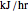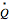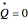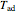Combustion Reactions in a Furnace

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
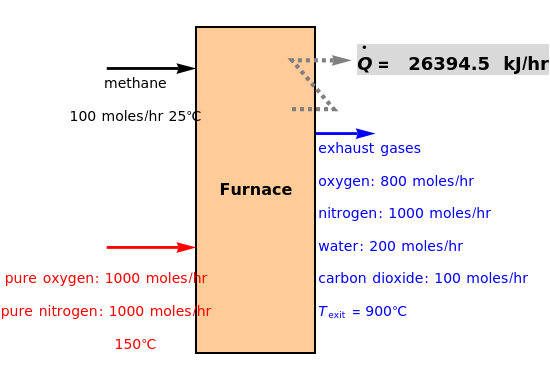
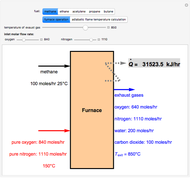
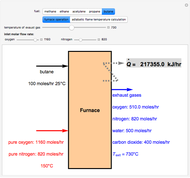
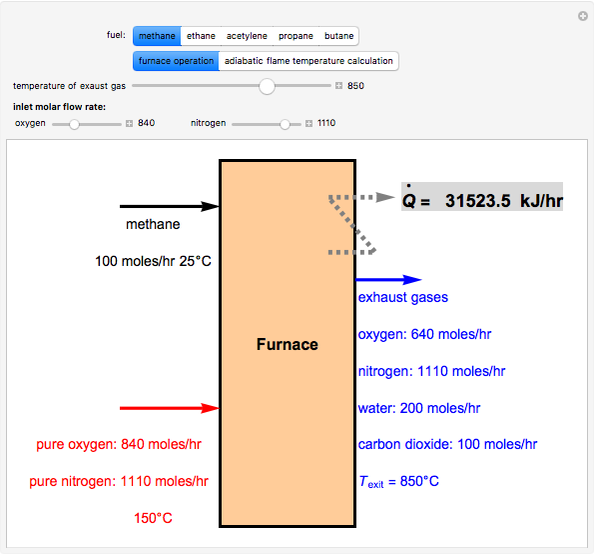
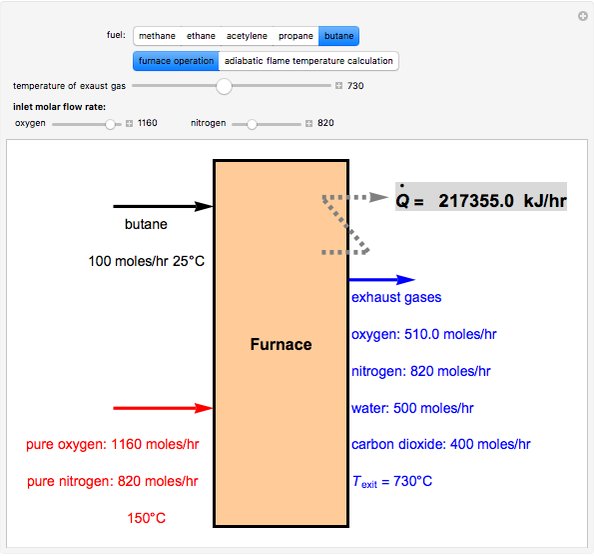
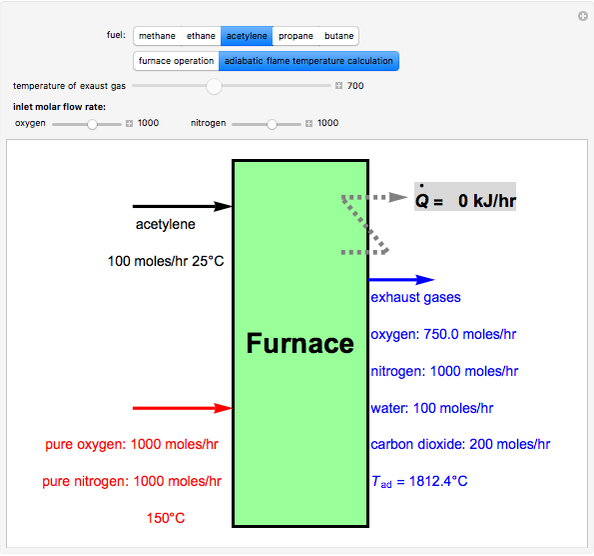
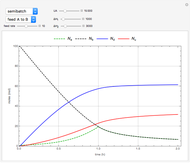
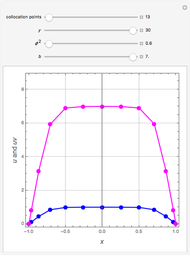
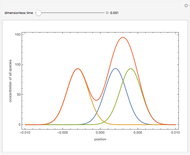
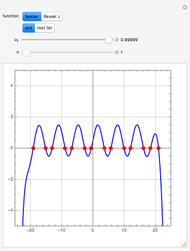
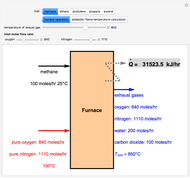
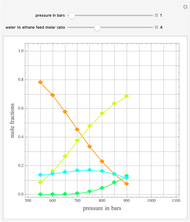
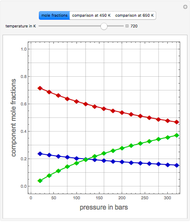
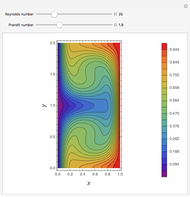
Fuel is fed to a furnace at 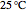 and a molar flow rate of
and a molar flow rate of 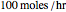 . This fuel is one of these hydrocarbons: methane, ethane, acetylene, propane, or butane. The fuel is subject to a combustion reaction in the furnace:
. This fuel is one of these hydrocarbons: methane, ethane, acetylene, propane, or butane. The fuel is subject to a combustion reaction in the furnace: 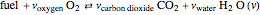 , where
, where 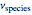 is the stoichiometric coefficient of the chemical species. An excess of oxygen entering at
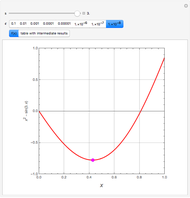
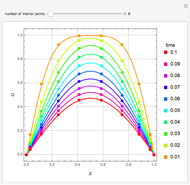
is the stoichiometric coefficient of the chemical species. An excess of oxygen entering at 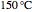 is used for the combustion reaction, so that the conversion of the fuel is total. You can select the value of the inlet molar flow rate of oxygen and nitrogen. We apply the energy balance for reacting systems using the heat of reaction method [1]. The Demonstration determines:
is used for the combustion reaction, so that the conversion of the fuel is total. You can select the value of the inlet molar flow rate of oxygen and nitrogen. We apply the energy balance for reacting systems using the heat of reaction method [1]. The Demonstration determines:
Contributed by: Housam Binous, Ahmed Bellagi, and Brian G. Higgins (January 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] R. M. Felder and R. W. Rousseau, Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, 3rd ed., New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2004.
Permanent Citation