Elementary Processes in Protein Folding
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
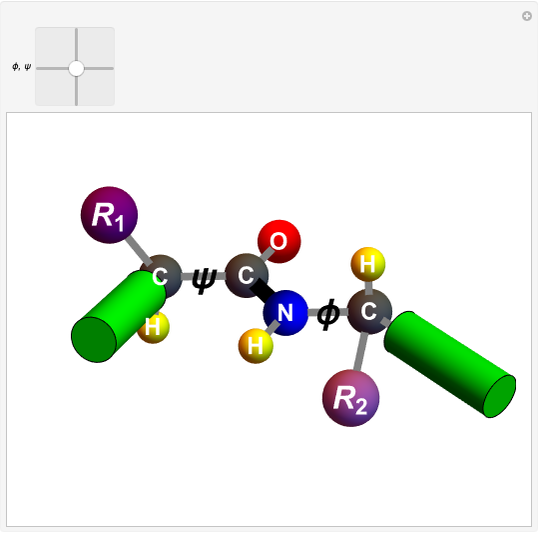
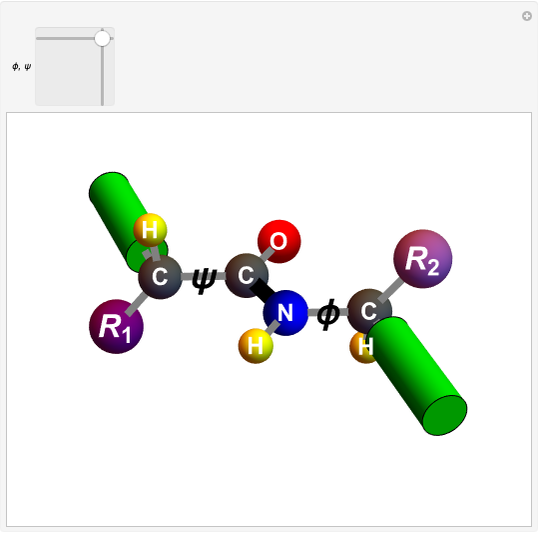
Biologically active  -amino acids are compounds with the general formula
-amino acids are compounds with the general formula  , where
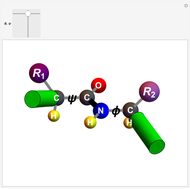
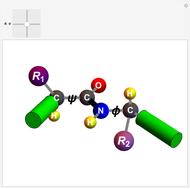
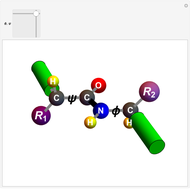
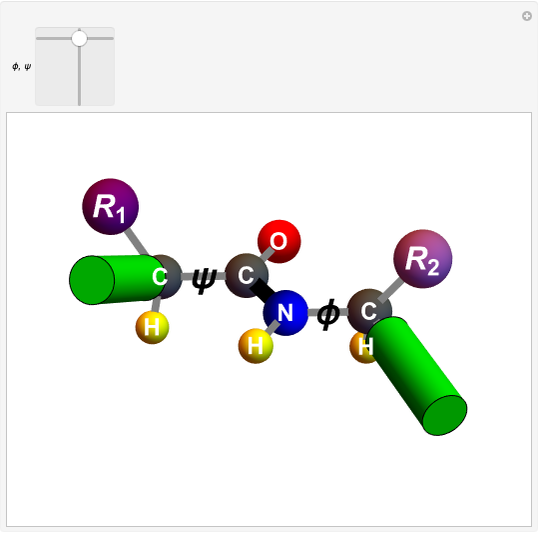
, where  represents one of about 20 possible side groups (or residues). An amide linkage is formed by the reaction of the carboxyl group of one molecule with the amide group of another. Proteins are built up of chains of amino acids connected by amide (or peptide) linkages, with the general structure
represents one of about 20 possible side groups (or residues). An amide linkage is formed by the reaction of the carboxyl group of one molecule with the amide group of another. Proteins are built up of chains of amino acids connected by amide (or peptide) linkages, with the general structure  . Chains can vary in length from about 100 to several thousand amino acid units.
. Chains can vary in length from about 100 to several thousand amino acid units.
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (January 2008)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Permanent Citation