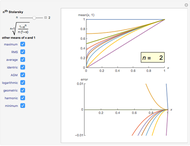
Stolarsky Approximations to Popular Means

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
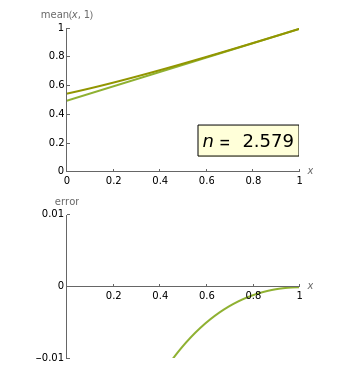
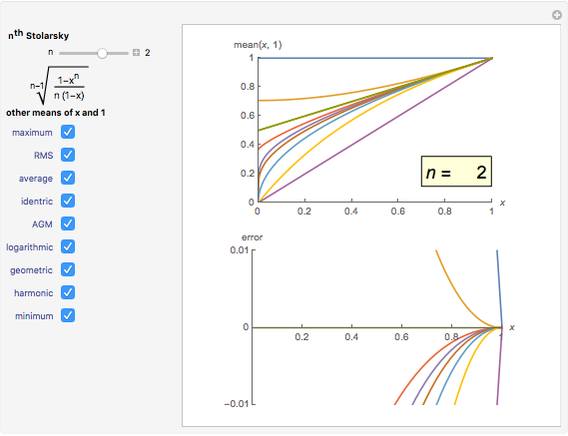
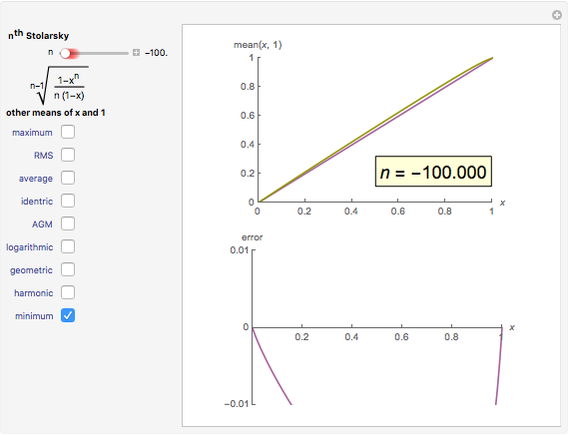
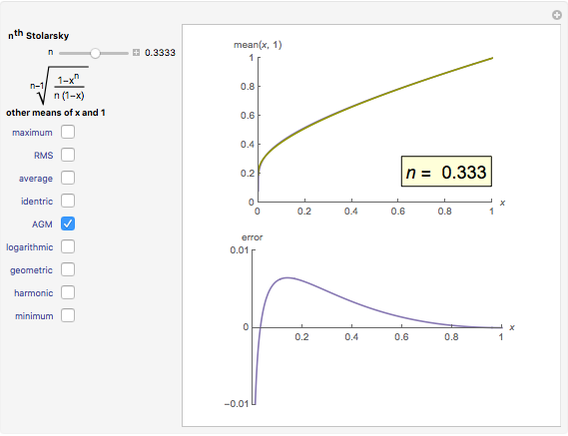
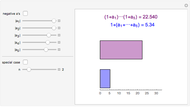
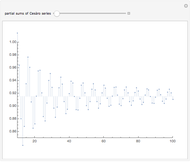
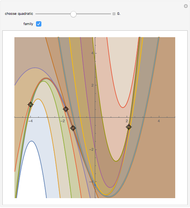
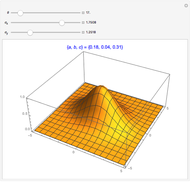
The Stolarsky mean provides approximations to popular means, which shows that it generalizes some of them and that these means are strictly ordered by strict inequality over  on
on 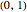 .
.
Contributed by: Robert L. Brown (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
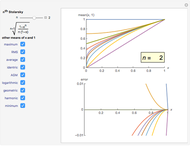
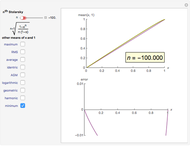
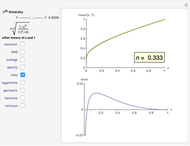
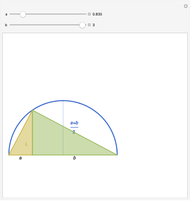
The Stolarsky mean is is derived from the mean value theorem and its form depends upon the independent parameter  . As the parameter
. As the parameter  is varied, approximations can be made to popular means. Most approximations become exact for some value of
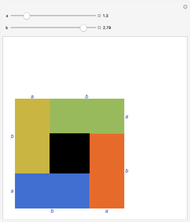
is varied, approximations can be made to popular means. Most approximations become exact for some value of  ; the Stolarsky is a true generalization for those means. Strict ordering of the Pythagorean Means (Wolfram MathWorld) is the basis of many proofs in number theory.
; the Stolarsky is a true generalization for those means. Strict ordering of the Pythagorean Means (Wolfram MathWorld) is the basis of many proofs in number theory.
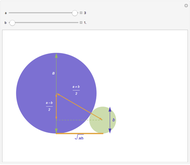
Note that, although we consider means 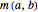 of two positive numbers, we only need to consider
of two positive numbers, we only need to consider  for
for  , because each of these means is a homogeneous function:
, because each of these means is a homogeneous function: 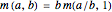 where
where  .
.
Like the Hölder mean, the Stolarsky mean parameter  will approximate, match exactly, or match in the limit many popular means. The following table contrasts these two generalized forms.
will approximate, match exactly, or match in the limit many popular means. The following table contrasts these two generalized forms.

Bookmarks provide the most uncluttered way to examine the estimation error for a given mean. Additional reference can be obtained by clicking a mean's name next to its checkbox.
Permanent Citation