Gas Absorption with a Rapid Chemical Reaction

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
A gas species,  , is absorbed by a solvent,
, is absorbed by a solvent,  , containing a solute,
, containing a solute,  . The gas-liquid interface is at
. The gas-liquid interface is at  . Assume that the liquid phase concentration of
. Assume that the liquid phase concentration of  at
at  is equal to 1 gmol/liter. The concentration of species
is equal to 1 gmol/liter. The concentration of species  in the solvent at
in the solvent at  is chosen to be equal to 4 gmol/liter. An instantaneous irreversible chemical reaction takes place between
is chosen to be equal to 4 gmol/liter. An instantaneous irreversible chemical reaction takes place between  and
and  (
( ). The species
). The species  ,
,  , and
, and  are present in low concentrations and Fick's second law applies. The diffusivities of species
are present in low concentrations and Fick's second law applies. The diffusivities of species  and
and  in
in  are taken to be
are taken to be  and
and  , respectively. Because the chemical reaction between
, respectively. Because the chemical reaction between  and
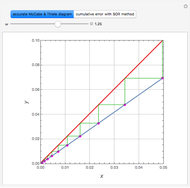
and  is considered as instantaneous, there is an interface parallel to the plane
is considered as instantaneous, there is an interface parallel to the plane  where neither
where neither  nor
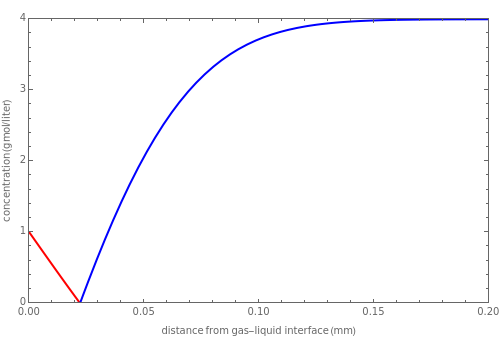
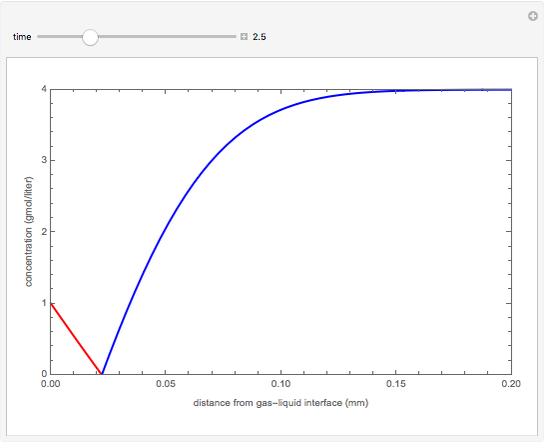
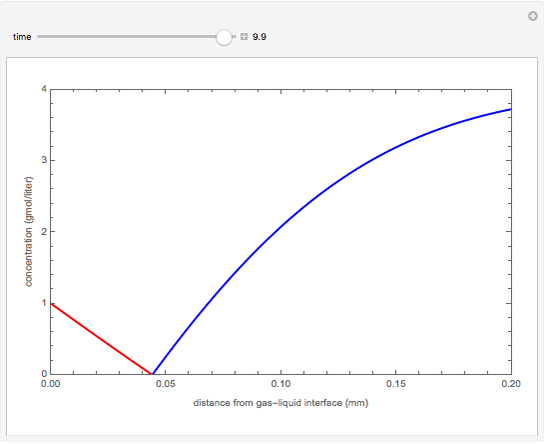
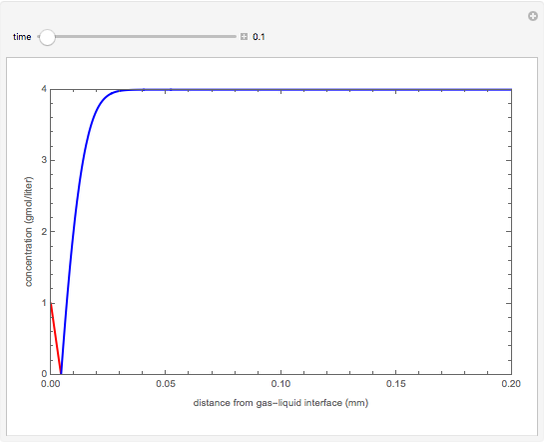
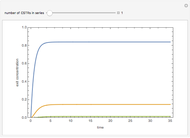
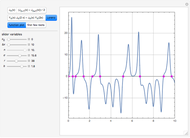
nor  is present. The position of this interface increases with time as
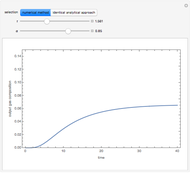
is present. The position of this interface increases with time as  is used up by the chemical reaction. This Demonstration displays the position of this interface and the concentration of species
is used up by the chemical reaction. This Demonstration displays the position of this interface and the concentration of species  and
and  (shown in red and blue, respectively). The computations of the interface position and the species concentrations are based on an analytical solution derived by Bird et al. (see reference below for details).
(shown in red and blue, respectively). The computations of the interface position and the species concentrations are based on an analytical solution derived by Bird et al. (see reference below for details).
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
R. B. Bird, W. E. Stewart and E. N. Lightfoot, Transport Phenomena, New York: Wiley, 1960.
Permanent Citation
"Gas Absorption with a Rapid Chemical Reaction"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/GasAbsorptionWithARapidChemicalReaction/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7 2011