Polarized Polariton Fields on the Poincaré Sphere

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
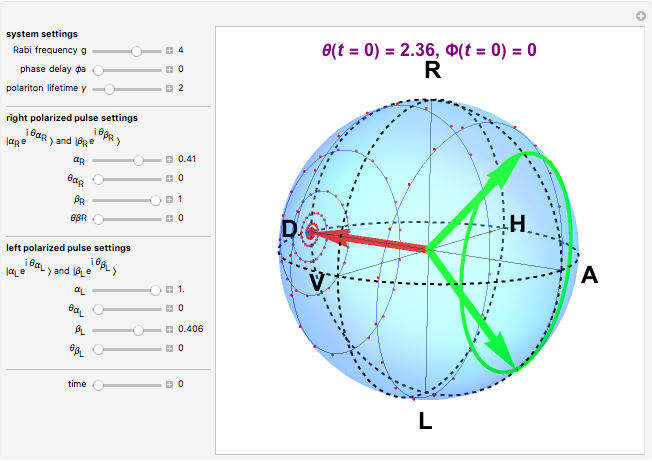
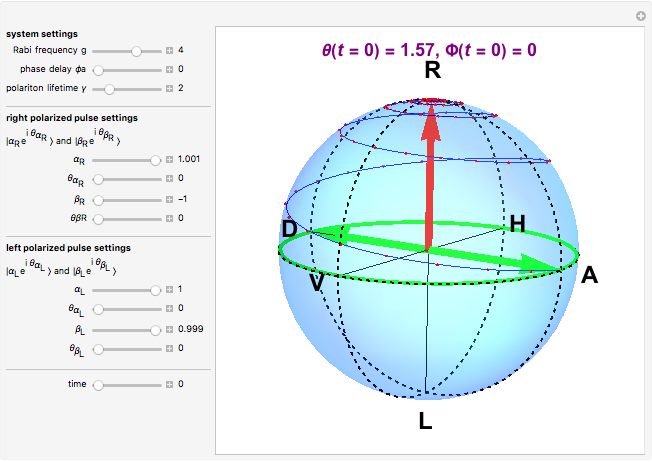
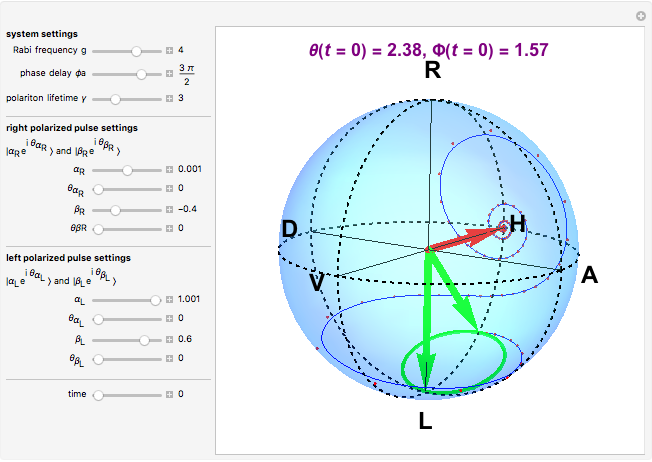
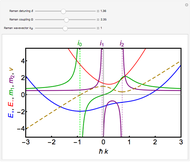
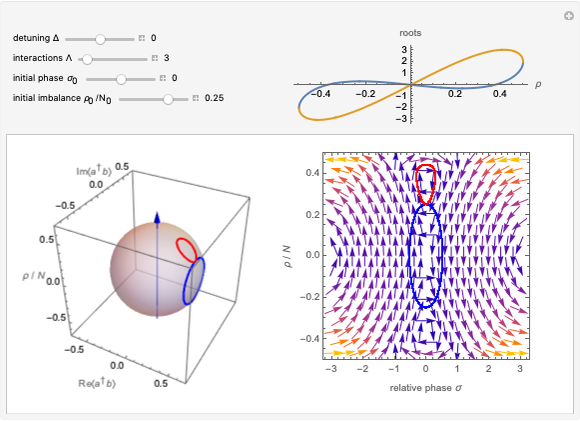
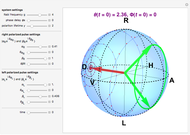
The state of polarization of light can be represented on the so-called Poincaré sphere, which provides a graphic representation of the Stokes parameters [1]. The circular-right polarization R corresponds to the north pole of the sphere and the circular-left polarization L to the south pole. The other cardinal points define the diagonal D, antidiagonal A, horizontal H, and vertical V polarizations. The Poincaré sphere can be used to track the state of polarization in a variety of contexts, such as spatial variations [2].
[more]
Contributed by: David Colas, Elena del Valle, and Fabrice P. Laussy (February 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
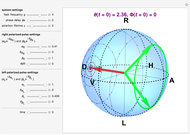
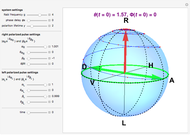
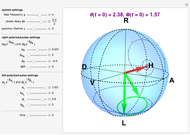
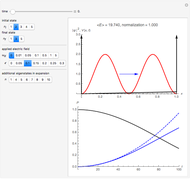
Various trajectories of the polarization on the Poincaré sphere:
Snapshot 1: spanning of the hemisphere from linear to right-circular polarization
Snapshot 2: close to full span of the Poincaré sphere, approaching so-called full Poincaré beams
Snapshot 3: nontrivial fast-varying polarization trajectory in strongly dissipative systems
References
[1] D. Colas, L. Dominici, S. Donati, A. A. Pervishko, T. C. H. Liew, I. A. Shelykh, D. Ballarini, M. de Giorgi, A. Bramati, G. Gigli, E. del Valle, F. P. Laussy, A. V. Kavokin, and D. Sanvitto, "Spanning the Full Poincaré Sphere with Polariton Rabi Oscillations." arxiv.org/abs/1412.4758.
[2] L. Dominici, D. Colas, S. Donati, J. P. Restrepo Cuartas, M. De Giorgi, D. Ballarini, G. Guirales, J. C. López Carreño, A. Bramati, G. Gigli, E. del Valle, F. P. Laussy, and D. Sanvitto, "Ultrafast Control and Rabi Oscillations of Polaritons," Physical Review Letters, 113, 2014 p. 226401. journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.226401.
Permanent Citation