General Divisor Methods

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
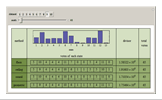
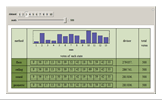
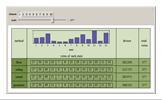
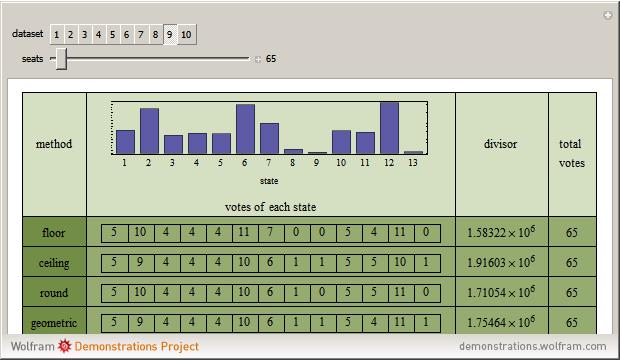
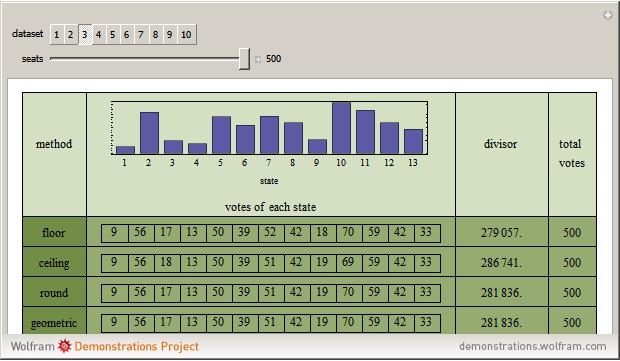
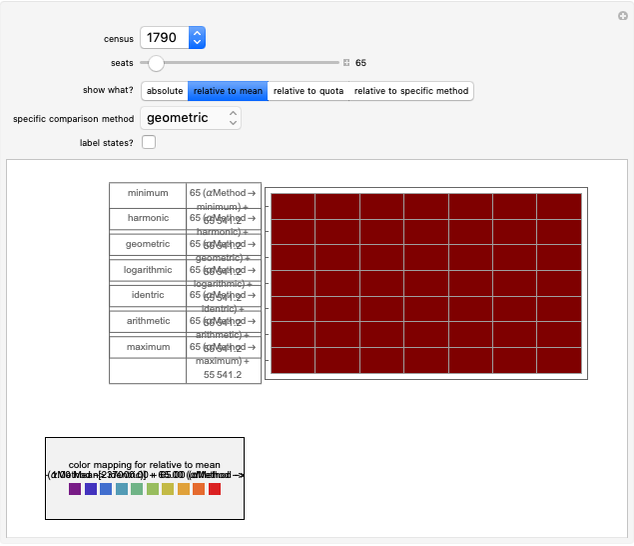
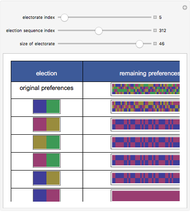
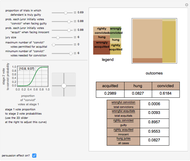
The United States Constitution states that representatives in the House of Representatives "shall be apportioned among the several States according to their respective numbers, counting the whole number of persons in each State, excluding Indians not taxed" (14th amendment, section 2). The Constitution further places a ceiling on the number of total representatives at 1 per 30,000 of total population and states that every state shall have at least one member in the House of Representatives (Article I, section 2). The Constitution does not specify, however, how to deal with the issue of rounding in the resulting computations.
[more]
Contributed by: Seth J. Chandler (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
An article on general divisor methods may be found in: E. Park, "The Mathematics of Apportionment," University of Chicago Law School Roundtable, 7, 2000 pp. 227-235. This Demonstration draws significantly on his work.
The "floor" method is essentially that of Thomas Jefferson and was used from 1790 through 1830. The "round" method is essentially that proposed by Daniel Webster and was used in 1840 and again with minor variation in 1910 and 1930. The geometric method is roughly what is used today.
Permanent Citation
"General Divisor Methods"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/GeneralDivisorMethods/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011