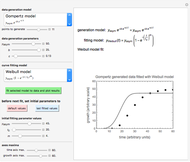
Weibullian Inactivation Rate as a Function of Temperature

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
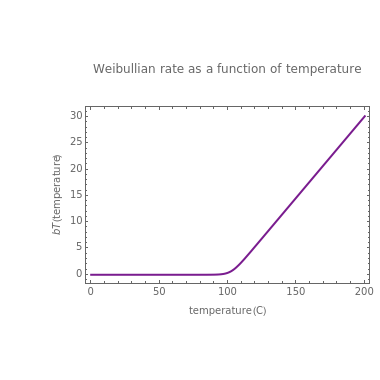
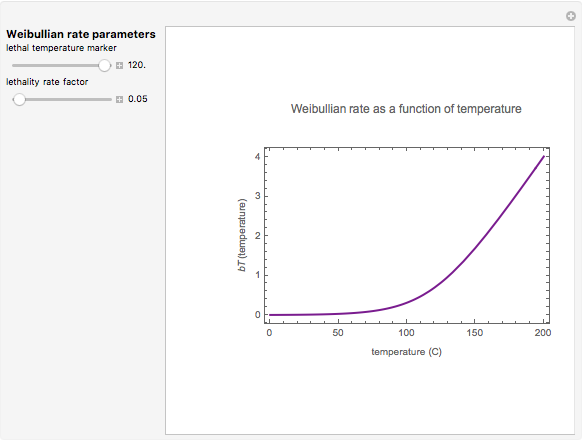
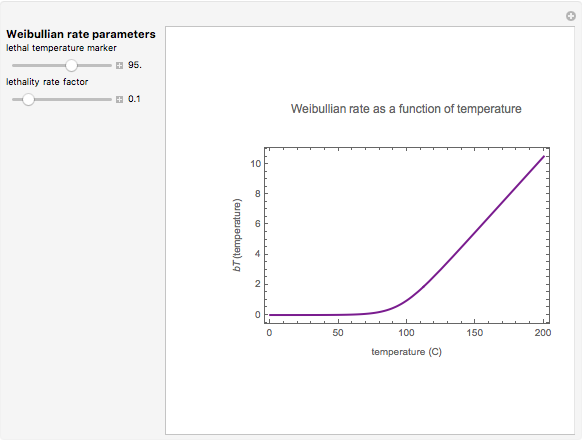
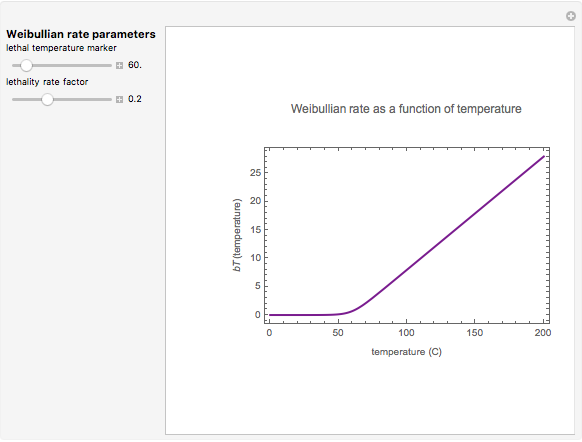
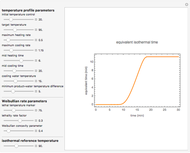
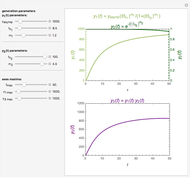
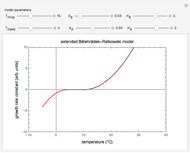
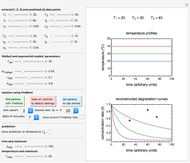
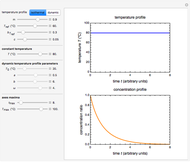
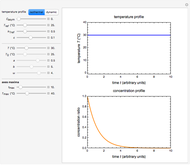
This second of five Demonstrations is a plot of the nonlinear Weibullian inactivation rate,  , a measure of a microorganism's heat resistance, as a function of temperature (in degrees C). You can vary the two parameters of the log-logistic equation: the lethal temperature marker,
, a measure of a microorganism's heat resistance, as a function of temperature (in degrees C). You can vary the two parameters of the log-logistic equation: the lethal temperature marker,  , and the lethality rate factor,
, and the lethality rate factor,  , which controls the slope of the curve at temperatures >>
, which controls the slope of the curve at temperatures >>  . Notice the automatic scaling of the
. Notice the automatic scaling of the 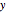 axis; it is different in each example.
axis; it is different in each example.
Contributed by: Mark D. Normand and Micha Peleg (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
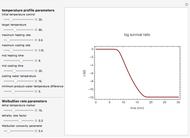
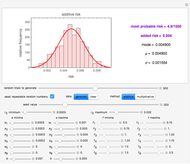
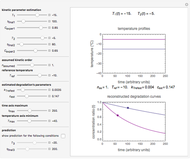
This is the second of five Demonstrations of functions used to model thermal processing of foods for the purpose of eliminating the presence of pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms. The five Demonstrations allow slider-control manipulation of the plots of:
1) an 8-parameter nonlinear "temperature profile", temperature (in degrees C) versus time (in minutes)
2) a 2-parameter nonlinear Weibullian rate, 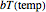 , as a function of temperature (in degrees C)
, as a function of temperature (in degrees C)
3) a 10-parameter nonlinear Weibullian rate, 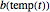 , as a function of time (in minutes)
, as a function of time (in minutes)
4) an 11-parameter dynamic microbial log survival, 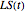 , as a function of time (in minutes)
, as a function of time (in minutes)
5) a 12-parameter equivalent isothermal time as a function of time (in minutes)
Snapshot 1: extremely resistant bacterial spores
Snapshot 2: resistant bacterial spores
Snapshot 3: sensitive bacterial cells
Permanent Citation