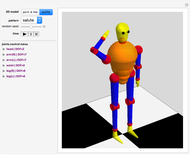
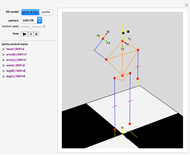
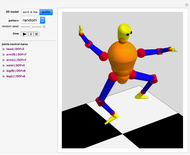
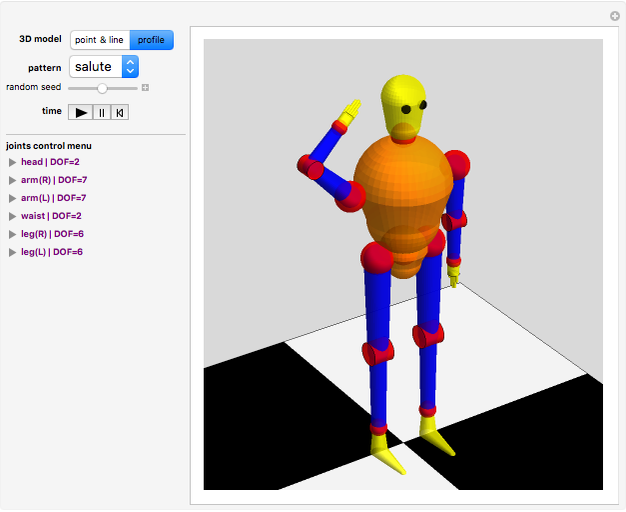
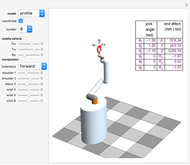
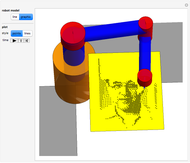
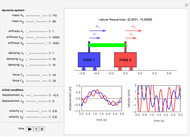
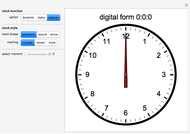
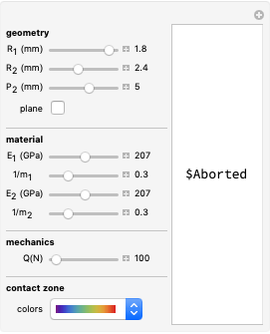
Forward Kinematics of Humanoid Robots

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
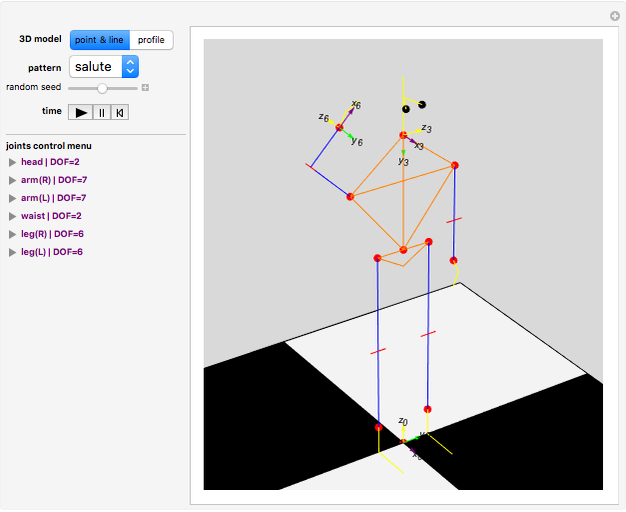
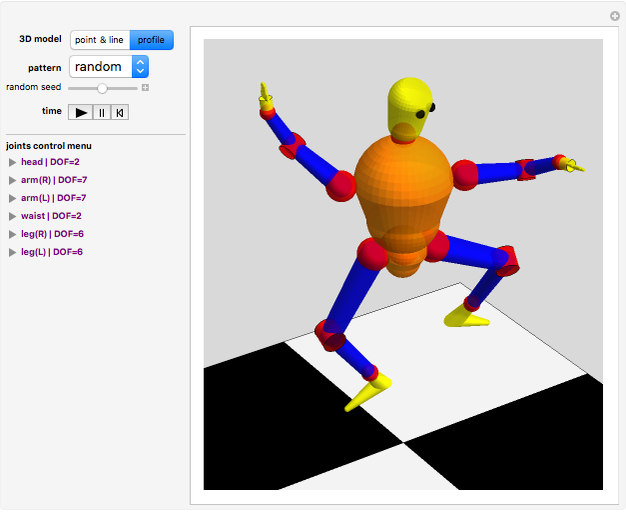
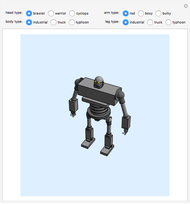
A humanoid robot is designed to replicate human characteristics such as height, shape, behavior, language, and cognition, so that it can function in human environments, interact with humans in daily life, or even replace humans at work. Many humanoid robots have been created in the past few decades by worldwide research, with examples such as the Honda ASIMO, AIST HRP, Aldebaran Nao, and so on. Intelligent-humanoid robotics is a cutting-edge challenge that will continue to play a central role in robotics research and applications in the twenty-first century.
[more]
Contributed by: Frederick Wu (September 2014)
Additional contributed by: Qixin Xu and Fan Wang
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
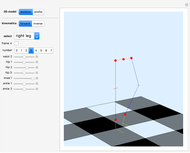
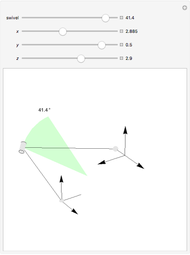
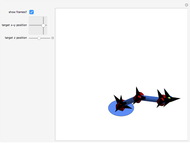
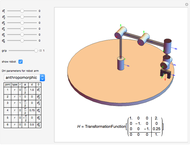
Snapshots
Details
This Demonstration was inspired by Professor Oussama Khatib's Introduction to Robotics Course, available free online through Stanford Engineering Everywhere (SEE).
References
[1] J. J. Craig, Introduction to Robotics: Mechanics and Control, 3rd ed., Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Prentice Hall, 2005 pp. 62–82.
[2] J. Denavit and R. S. Hartenberg, "A Kinematic Notation for Lower-Pair Mechanisms Based on Matrices," Journal of Applied Mechanics, 22(2), 1955 pp. 215–221.
[3] B. Siciliano and O. Khatib, Springer Handbook of Robotics, Berlin: Springer–Verlag, 2008.
Permanent Citation
"Forward Kinematics of Humanoid Robots"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ForwardKinematicsOfHumanoidRobots/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 26 2014