Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium for an Ethanol-Water Mixture

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
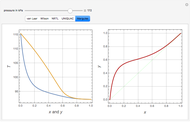
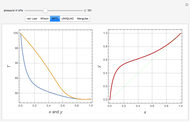
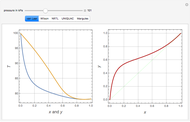
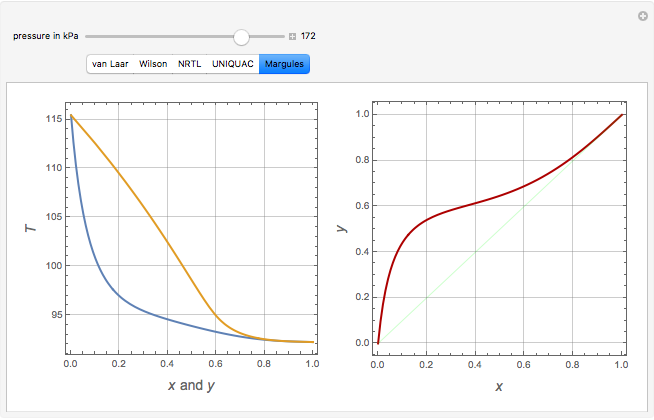
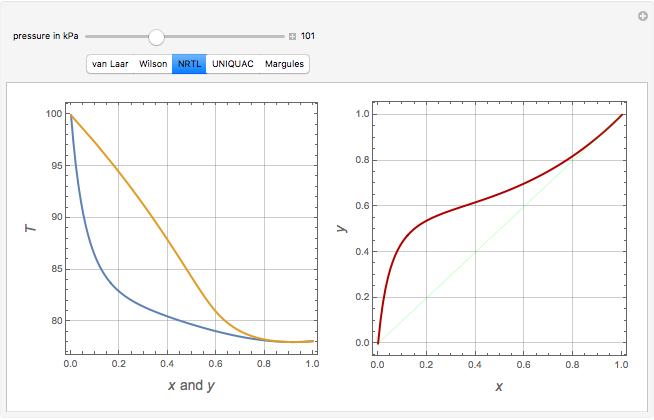
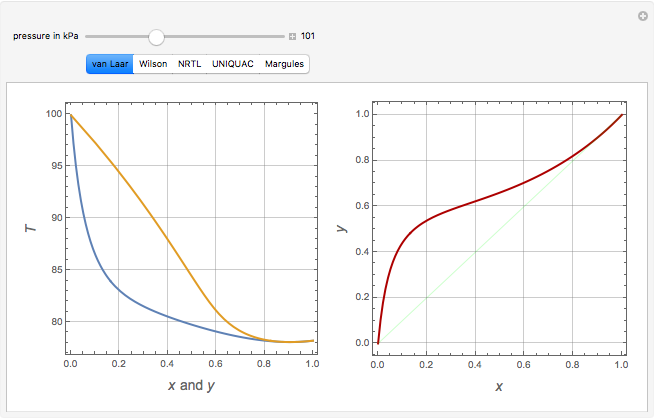
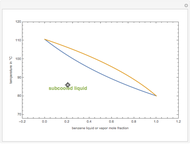
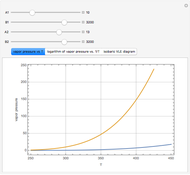
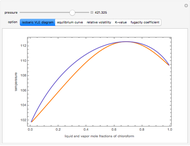
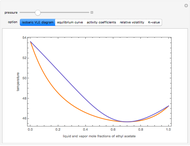
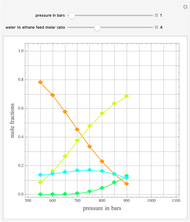
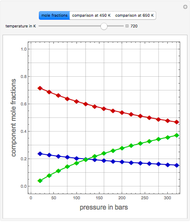
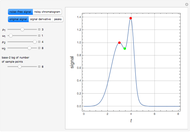
Consider a binary mixture of ethanol and water. Vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) data can be computed using the modified Raoult's law: 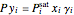 , where
, where  is the vapor pressure,
is the vapor pressure, 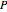 is the total pressure,
is the total pressure,  and
and 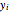 are the liquid and vapor phase mole fractions of the light component (i.e., ethanol) when
are the liquid and vapor phase mole fractions of the light component (i.e., ethanol) when  , and finally,
, and finally,  is the activity coefficient. You can vary the pressure
is the activity coefficient. You can vary the pressure 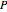 to any value between
to any value between  and
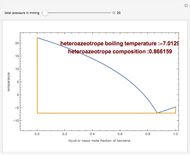
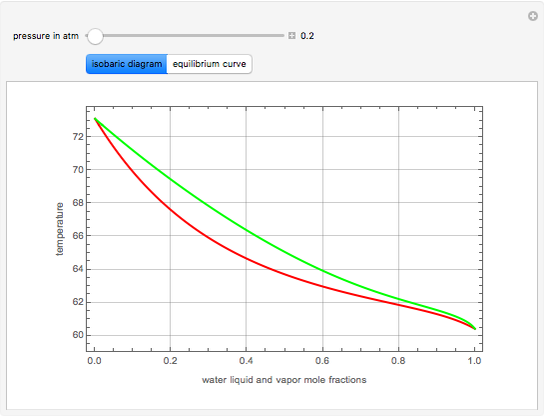
and 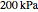 (i.e., low to moderate pressure so that the ideal gas-phase assumption holds). You can choose among five activity coefficient models (i.e., van Laar, NRTL, Wilson, Margules, or UNIQUAC). The Demonstration plots the isobaric vapor-liquid equilibrium diagram as well as the equilibrium curve. You can check that all models used to predict activity coefficients give similar results (i.e., a minimum boiling or positive azeotrope at
(i.e., low to moderate pressure so that the ideal gas-phase assumption holds). You can choose among five activity coefficient models (i.e., van Laar, NRTL, Wilson, Margules, or UNIQUAC). The Demonstration plots the isobaric vapor-liquid equilibrium diagram as well as the equilibrium curve. You can check that all models used to predict activity coefficients give similar results (i.e., a minimum boiling or positive azeotrope at  ).
).
Contributed by: Housam Binous, Mamdouh Al-Harthi, and Brian G. Higgins (December 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation