Different Perspectives on Achieving the Mean of a Distribution

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
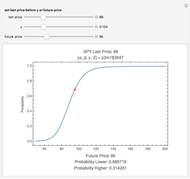
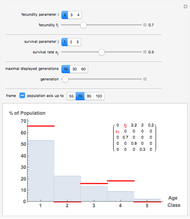
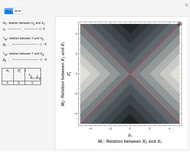
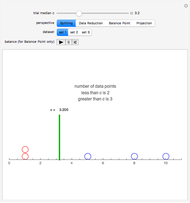
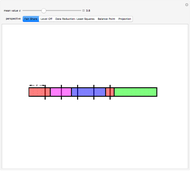
Using a small dataset 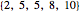 , we can determine the mean value corresponding to five different perspectives on an equitable distribution. Within each perspective, use the slider to accomplish the desired goal.
, we can determine the mean value corresponding to five different perspectives on an equitable distribution. Within each perspective, use the slider to accomplish the desired goal.
Contributed by: Alexander White, Matthew Straughn, and Layla Guyot (July 2016)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
For each perspective, the choice of  achieves a particular goal. By sliding the control for
achieves a particular goal. By sliding the control for  , you can explore different properties of the mean.
, you can explore different properties of the mean.
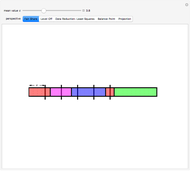
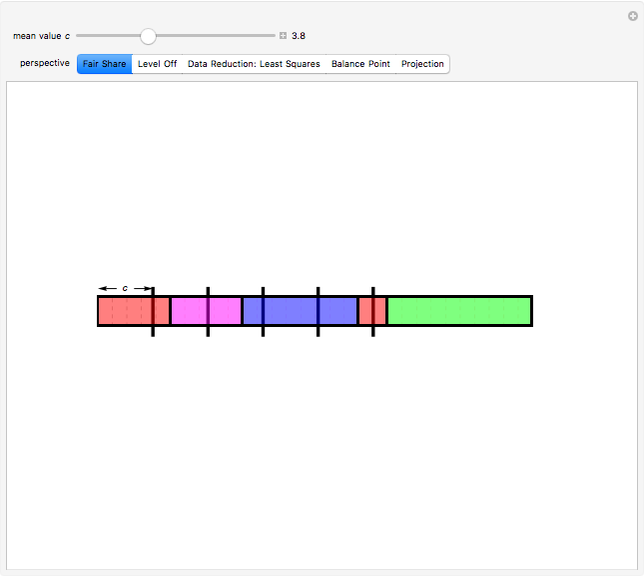
Snapshot 1: Colored bars represent data values. Choose  to divide the total into equal parts to show that the mean represents a "fair share."
to divide the total into equal parts to show that the mean represents a "fair share."
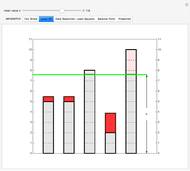
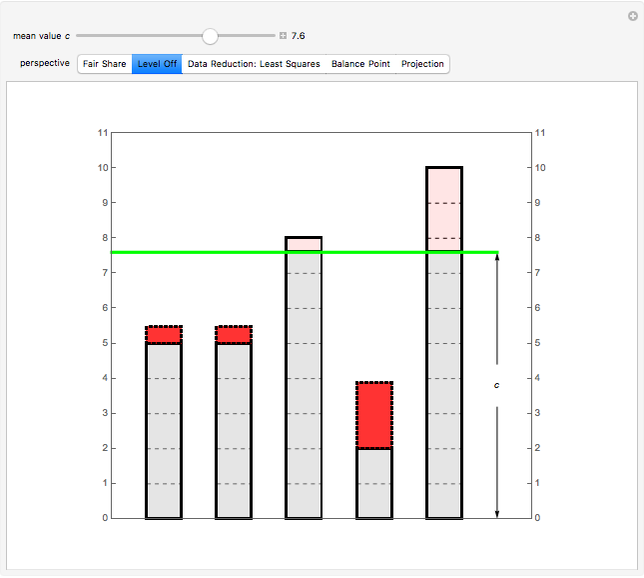
Snapshot 2: Towers represent data values. By varying  , remove area from the taller bars and add it to the shorter bars. Choose
, remove area from the taller bars and add it to the shorter bars. Choose  so that all the bars are leveled off at the same height.
so that all the bars are leveled off at the same height.
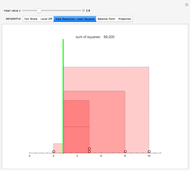
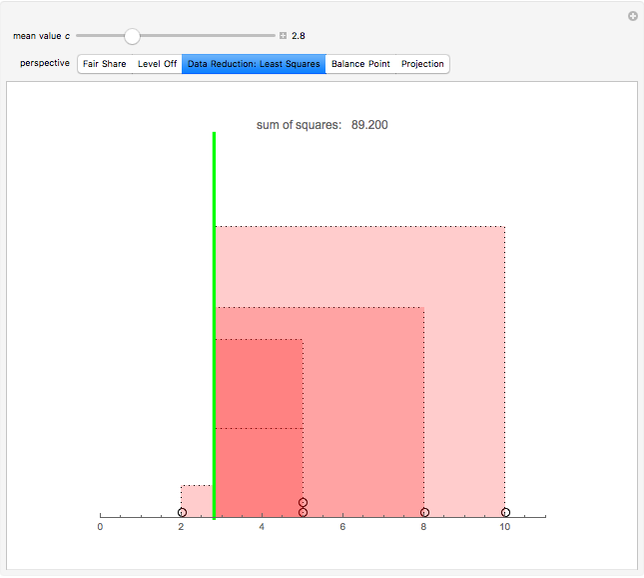
Snapshot 3: Circles on the number line represent data values. Each square represents the squared distance from an observation to  . Choose
. Choose  to minimize the sum of the areas of the squares.
to minimize the sum of the areas of the squares.
Snapshot 4: Circles with unit mass on the "teeter-totter" number line represent data values. The position of the fulcrum is given by  . Choose
. Choose  to achieve balance.
to achieve balance.
Permanent Citation