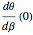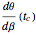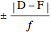Motion/Pursuit Law in 2D (Visual Depth Perception 3)

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
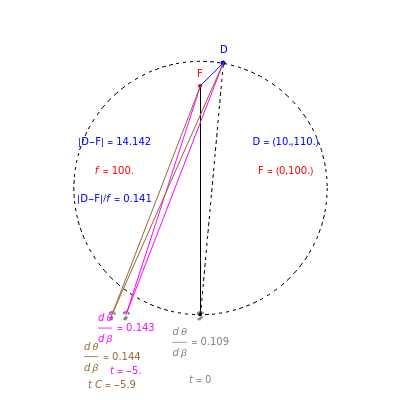
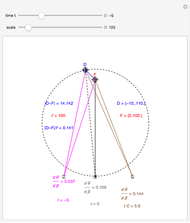
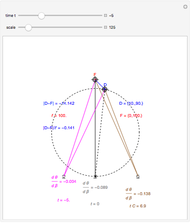
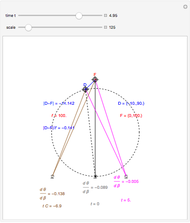
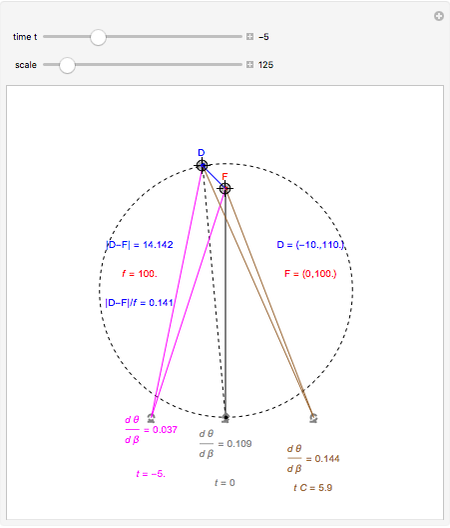
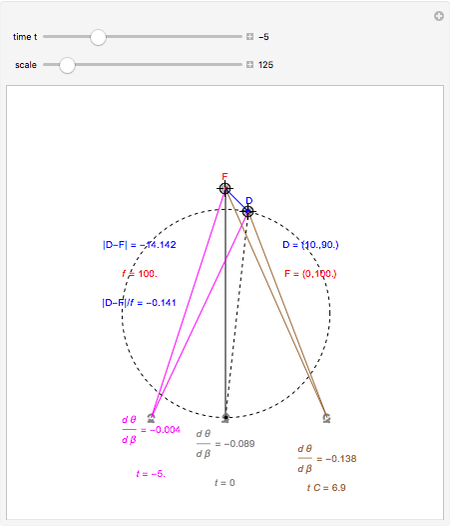
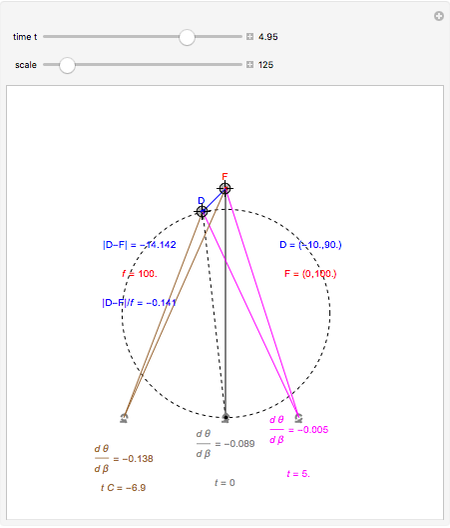
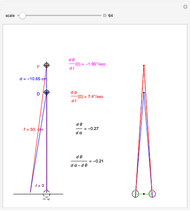
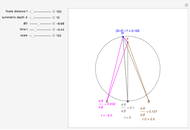
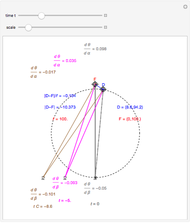
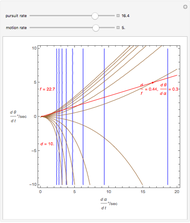
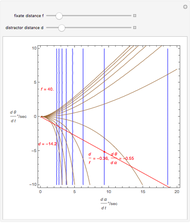
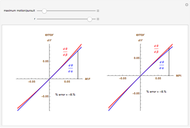
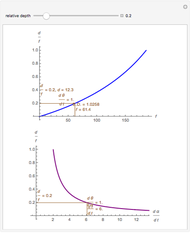
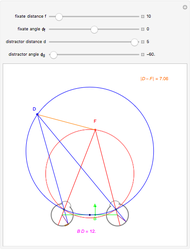
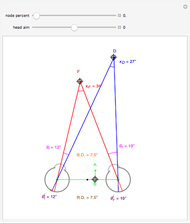
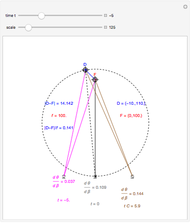
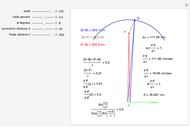
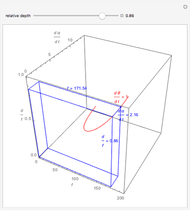
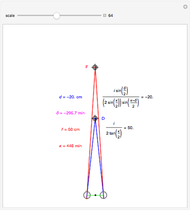
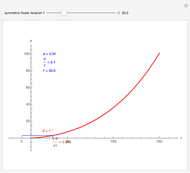
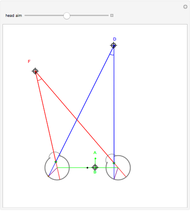
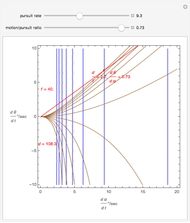
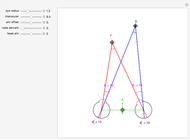
This Demonstration computes the motion/pursuit law in the two-dimensional horizontal fixation plane of the eyes. The observer is looking mainly at F on the vertical axis, but also sees D as he translates to the right at speed equal to the interocular distance per second.
[more]
Contributed by: Keith Stroyan (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation
"Motion/Pursuit Law in 2D (Visual Depth Perception 3)"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/MotionPursuitLawIn2DVisualDepthPerception3/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011