Descartes's Angle Trisection

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
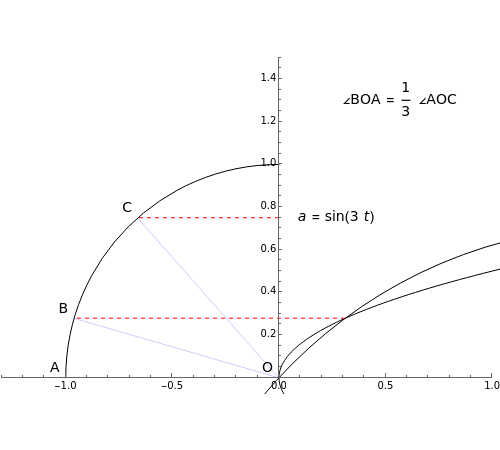
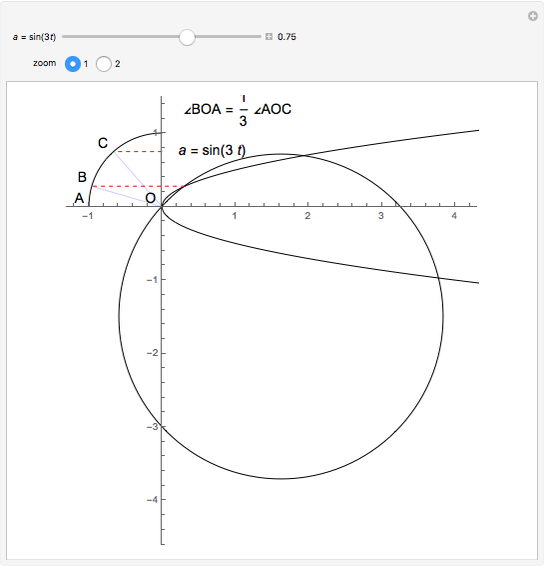
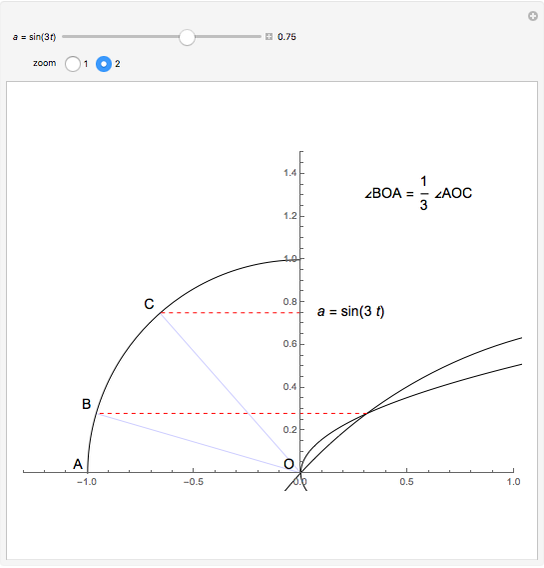
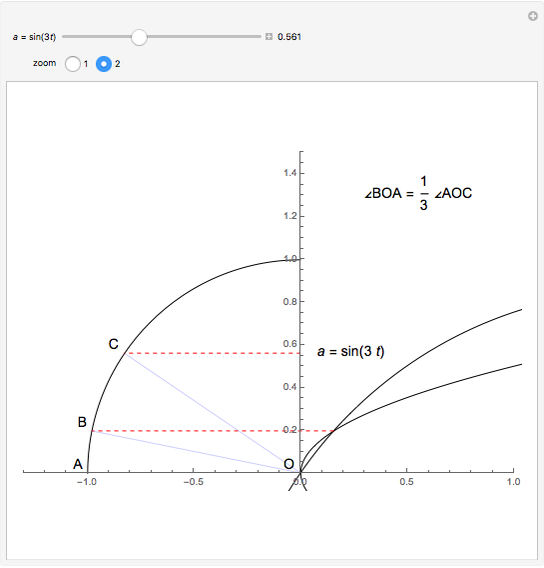
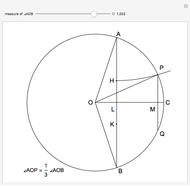
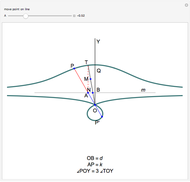
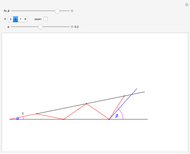
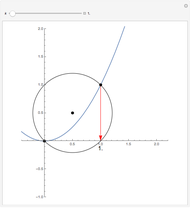
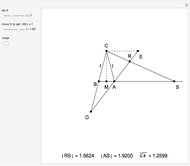
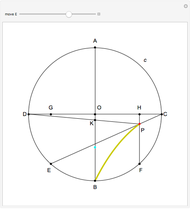
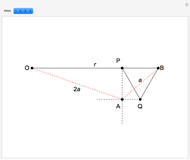
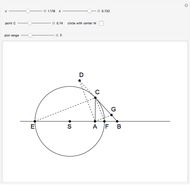
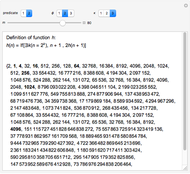
Descartes used the intersection of a circle and a parabola to trisect an angle. The equations of the circle and parabola are 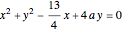 and
and 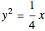 , respectively. The coordinates of the intersection satisfy
, respectively. The coordinates of the intersection satisfy 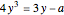 . Since
. Since 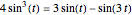 , by taking
, by taking 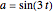 , the smaller positive root of the last equation is
, the smaller positive root of the last equation is 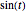

Contributed by: Izidor Hafner (September 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] W. W. Rouse Ball and H. S. M. Coxeter, Mathematical Recreations and Essays, 13th ed., New York: Dover Publications, 1987 p. 346.
Permanent Citation
"Descartes's Angle Trisection"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/DescartessAngleTrisection/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 19 2012