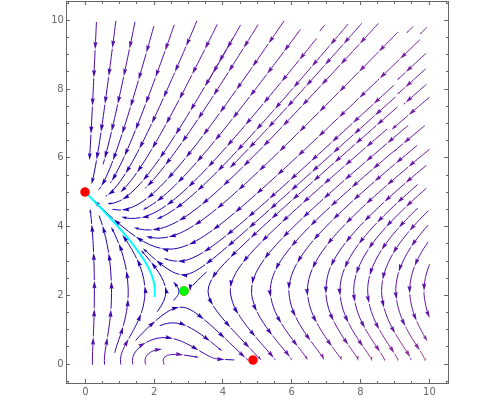
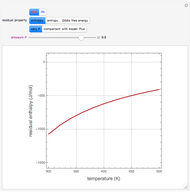
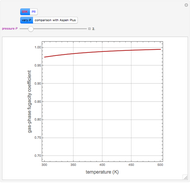
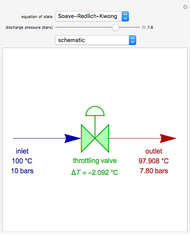
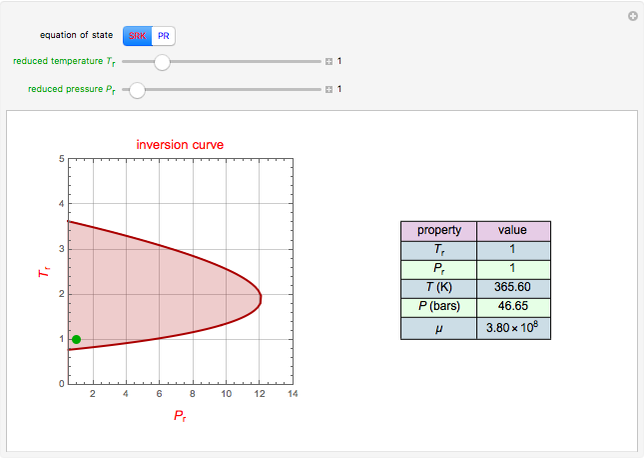
Multiple Steady States in Continuous Culture with Substrate Inhibition

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
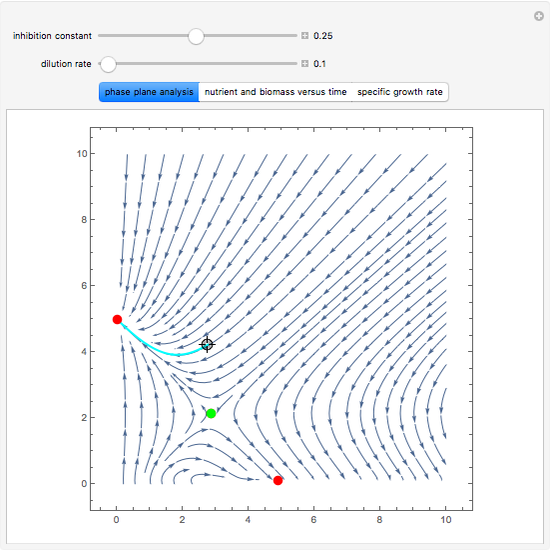
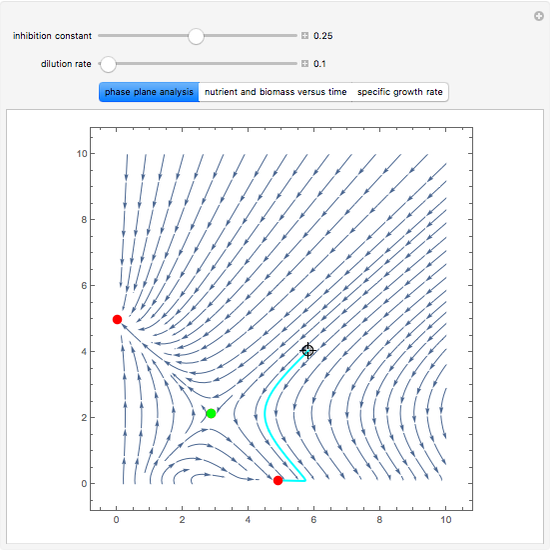
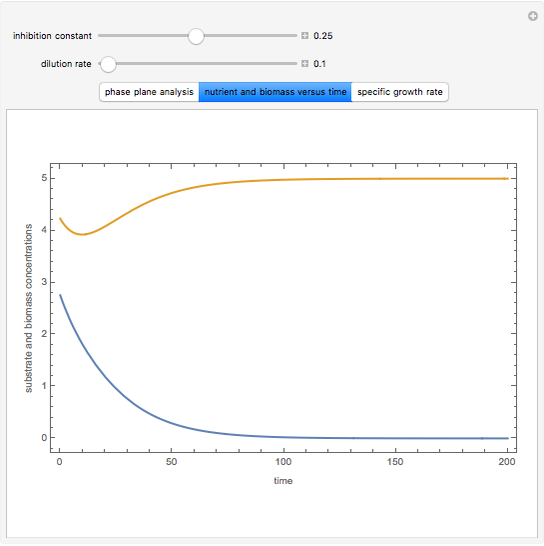
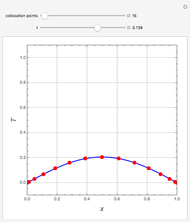
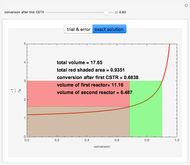
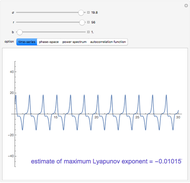
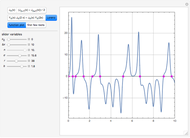
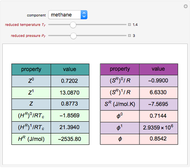
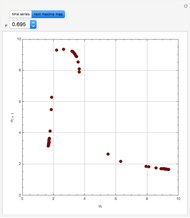
The dynamic behavior of a chemostat can be described with the following system of ordinary differential equations:

 ,
where
,
where  is the dilution rate in
is the dilution rate in  ,
,  is the biomass concentration in g/l,
is the biomass concentration in g/l,  is the substrate concentration in g/l,
is the substrate concentration in g/l,  is the feed substrate concentration,
is the feed substrate concentration,  is the yield, and
is the yield, and  is the specific growth rate (where
is the specific growth rate (where  is the half-saturation constant,
is the half-saturation constant,  is the inhibition constant, and
is the inhibition constant, and  is the maximum value of the specific growth rate, with
is the maximum value of the specific growth rate, with  here).
here).
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
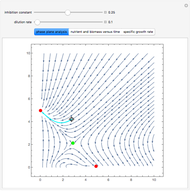
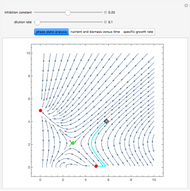
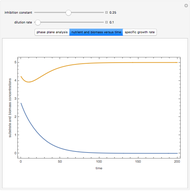
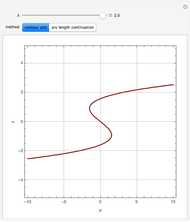
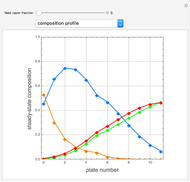
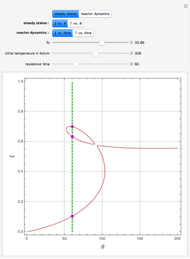
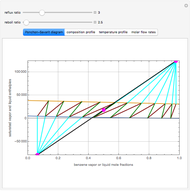
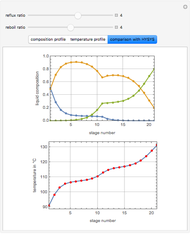
Snapshots
Details
I. J. Dunn, E. Heinzle, J. Ingham, and J. E. Prenosil, Biological Reaction Engineering: Dynamic Modelling Fundamentals with Simulation Examples, 2nd ed., Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2003.
Permanent Citation