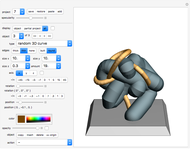
Model of an Industrial Robot Arm

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
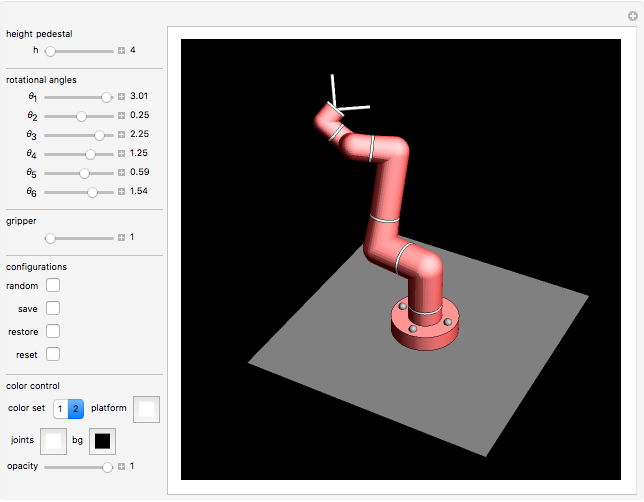
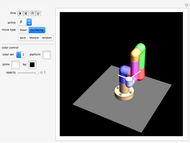
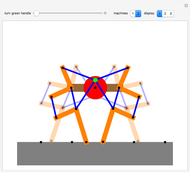
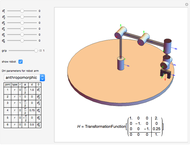
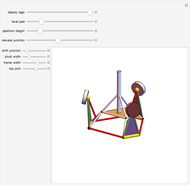
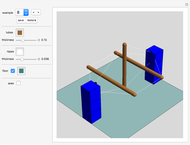
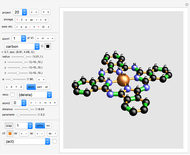
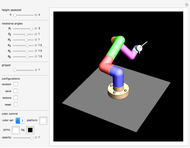
This Demonstration simulates the operation of a robot arm modeled after a real industrial machine. There are nine degrees of freedom: lifting the arm, seven rotations and one gripper. The model applies the equations of forward kinematics to represent the results of manipulation of the seven rotation angles.
Contributed by: Karl Scherer (May 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Controls
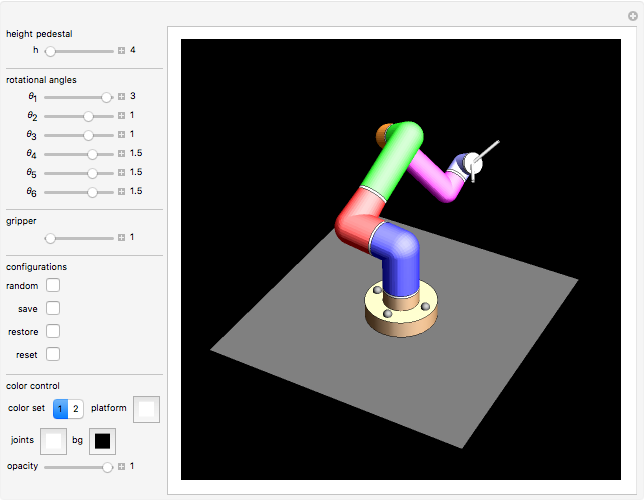
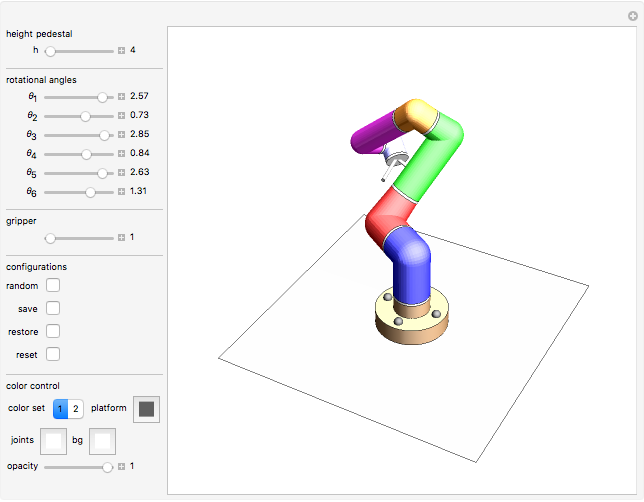
In this Demonstration you can vary the height of the brown pedestal, but in reality the height of this pedestal is usually fixed and the pedestal firmly bolted to the ground.
Move the seven angle sliders to control the various parts of the robot arm.
Use the gripper slider to open and close the gripper to various degrees.
"color set"
For the parts of the arms, you can choose one of two given sets of colors.
"opacity"
Move the opacity slider to make the structure transparent.
"platform"
Here you control the color of the square platform the robot arm stands on. The platform is half-transparent.
"joints"
The gray square platform the robot arm stands on will always be half-transparent.
"bg"
Controls the background color.
"store"
Click the store button to store the currrent arm configuration.
"res"
Click the restore button to restore the stored arm configuration.
"rnd"
Click the randomising button to let the system select a random position of the robot arm.
"reset"
Click the reset button to reset the robot arm to its default position.
Arm thinning
Limitations
This model does not check for intersection with itself.
Security for humans
When a robot arm has to work side-by-side with humans, safety is paramount, so a real robot arm might have sensors such as "elbow patches" on each part that might make contact with humans or other machines. These patches are not displayed here.
Technical notes
The programming code used is extremely simple and hence can be easily used to describe the control of similar robot arms via rotations of joints.
Permanent Citation
"Model of an Industrial Robot Arm"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ModelOfAnIndustrialRobotArm/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: May 13 2015