Gas Absorption Computed Using the Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR) Method

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
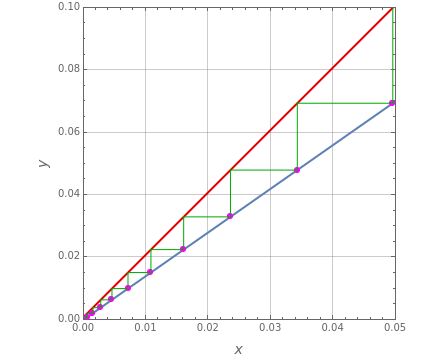
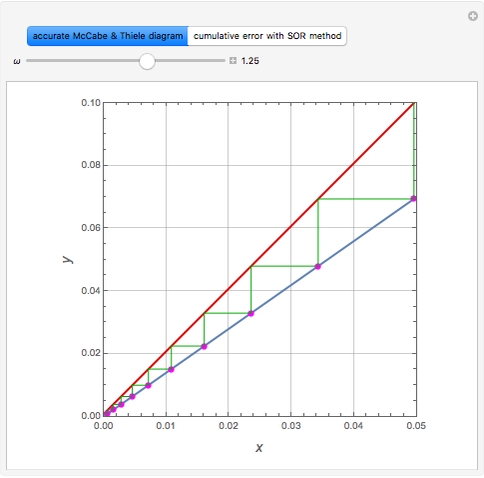
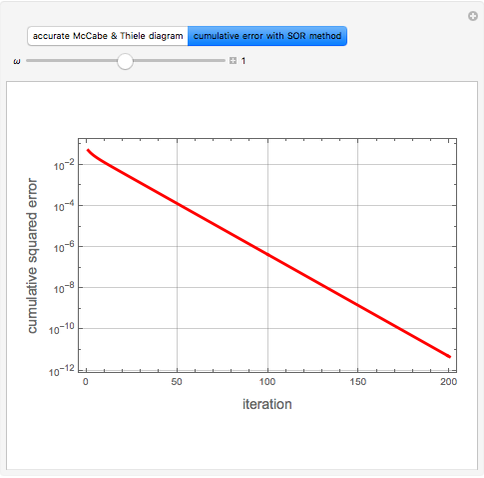
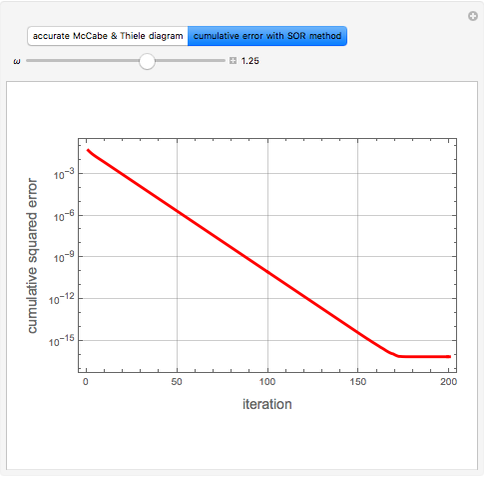
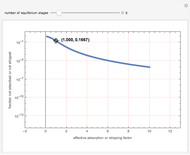
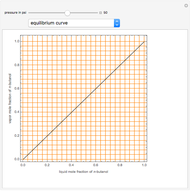
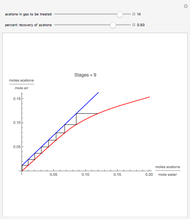
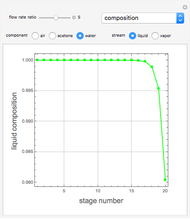
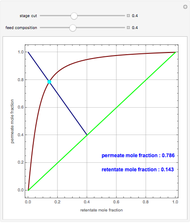
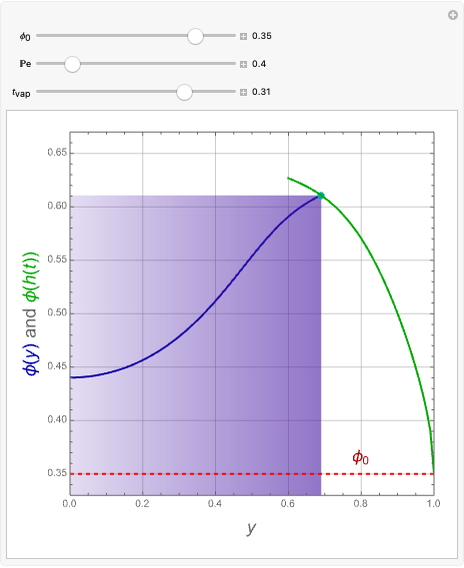
Consider a tray absorption column used to remove an impurity from a gas stream. A pure solvent is used for this absorption operation. The solvent molar flow rate is  and the gas molar flow rate is
and the gas molar flow rate is 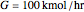 . Both
. Both  and
and 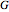 are considered constant (i.e., the dilute system hypothesis remains valid). The number of equilibrium stages is
are considered constant (i.e., the dilute system hypothesis remains valid). The number of equilibrium stages is 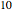 , the value of the slope
, the value of the slope 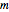 of the equilibrium line (
of the equilibrium line ( ) is set to
) is set to 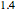 , the solvent-to-gas molar flow rate ratio
, the solvent-to-gas molar flow rate ratio 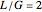 , and the mole fraction of the impurity in the gas fed to the absorption column is chosen to be
, and the mole fraction of the impurity in the gas fed to the absorption column is chosen to be  .
.
Contributed by: Housam Binous (April 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
After work by John H. Mathews
Permanent Citation