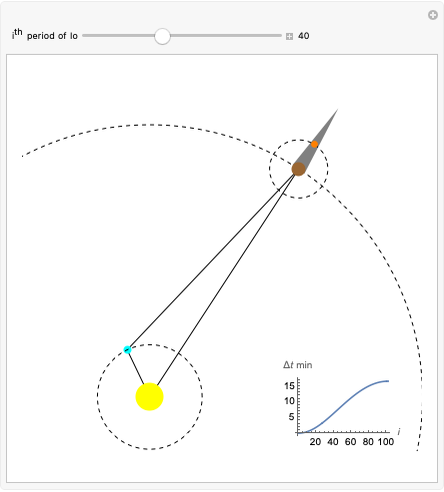
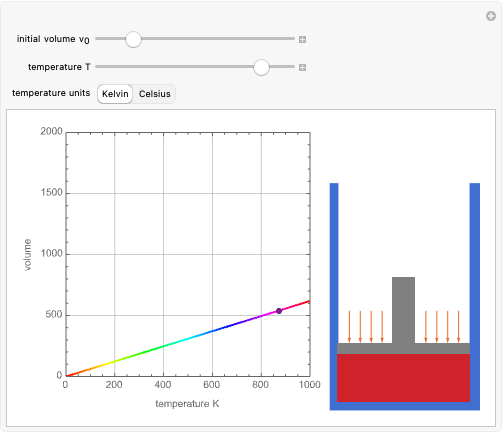
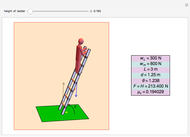
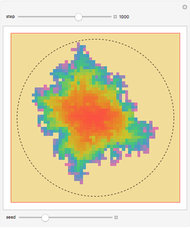
Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
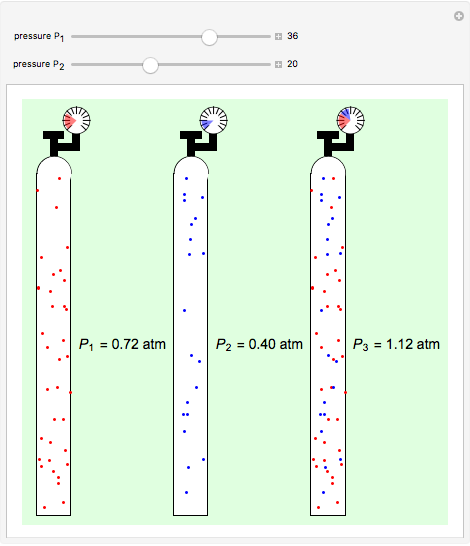
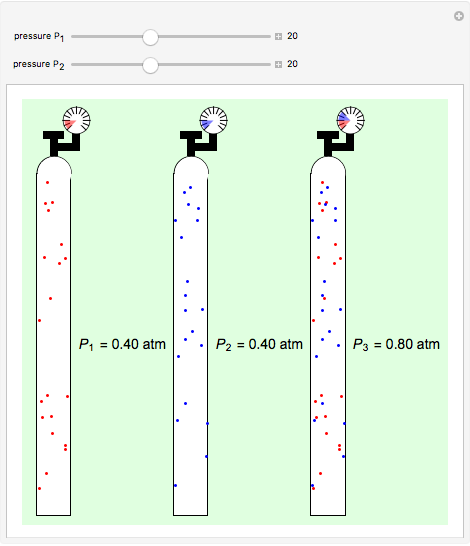
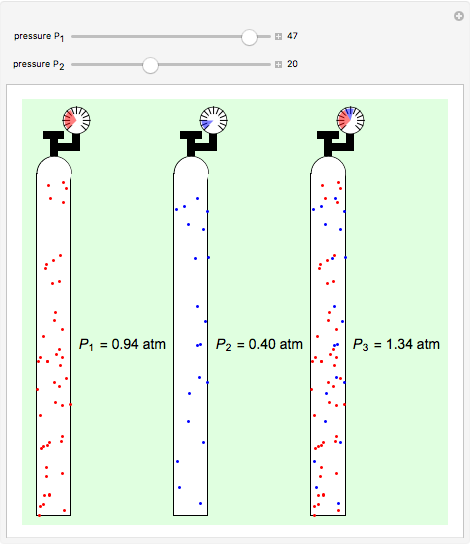
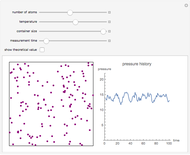
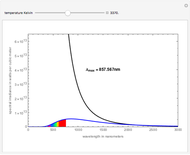
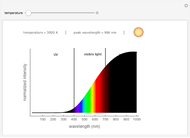
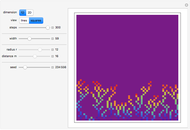
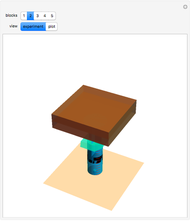
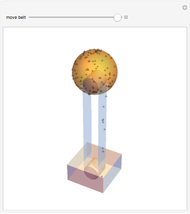
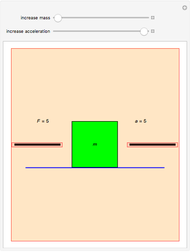
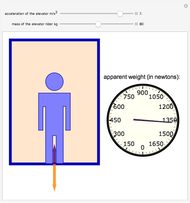
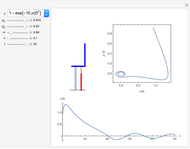
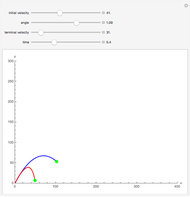
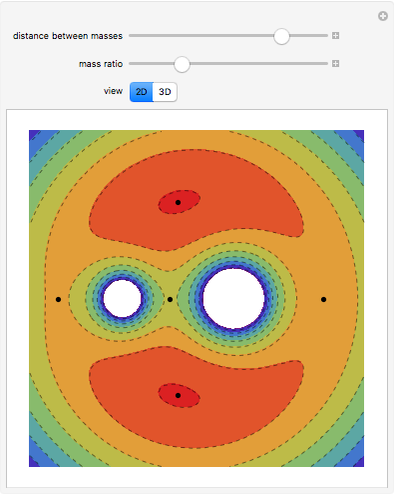
Dalton's law of partial pressures states that the total pressure 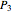 of a mixture of gases (the last tank in the picture) is equal to the sum
of a mixture of gases (the last tank in the picture) is equal to the sum 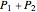 of partial pressures exerted by each component gas (the first two tanks). This represents the limit of ideal behavior. Deviations can occur at higher pressures.
of partial pressures exerted by each component gas (the first two tanks). This represents the limit of ideal behavior. Deviations can occur at higher pressures.
Contributed by: Enrique Zeleny (December 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The units used for pressure are atmospheres (atm). The gases can be oxygen and nitrogen, the major components of air, for example.
Permanent Citation
"Dalton's Law of Partial Pressures"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/DaltonsLawOfPartialPressures/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 15 2011