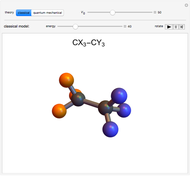
Internal Rotation in Ethane and Substituted Analogs

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
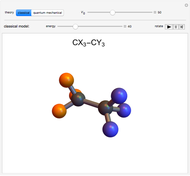
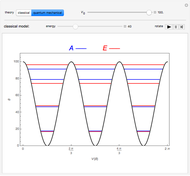
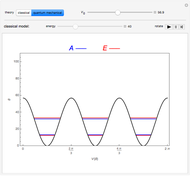
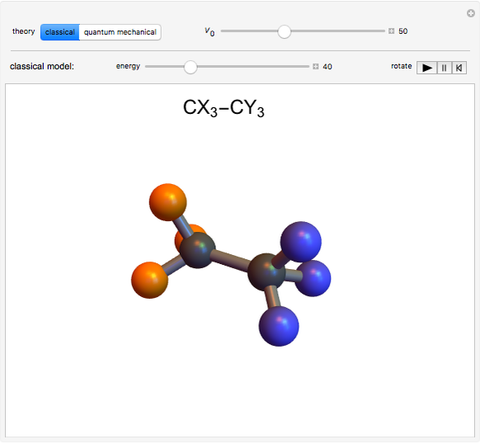
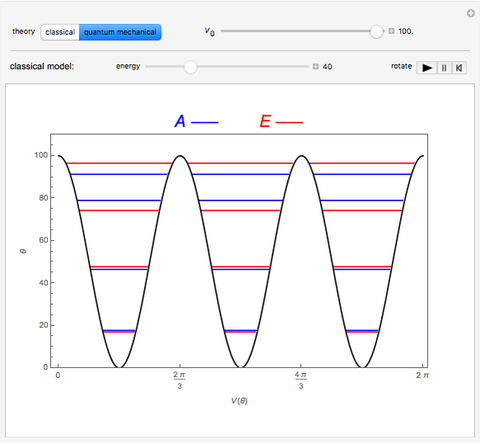
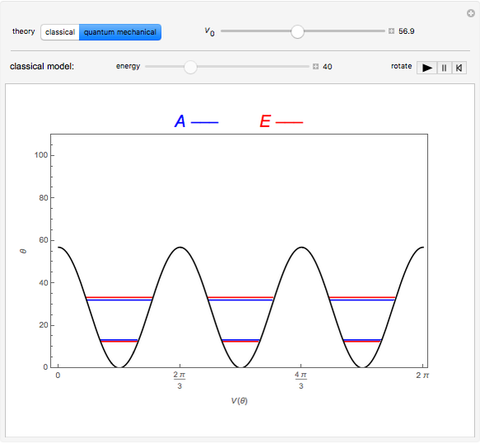
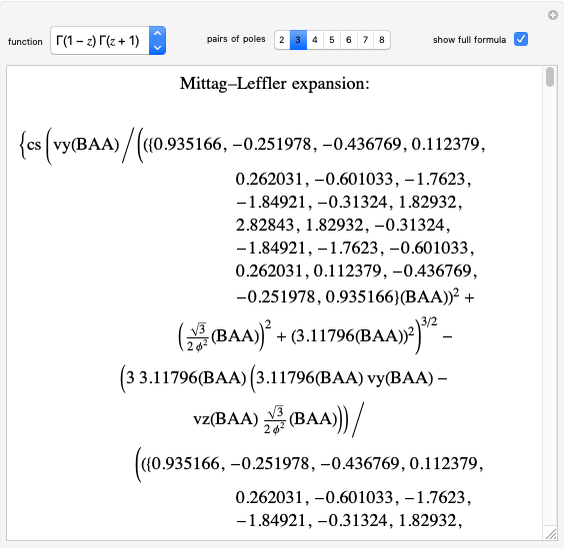
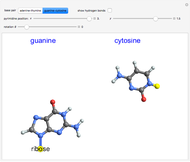
Rotation about C-C single bonds has been a topic of interest in chemistry since the 1870s [1]. It has been found that the rotation is often hindered by torsional forces arising from interactions among the substituents on the carbon atoms. The potential energy of interaction for the torsional motion of ethane  , or substituted ethanes such as
, or substituted ethanes such as  , can be approximated by a potential energy of the form
, can be approximated by a potential energy of the form
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (May 2018)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
References
[1] R. M. Pitzer, "The Barrier to Internal Rotation in Ethane," Accounts of Chemical Research, 16(6), 1983 pp. 207–210. doi:10.1021/ar00090a004.
[2] L. C. Krisher, "Inversion and Internal Rotation," in Encyclopedia of Physics (R. G. Lerner and G. L. Trigg, eds.), 2nd ed., New York: Wiley-VCH, 1991 pp. 557–558.
Permanent Citation