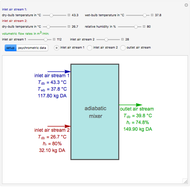
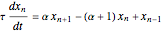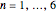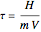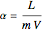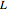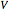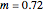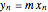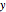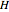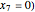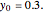Start-Up of a Plate Gas Absorption Unit
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
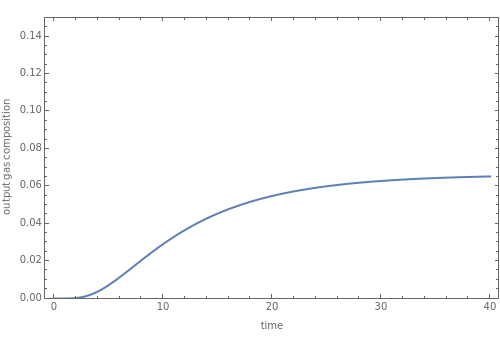
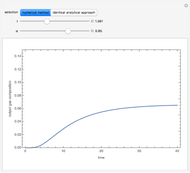
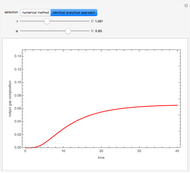
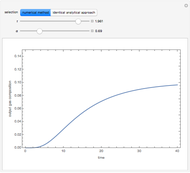
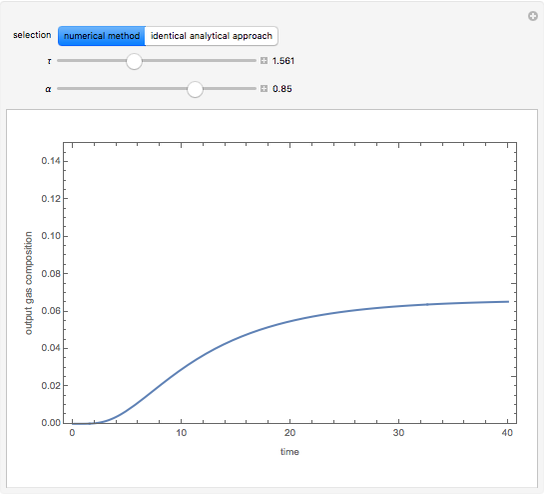
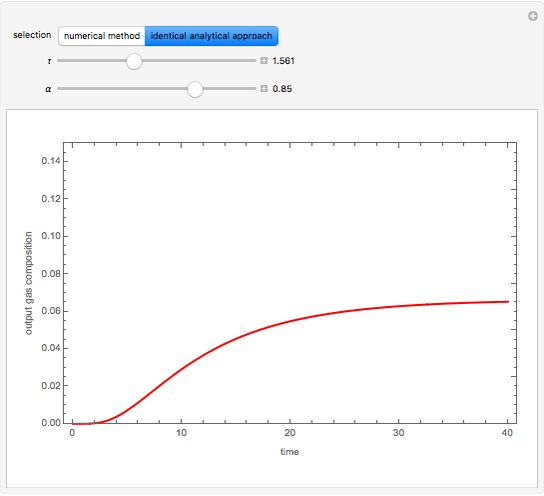
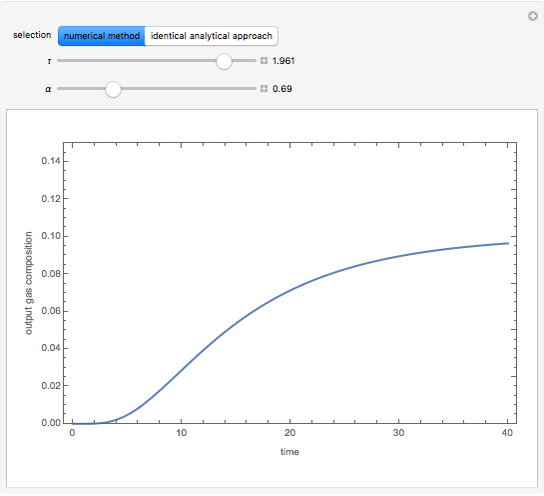
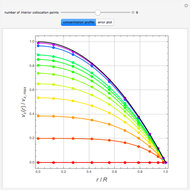
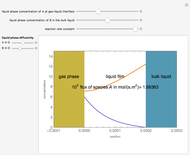
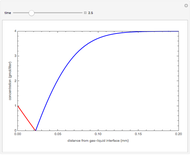
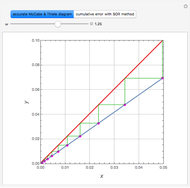
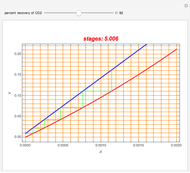
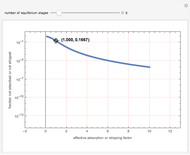
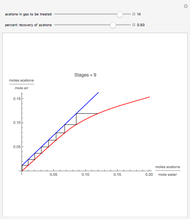
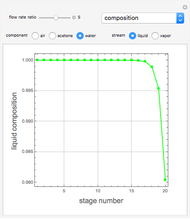
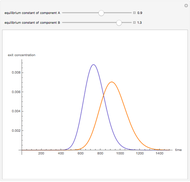
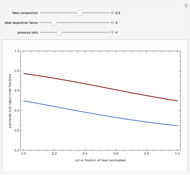
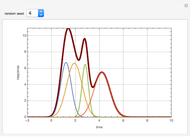
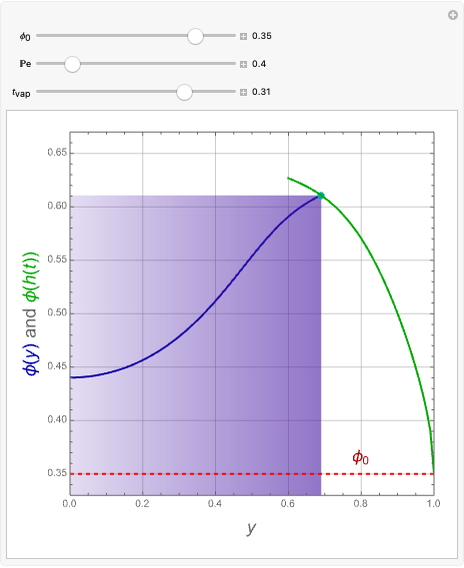
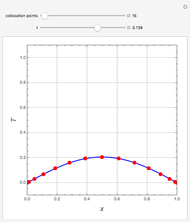
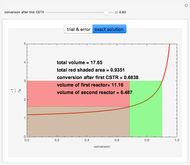
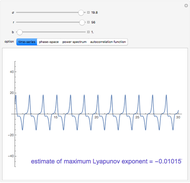
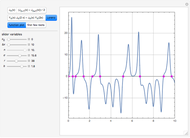
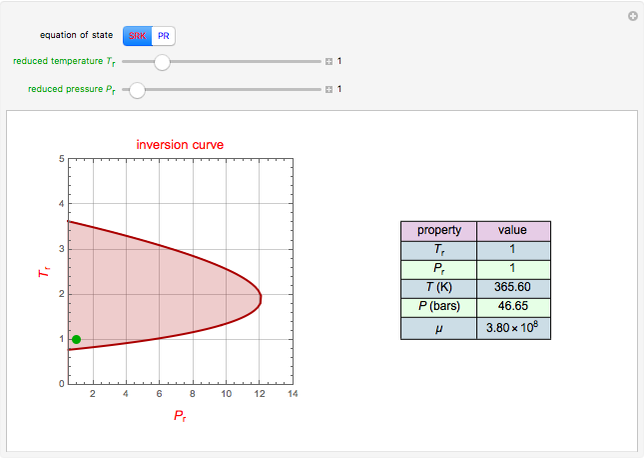
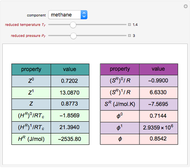
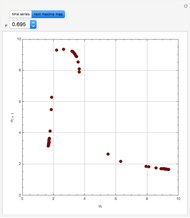
The start-up behavior of a six-plate gas absorption unit is described by the following equations:
[more]
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
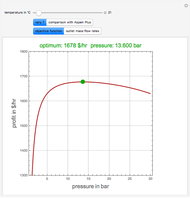
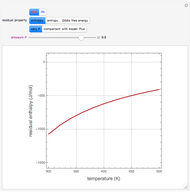
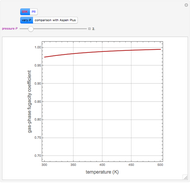
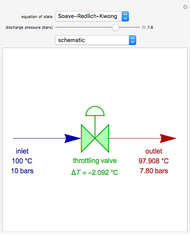
Snapshots
Details
J. M. Douglas, Process Dynamics and Control, Vol. 1: Analysis of Dynamic Systems, Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1972.
Permanent Citation