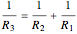Nomography for Beginners
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
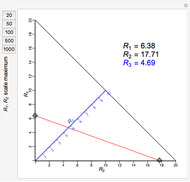
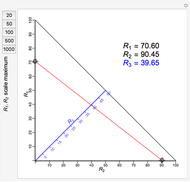
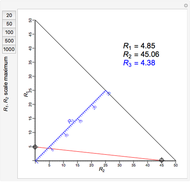
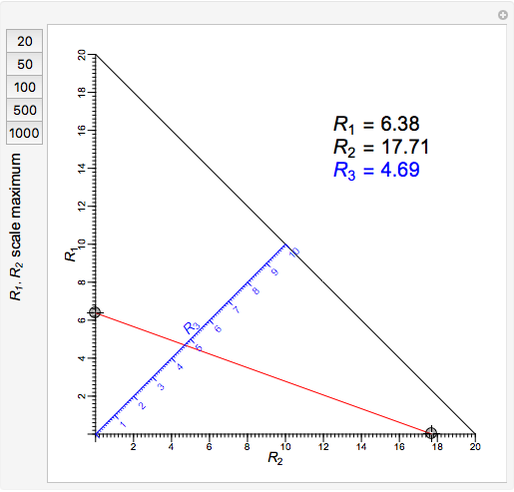
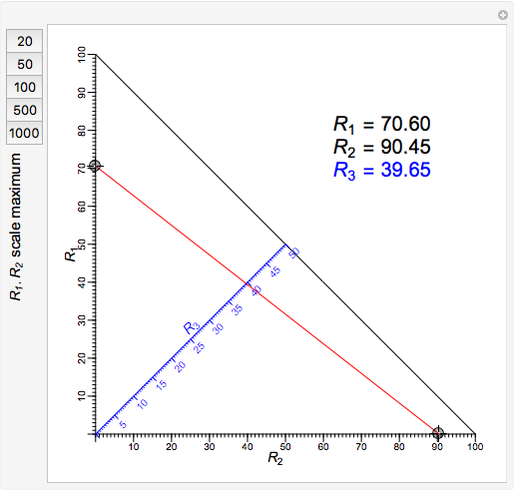
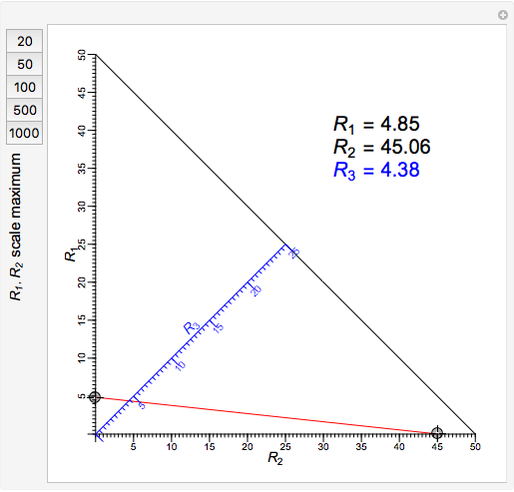
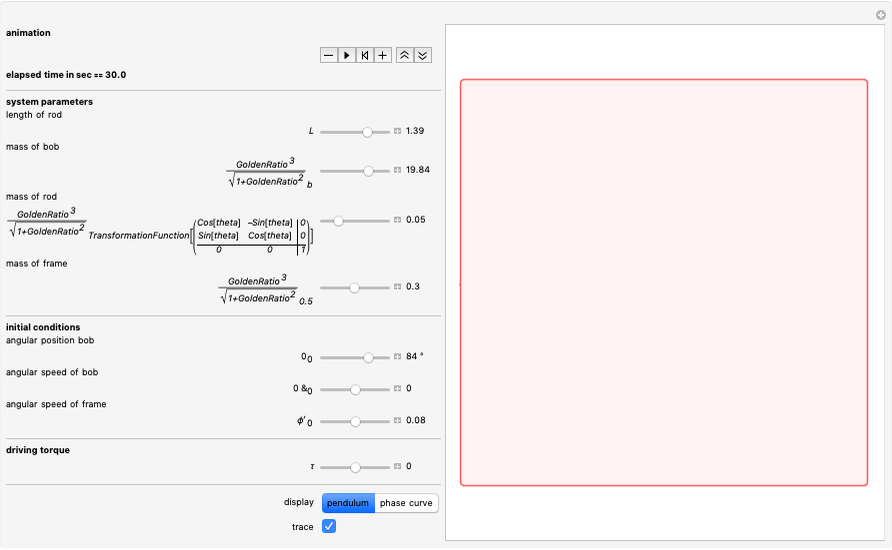
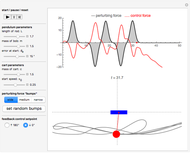
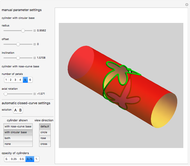
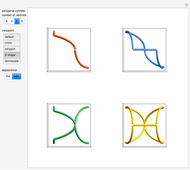
A nomogram (or nomograph) is a two-dimensional diagram designed to quickly approximate the computation of a function.
[more]
Contributed by: Erik Mahieu (May 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
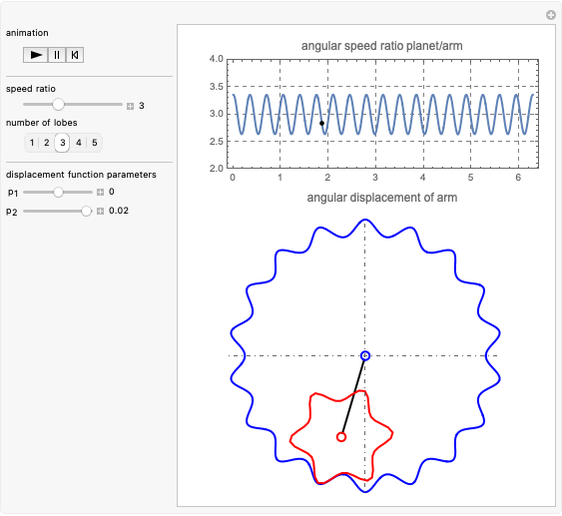
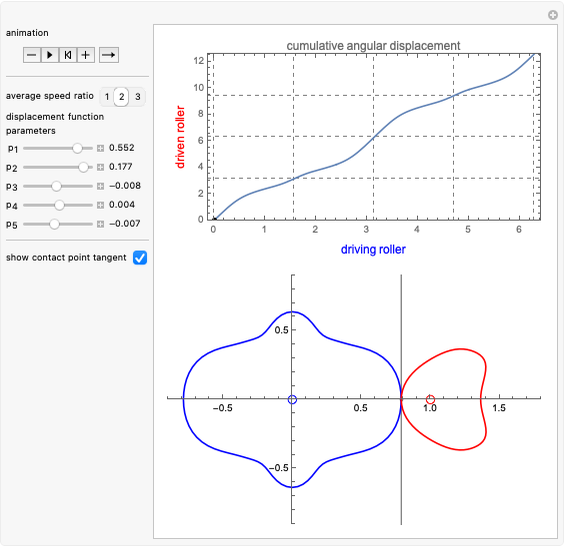
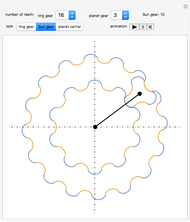
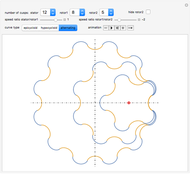
Snapshots
Details
For interesting information about nomograms, see [1].
Reference
[1] R. Doerfler, "The Lost Art of Nomography," The UMAP Journal 30(4), 2009 pp. 457–493.
Permanent Citation