Study of Successive First-Order Reversible Reactions

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
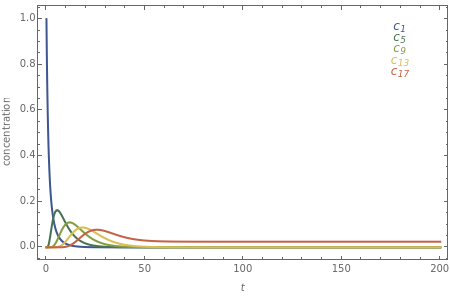
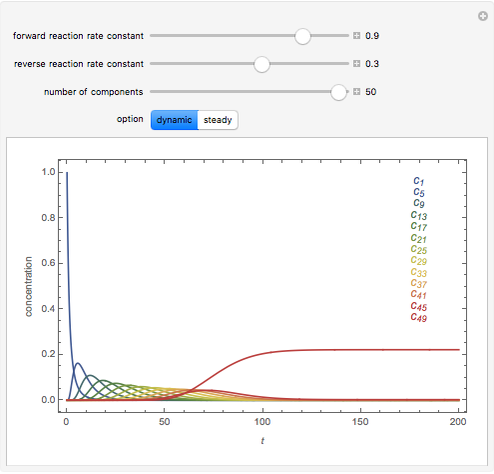
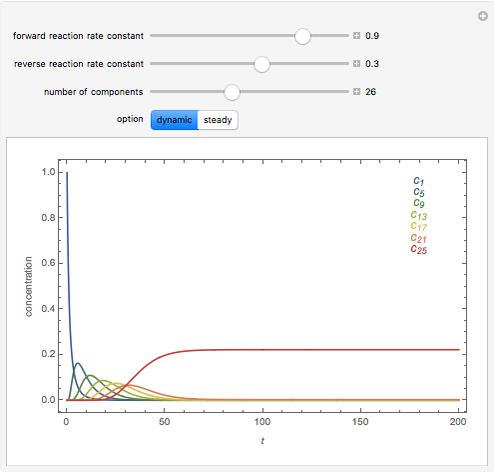
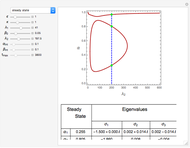
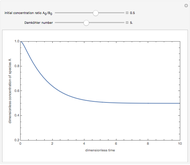
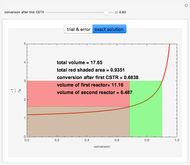
The following successive first-order reactions are considered: 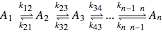 . For simplicity, assume that all forward and backward rate constants are equal to
. For simplicity, assume that all forward and backward rate constants are equal to 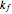 and
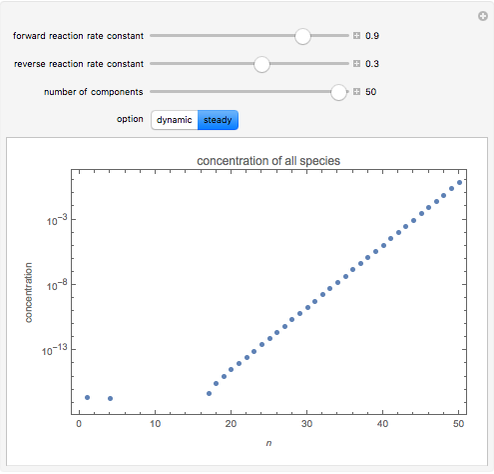
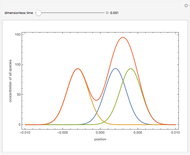
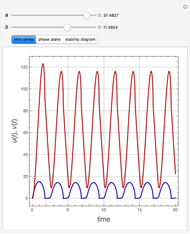
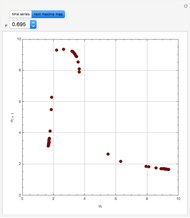
and 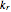 , respectively. The Demonstration displays the steady state solution for all species as well as the transient behavior only for species
, respectively. The Demonstration displays the steady state solution for all species as well as the transient behavior only for species 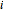 such that
such that 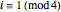 , for clarity of the plot.
, for clarity of the plot.
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reaction Networks Successive first-order reversible reactions are considered:
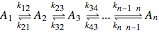 .
.
The kinetic expressions, where 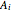 represents the molar concentration, can be written:
represents the molar concentration, can be written:
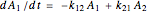
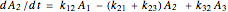
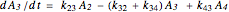

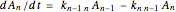 .
.
Adding the equations provides the differential mass balance:
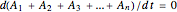 .
.
By setting the left-hand side of the differential equations equal to zero, the simultaneous linear algebraic equations can be solved to yield the steady state solutions.
With initial conditions on 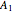 ,
, 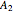 ,
, 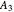 ,...
,... 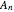 , the simultaneous ordinary differential equations can be solved to yield the transient solution.
, the simultaneous ordinary differential equations can be solved to yield the transient solution.
Permanent Citation