment is replaced by a polygonal line joining the following points:
are the endpoints of a segment in some iteration. In the next iteration the segment is replaced by a polygonal line joining the following points:
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 ,
,
 .
.
For details on Bolzano’s function, see:
V. Jarnik, Bolzano and the Foundations of Mathematical Analysis, Prague: Society of Czechoslovak Mathematicians and Physicists, 1981 pp. 67–81.
The history of continuous nowhere differentiable functions and the proof that Bolzano's function is an example of this kind can be found in:
J. Thim, "Continuous Nowhere Differentiable Functions," master's thesis, Lulea University of Technology, 2003.
M. Hyksova, "Karel Rychlik and Bernard Bolzano," (PDF).
Permanent Citation