Carbon Nanotubes

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
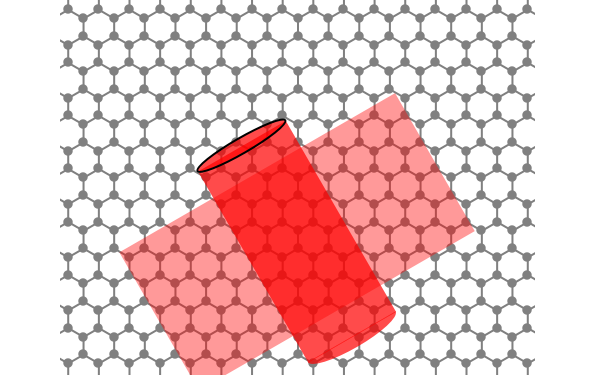
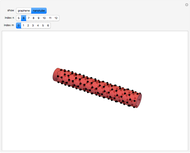
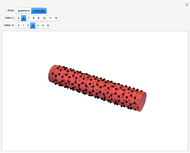
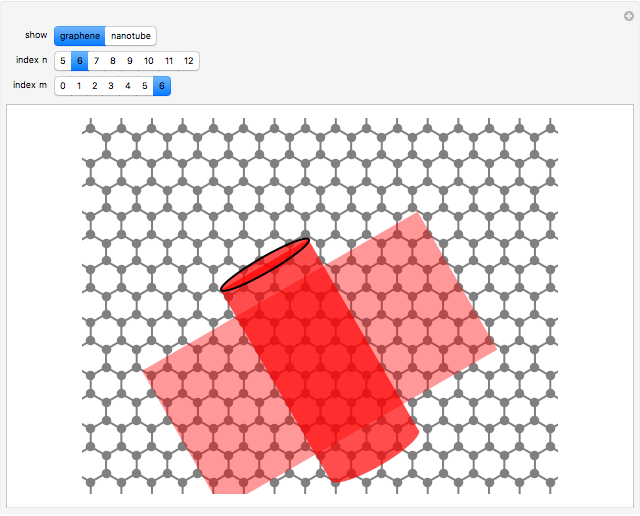
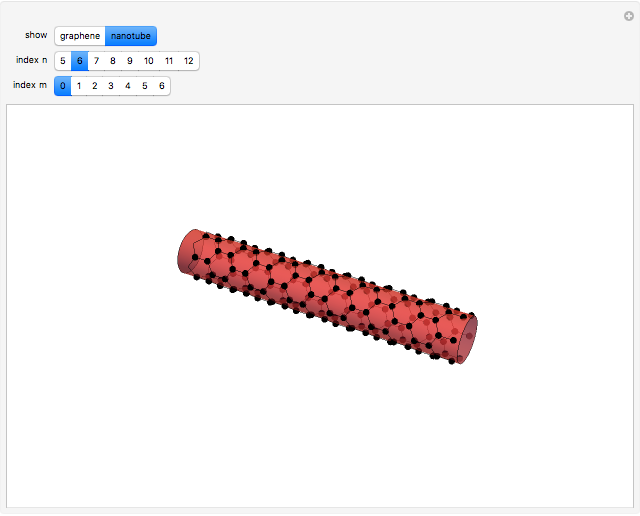
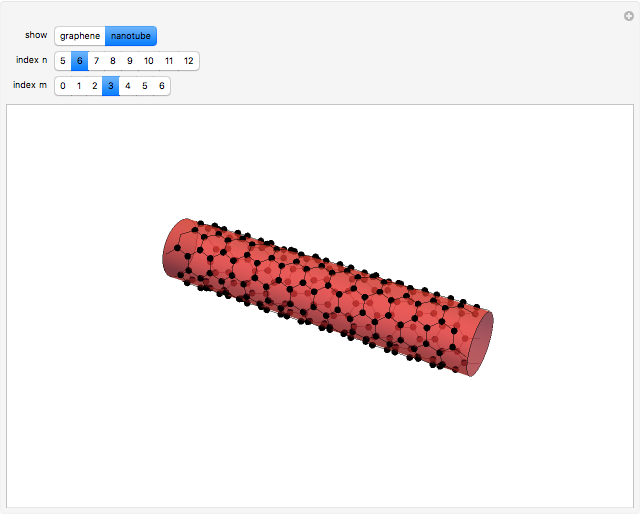
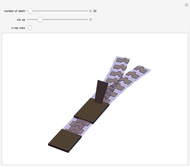
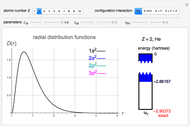
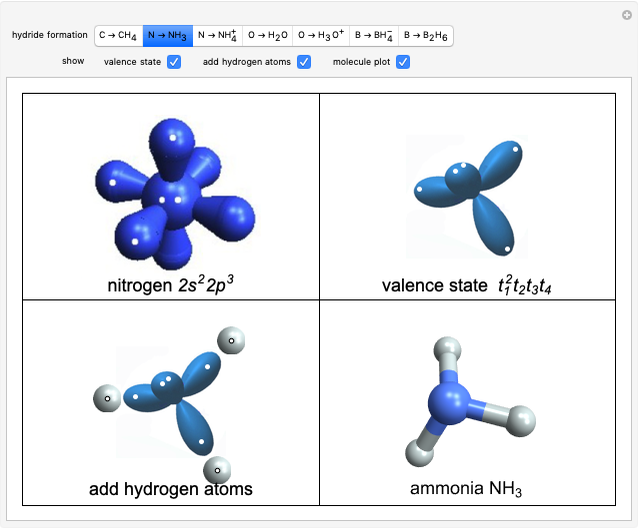
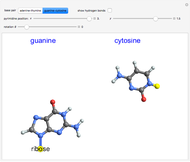
The first synthesis of carbon nanotubes is usually credited to Sumio Ijima in 1991. A single sheet of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice is known as graphene. Graphite consists of a stack of graphene sheets held together by van der Waals forces. A single-walled nanotube (SWNT) is, in concept, the result of rolling a graphene sheet into a cylindrical tube with a diameter of several nanometers. The length of the nanotube can be of the order of millimeters, giving a length to diameter ratio of up to 20 million. Nanotubes have tensile strengths per unit weight some 10-100 times greater than that of steel. They possess other unique mechanical, electrical, and optical properties that show promise in the development of new nanotechnology and electronics, including, possibly, quantum computers.
[more]
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Snapshot 1: construction of a (6,6) armchair nanotube from graphene sheet
Snapshot 2: (6,0) zigzag nanotube
Snapshot 3: (6,3) chiral nanotube
Reference: Wikipedia, "Carbon Nanotube."
Permanent Citation