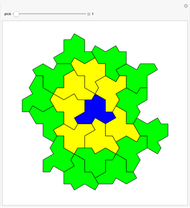
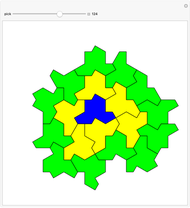
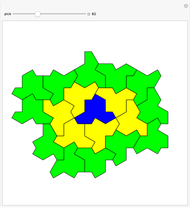
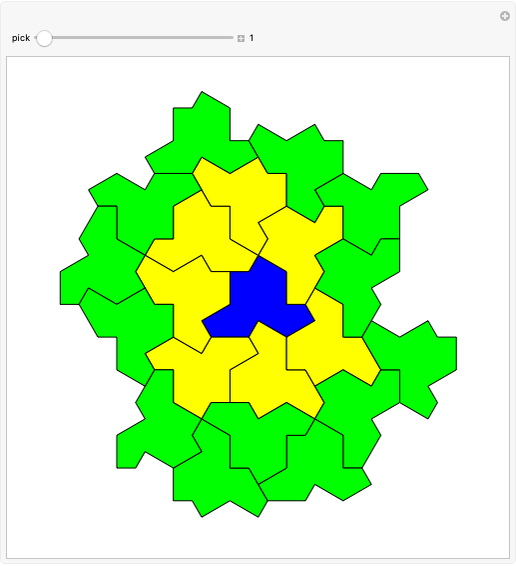
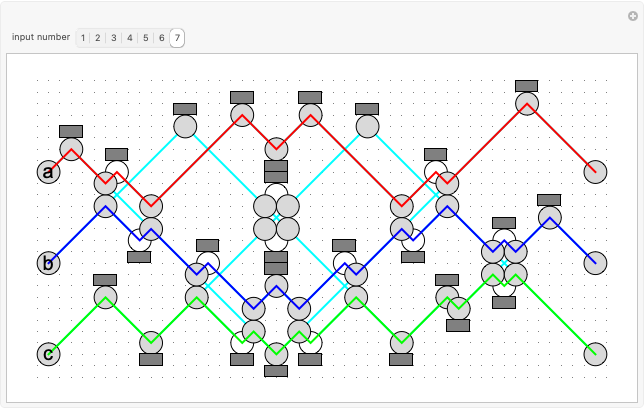
Hat Monotile Coronas

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
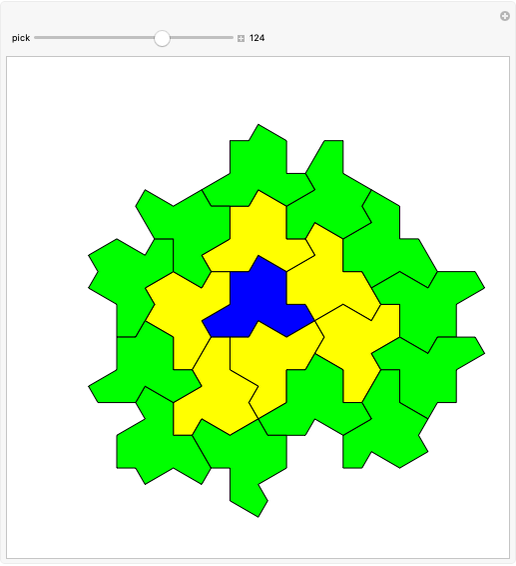
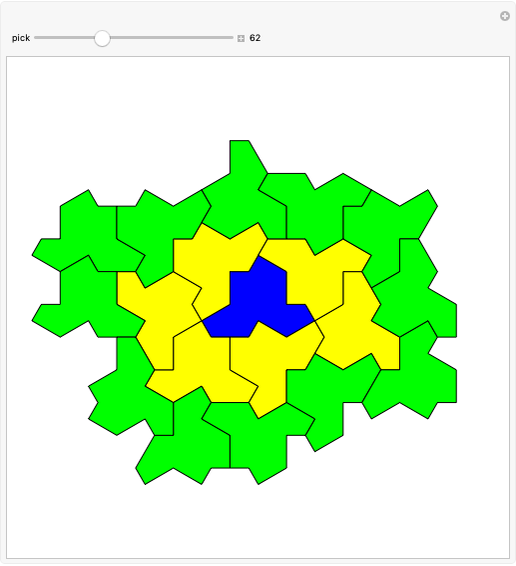
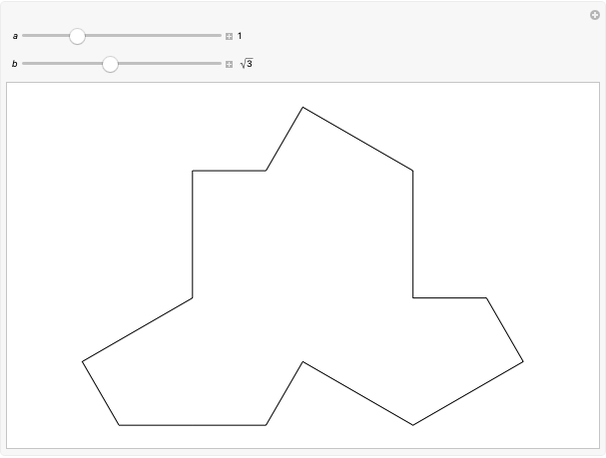
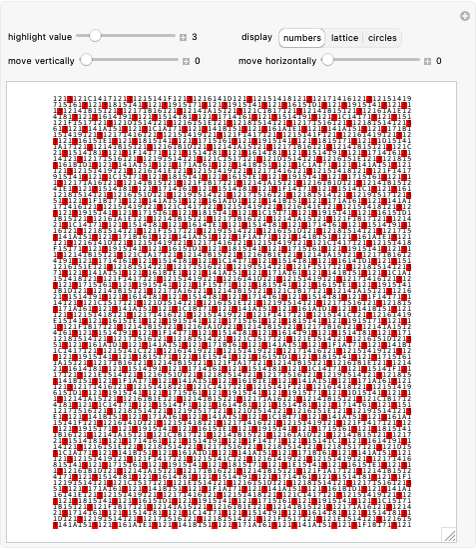
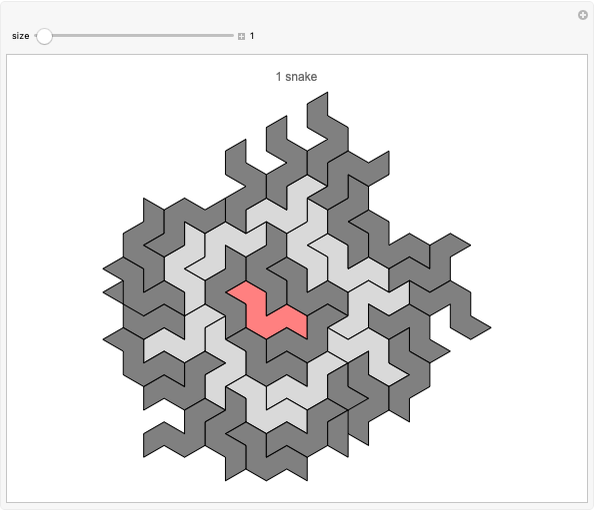
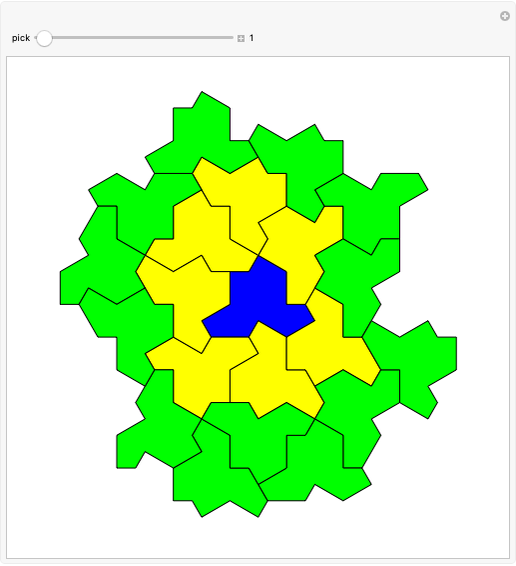
Consider a 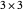 grid of squares. The central square is completely surrounded by eight squares. By shifting squares along the top and bottom, the central square may be completely surrounded by six or seven squares. Touching at the corners is allowed. All of these produce examples of a square surrounded with a 1-corona of squares. Surrounding the 1-corona to make a 2-corona requires anywhere between 19 and 25 squares.
grid of squares. The central square is completely surrounded by eight squares. By shifting squares along the top and bottom, the central square may be completely surrounded by six or seven squares. Touching at the corners is allowed. All of these produce examples of a square surrounded with a 1-corona of squares. Surrounding the 1-corona to make a 2-corona requires anywhere between 19 and 25 squares.
Contributed by: Ed Pegg Jr (June 13)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Details
References
[1] D. Smith, J. S. Myers, C. S. Kaplan and C. Goodman-Strauss, "An Aperiodic Monotile." arxiv.org/abs/2303.10798.
[2] E. Pegg. "Einstein Problem Solved (Aperiodic Monotile Discovery)" from Wolfram Community—A Wolfram Web Resource. community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/2861234.
[3] B. Klee. "Hat Tilings via HTPF Equivalence." from Wolfram Community—A Wolfram Web Resource. community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/2858759.
Snapshots
Permanent Citation