The Hodgkin-Huxley Equations for Transmission of Electrical Impulses along an Axon

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
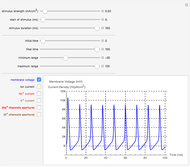
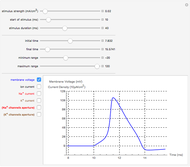
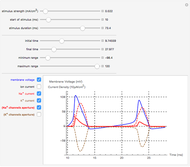
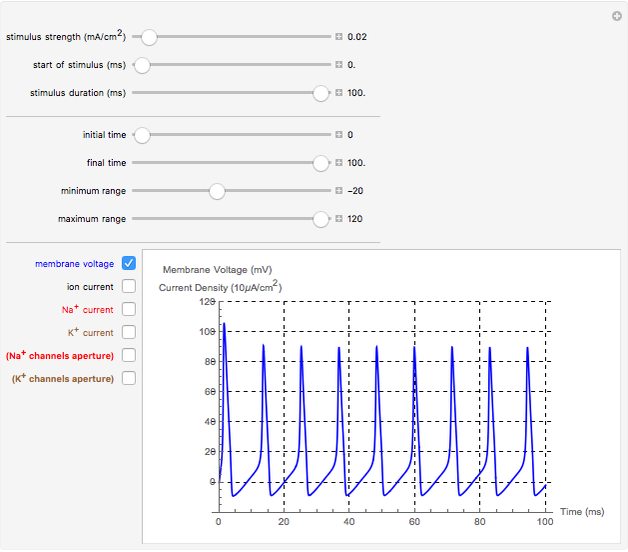
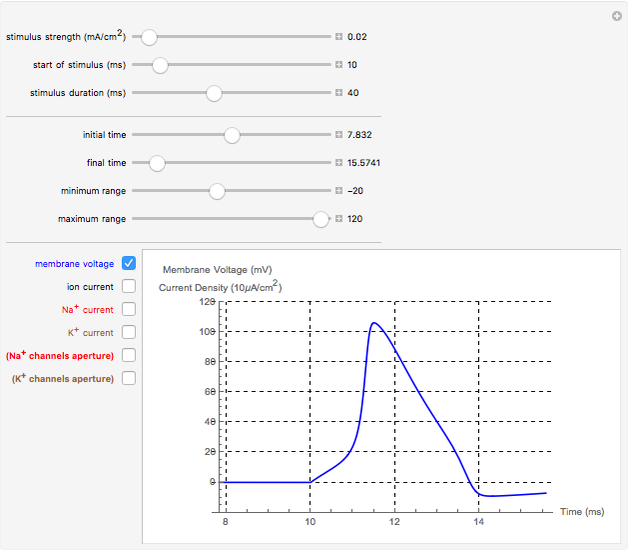
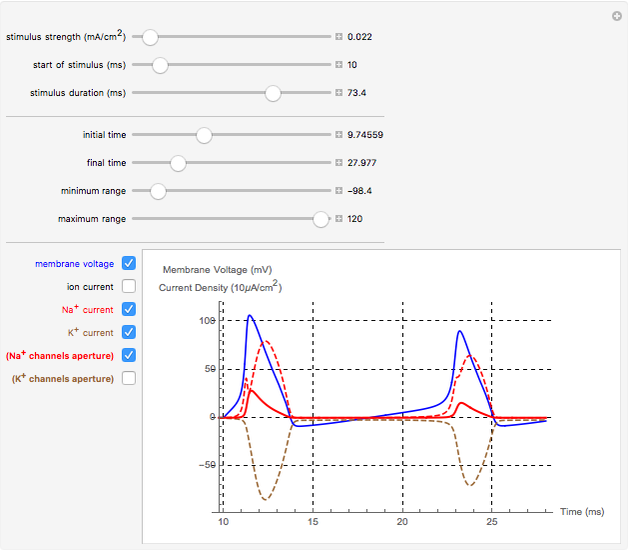
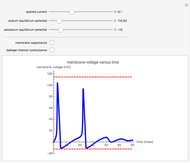
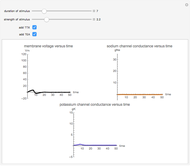
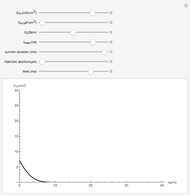
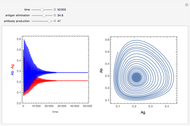
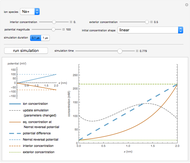
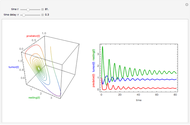
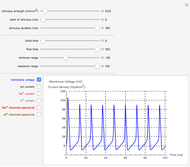
Neurons communicate primarily through electrical impulses that travel along their axons. These traveling impulses depend on the potential changes with time at each point along the axon. The physical and biological behavior at such a point depends on the simultaneous variation of the voltage, individual ion currents, and ion channels. The superposition of the curves that characterize these quantities gives a clearer idea of what is happening than each curve by itself.
Contributed by: Pedro Faria (September 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The overall structure and style of the model implemented here was taken from [1], which is strongly recommended to anyone who is interested in a careful and detailed introduction to the workings of neural impulse transmission along the axon.
Reference
[1] S. Alwyn, Neuroscience: A Mathematical Primer, New York: Springer-Verlag, 2002.