Quantum Alchemy

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
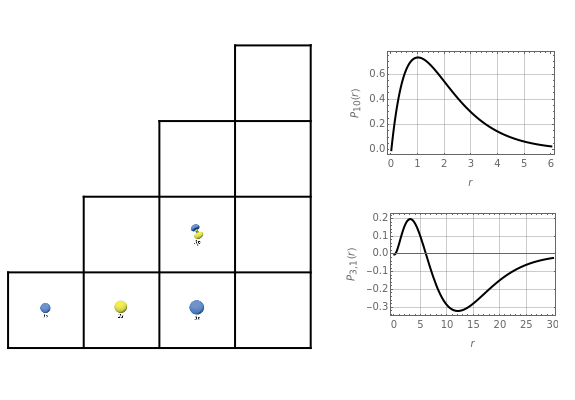
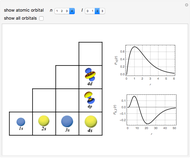
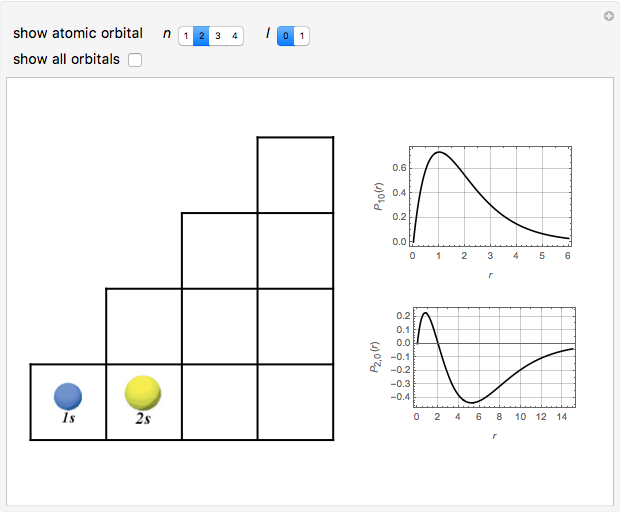
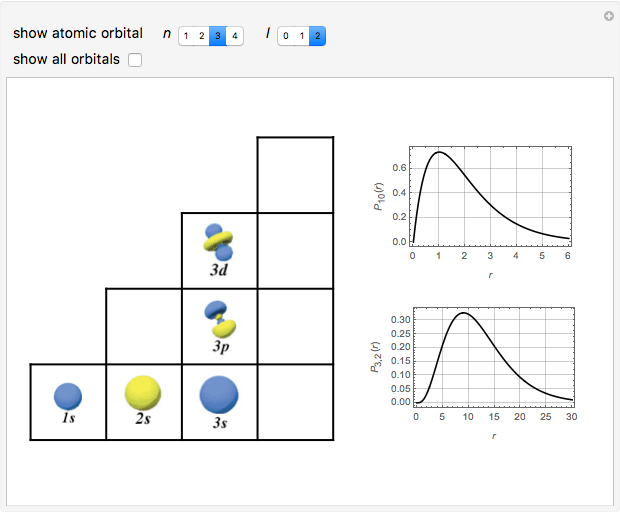
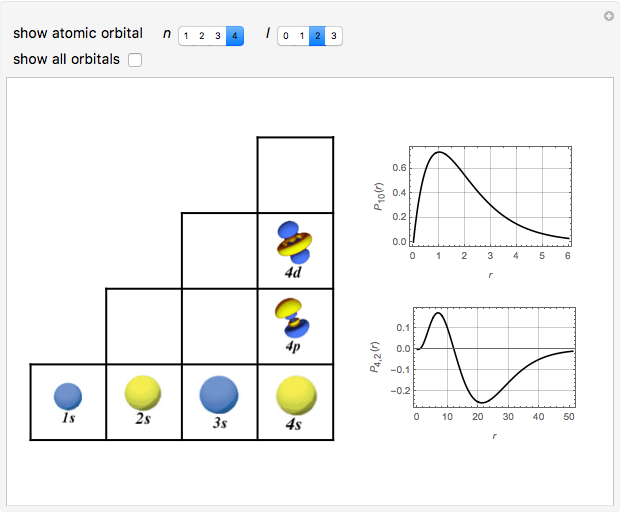
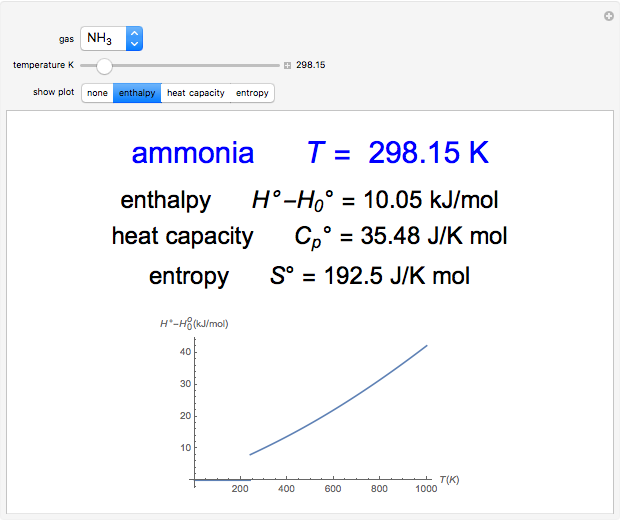
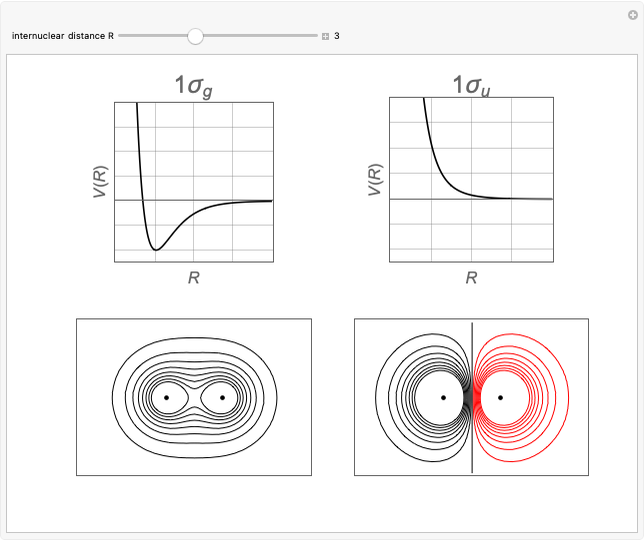
Schrödinger [1, 2] made use of a factorization method on the hydrogen atom radial equation to show that all solutions can be generated starting with the ground state. Such procedures are now usually categorized as supersymmetric quantum mechanics. In an earlier publication [3], we dubbed this modern form of alchemy: "quantum alchemy".
[more]
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (August 2013)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
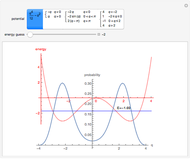
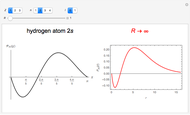
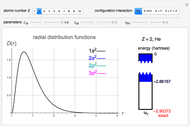
The supersymmetric operator is given by  . For example,
. For example,  (so that
(so that  ). To apply the ladder operator
). To apply the ladder operator 
 for principal quantum numbers, we must first express the radial function in the form
for principal quantum numbers, we must first express the radial function in the form  , where
, where  Then the quantum number is increased by 1 in the operation
Then the quantum number is increased by 1 in the operation  , where the square brackets represent the operator
, where the square brackets represent the operator  . For example, operating on a
. For example, operating on a  -orbital, for which
-orbital, for which  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  , we find
, we find  . The last expression reduces to
. The last expression reduces to  , after setting
, after setting 
References
[1] E. Schrödinger, "A Method of Determining Quantum-Mechanical Eigenvalues and Eigenfunctions," Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. Section A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 46, 1940 pp. 9–16.
[2] E. Schrödinger, "Further Studies on Solving Eigenvalue Problems by Factorization," Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy. Section A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 46, 1941 pp. 183–206.
[3] S. M. Blinder, "Quantum Alchemy: Transmutation of Atomic Orbitals," Journal of Chemical Education, 78(3), 2001 pp. 391–394.
Permanent Citation